Visual perception Math Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
57 filtered results
-
From - To


Count and Pair on the Farm Worksheet

Counting in the Neighborhood Part1 Worksheet

Sweet Counting - Part 1 Worksheet

Big Medium Small Worksheet

Count and Match Points 9 Math Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet
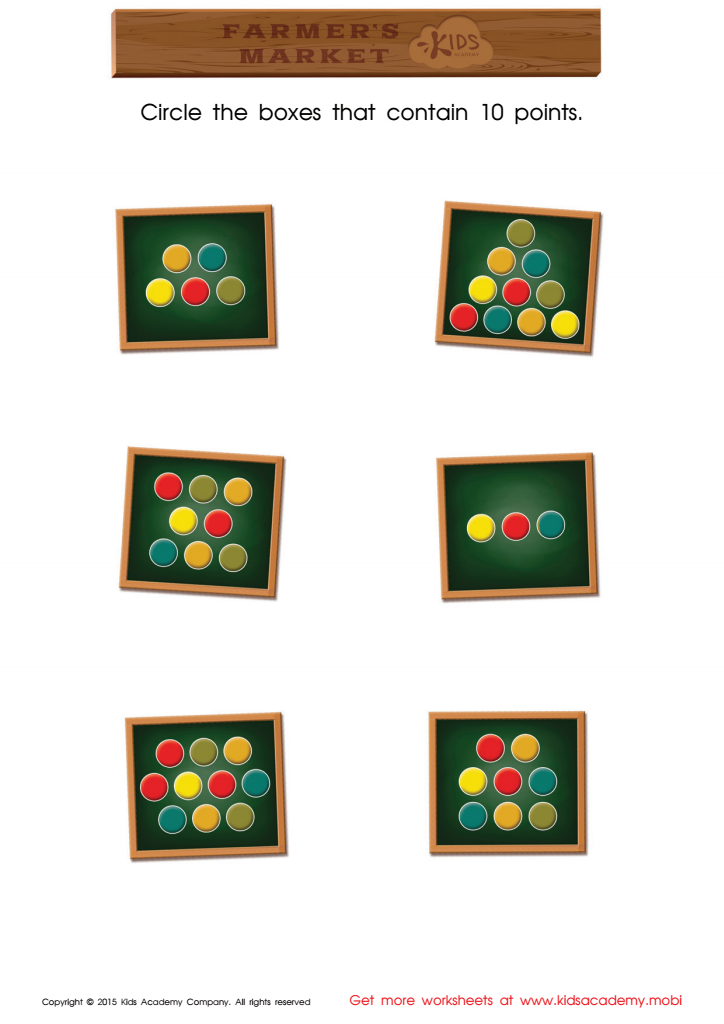

Count and Match Points 10 Math Worksheet


Classifying Toys by Type and Color Sorting Worksheet
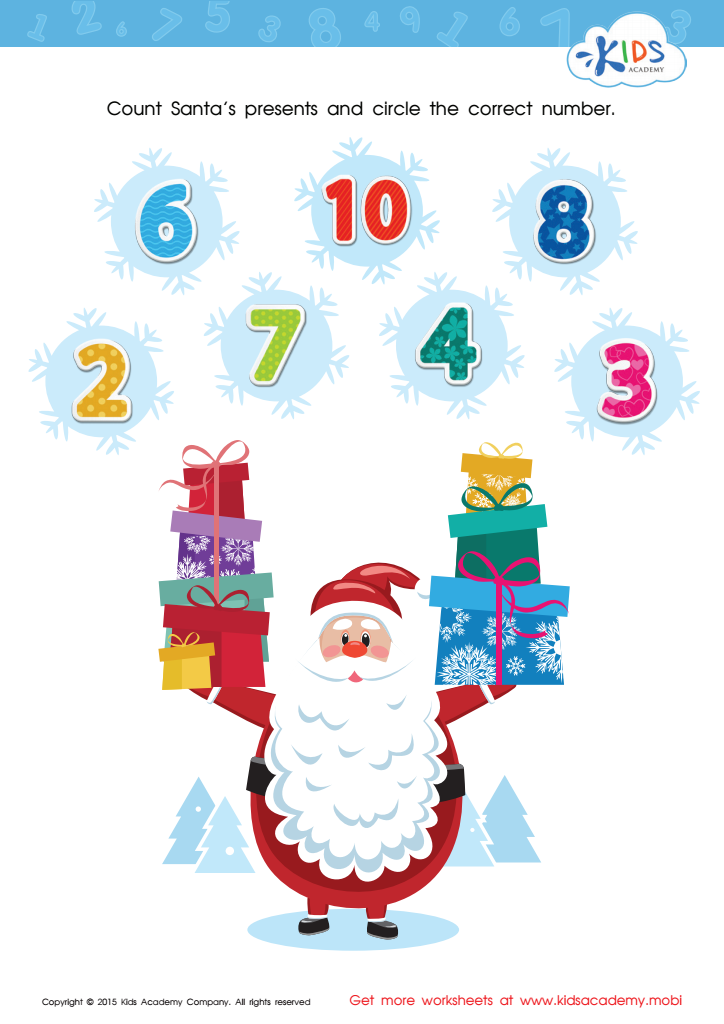


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet
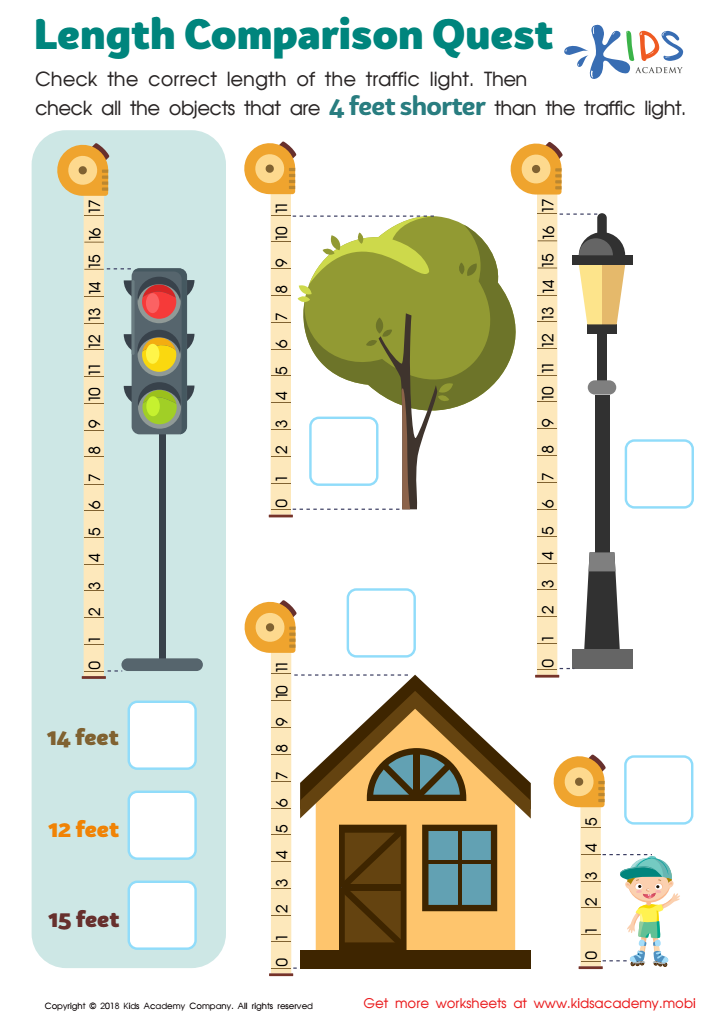

Length Comparison Quest Worksheet
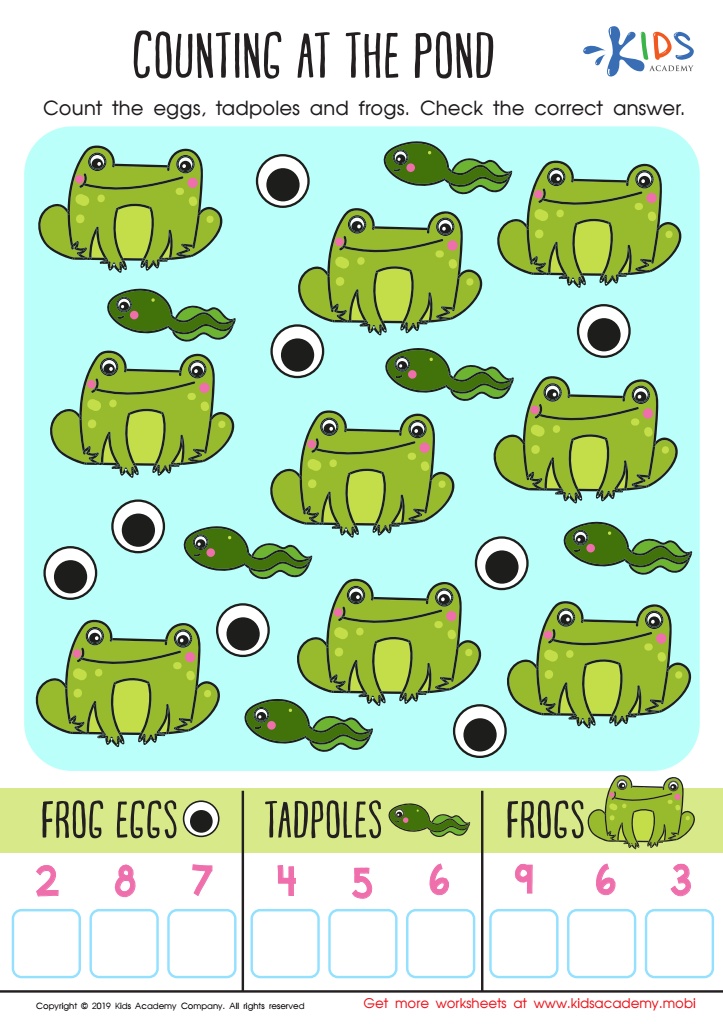

Counting at the Pond Worksheet
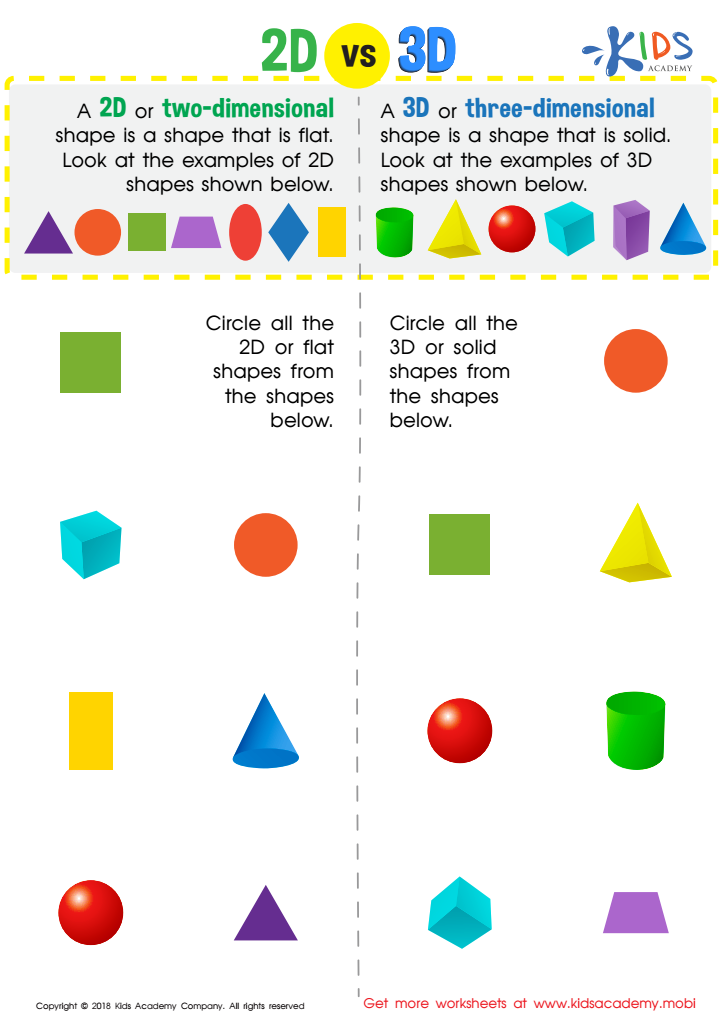

2D vs 3D Shapes Worksheet
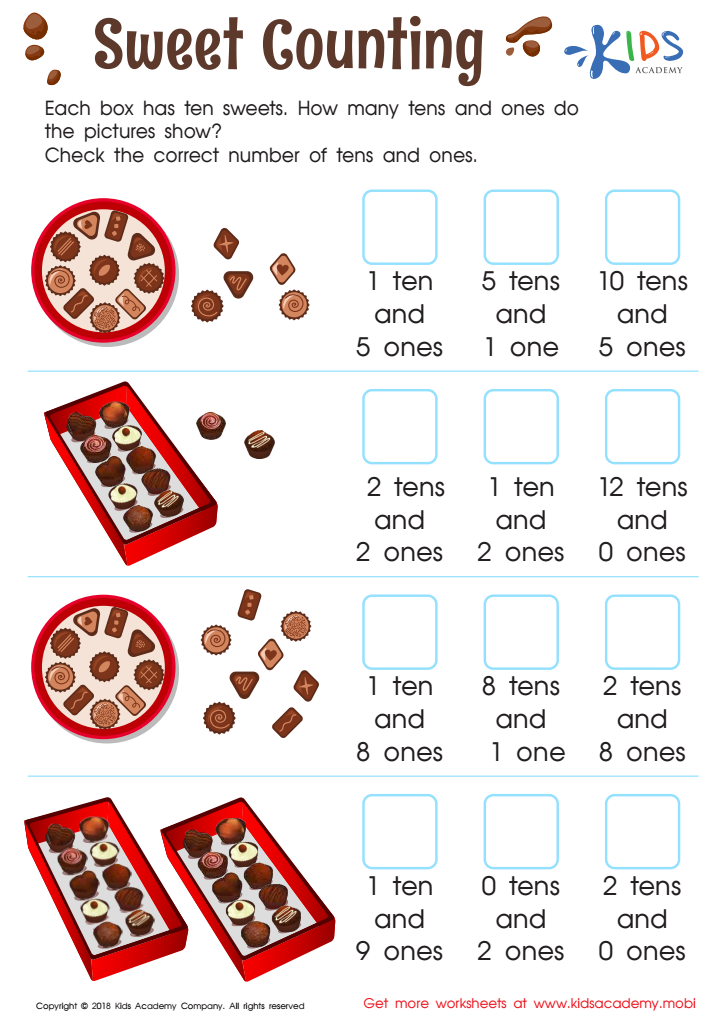

Sweet Counting - Part 2 Worksheet
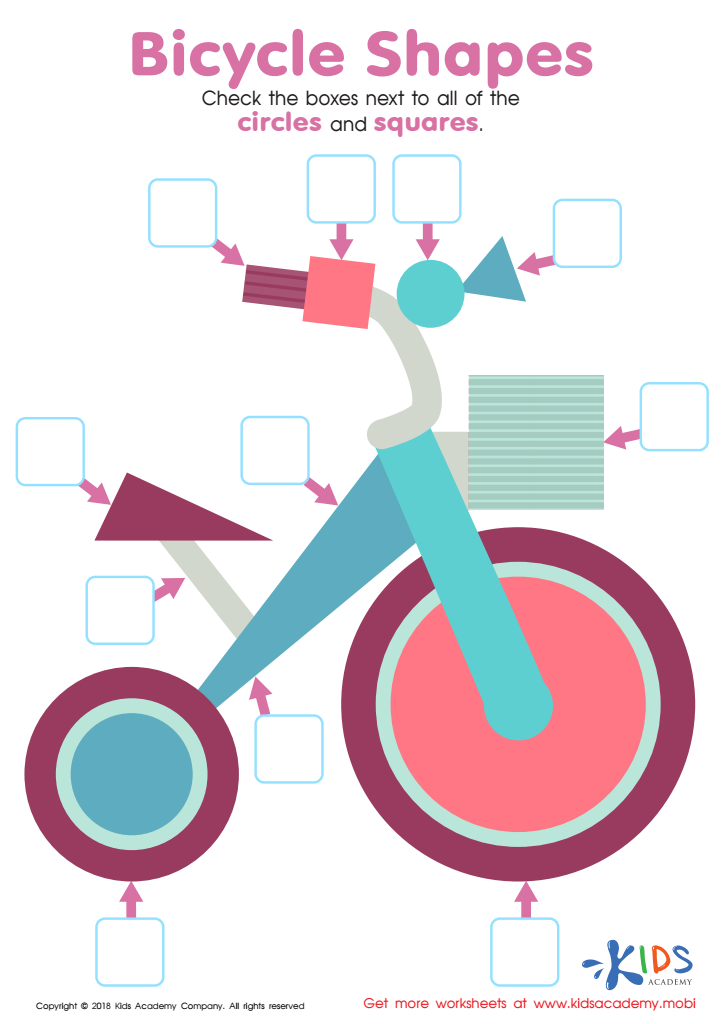

Bicycle Shapes Worksheet


Compare and Describe: Part 1 Worksheet
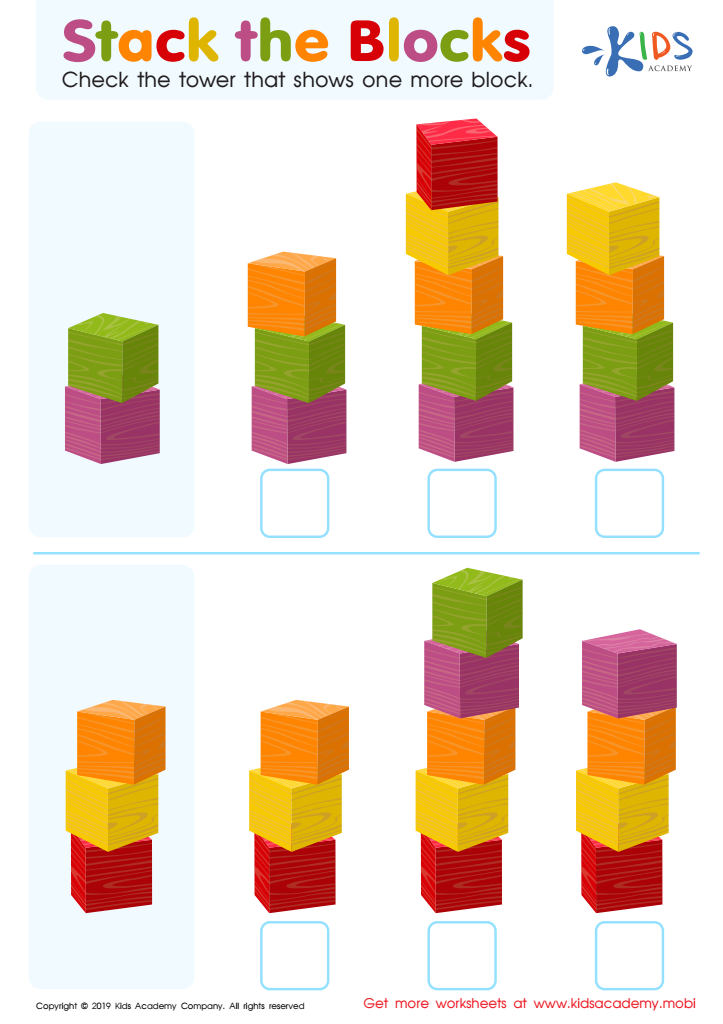

Stack the Blocks Worksheet
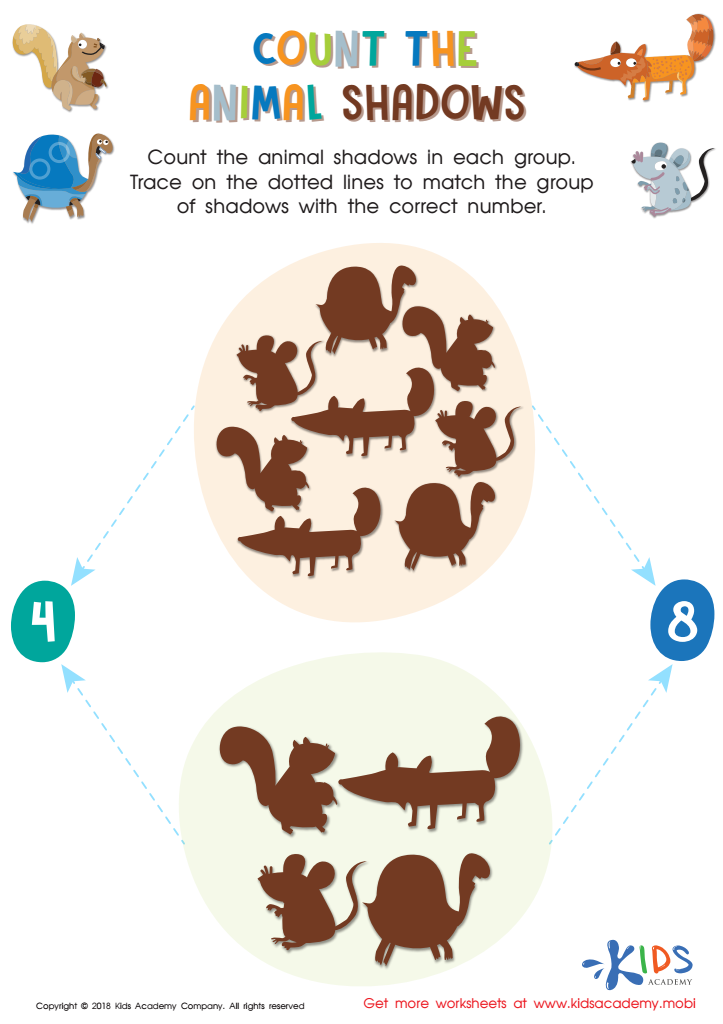

Count the Animal Shadows Worksheet
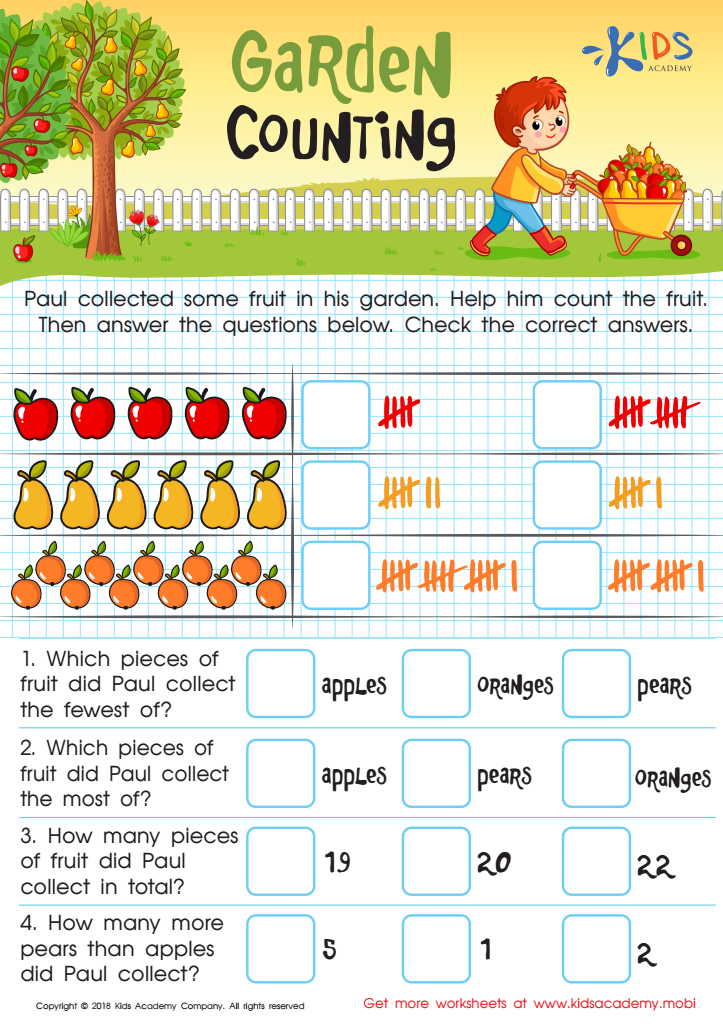

Garden Counting Worksheet


Counting Flowers Worksheet
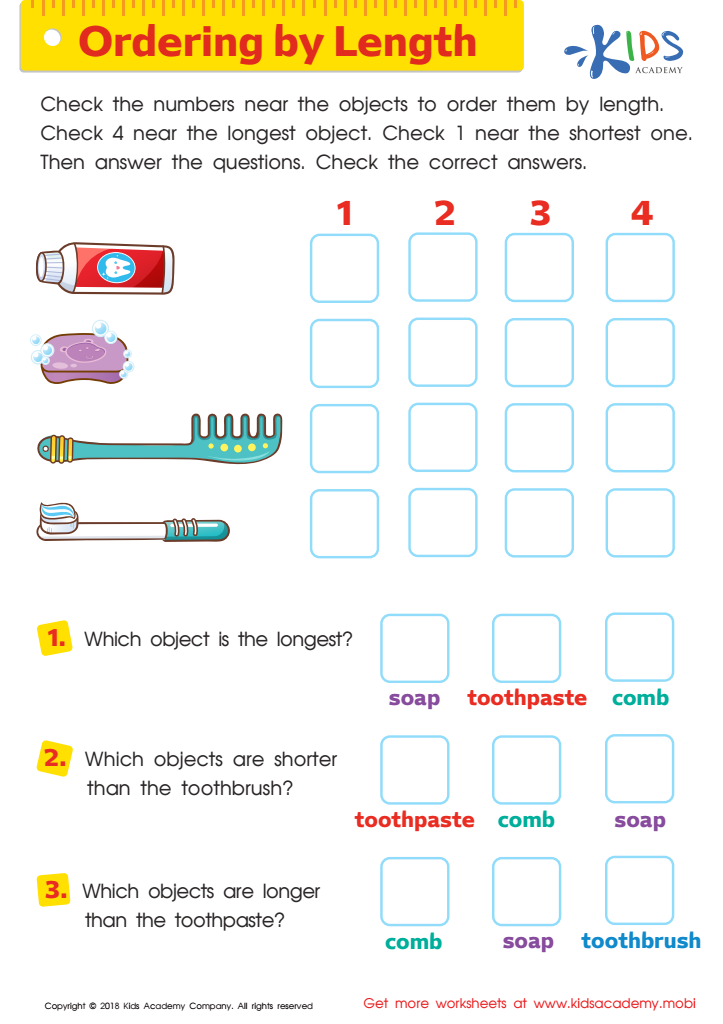

Ordering by Length Worksheet
Visual perception skills are crucial for young children aged 4-9 as they significantly influence their ability to learn and understand mathematical concepts. Visual perception refers to the brain's ability to make sense of what the eyes see. It encompasses skills such as visual discrimination, spatial awareness, and visual memory.
At this formative age, children are developing their ability to recognize shapes, sizes, and patterns, which are foundational for math. For instance, understanding geometric shapes and their properties involves visual discrimination, while comprehending the concept of numbers and understanding their placement in space involves spatial awareness.
Visual perception skills are also integral to problem-solving and logical thinking. When children solve puzzles or engage in activities that require them to match or sort objects, they enhance their ability to analyze and organize information—skills that are critical in learning math.
Moreover, strong visual perception skills help children in their daily tasks, improving their hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. This development is beneficial for tasks such as writing numbers, drawing shapes, and accurately interpreting visual presentations of mathematical problems.
Therefore, both parents and teachers should care about fostering these skills through engaging, hands-on activities. Better visual perception skills establish a strong foundation not only for math but also for broader cognitive development and overall academic success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students





.jpg)













