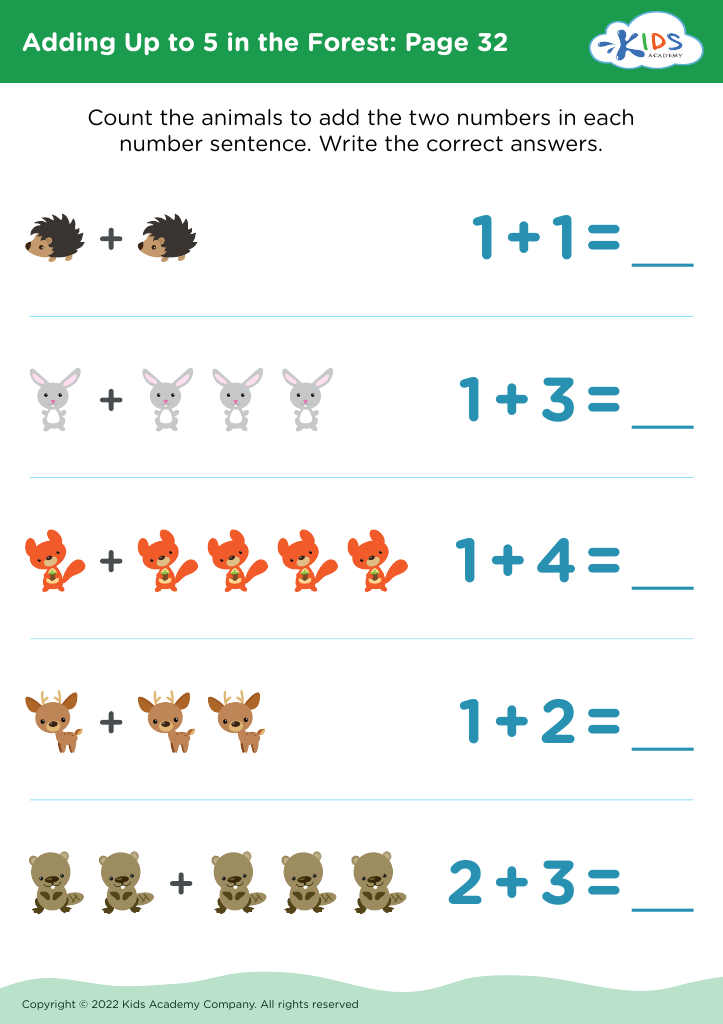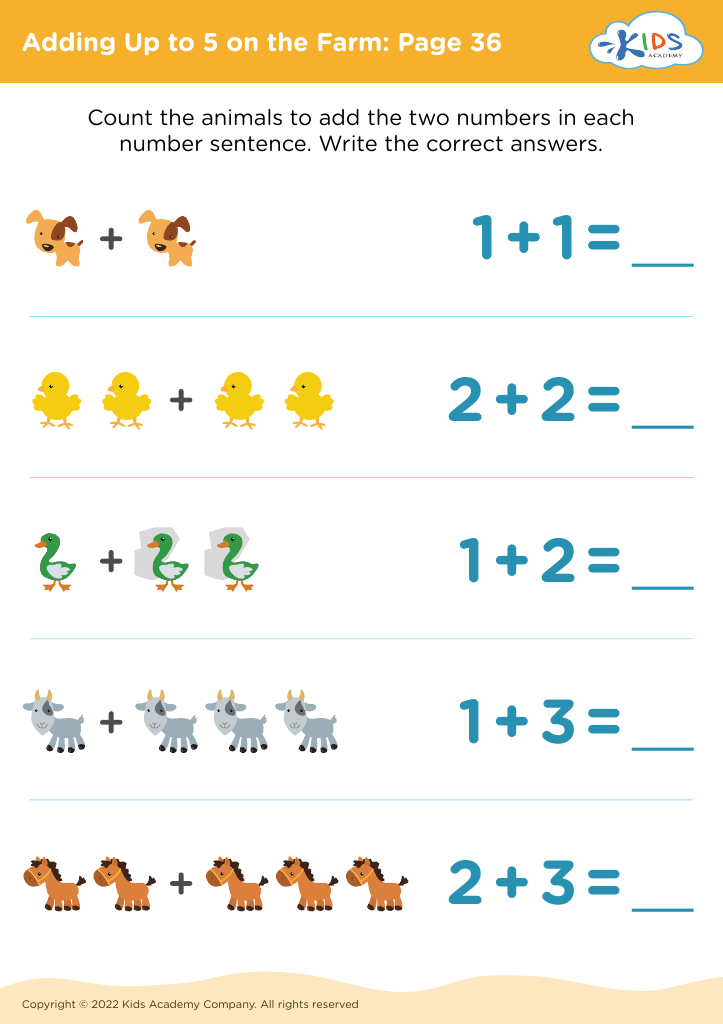Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 5-6 - Page 2
60 filtered results
-
From - To
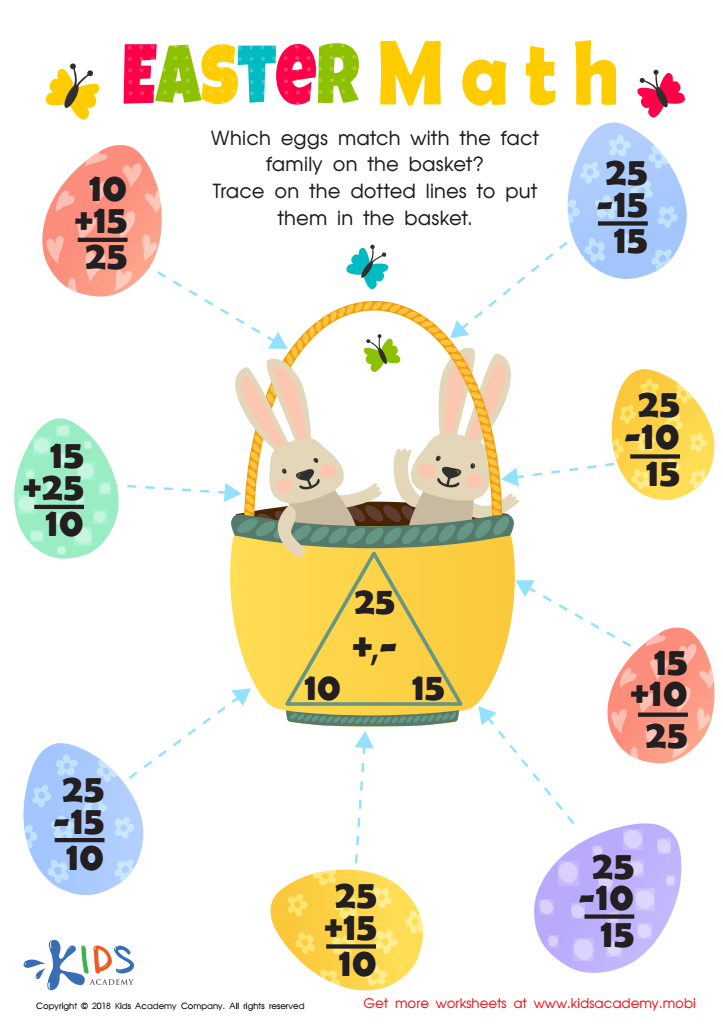

Fact Families: Easter Math Worksheet
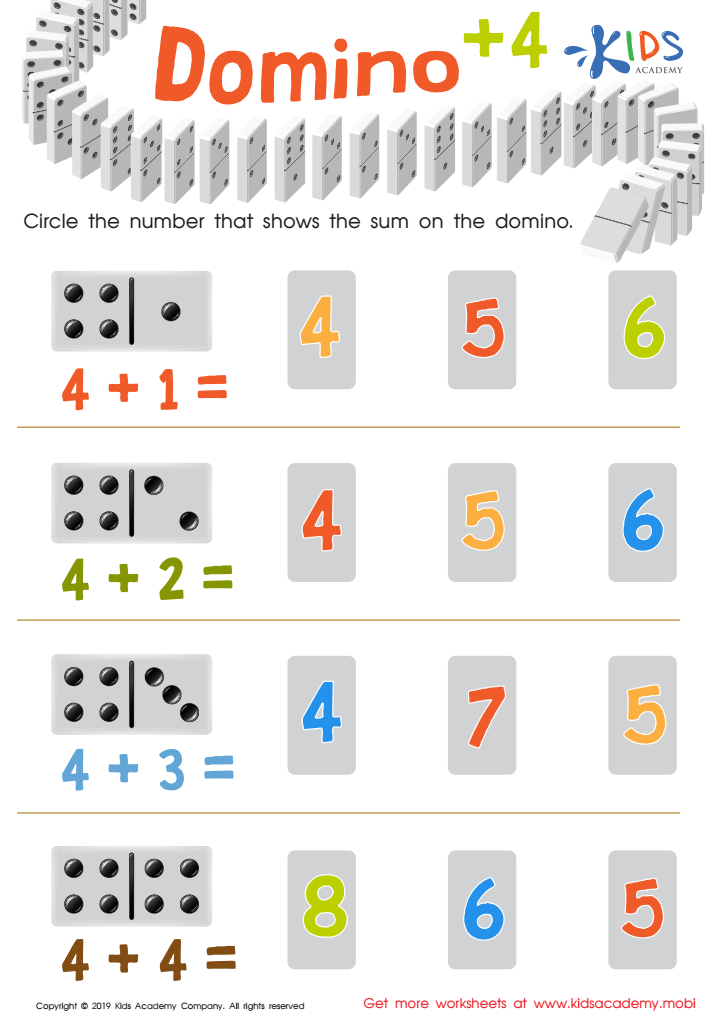

Domino +4 Worksheet
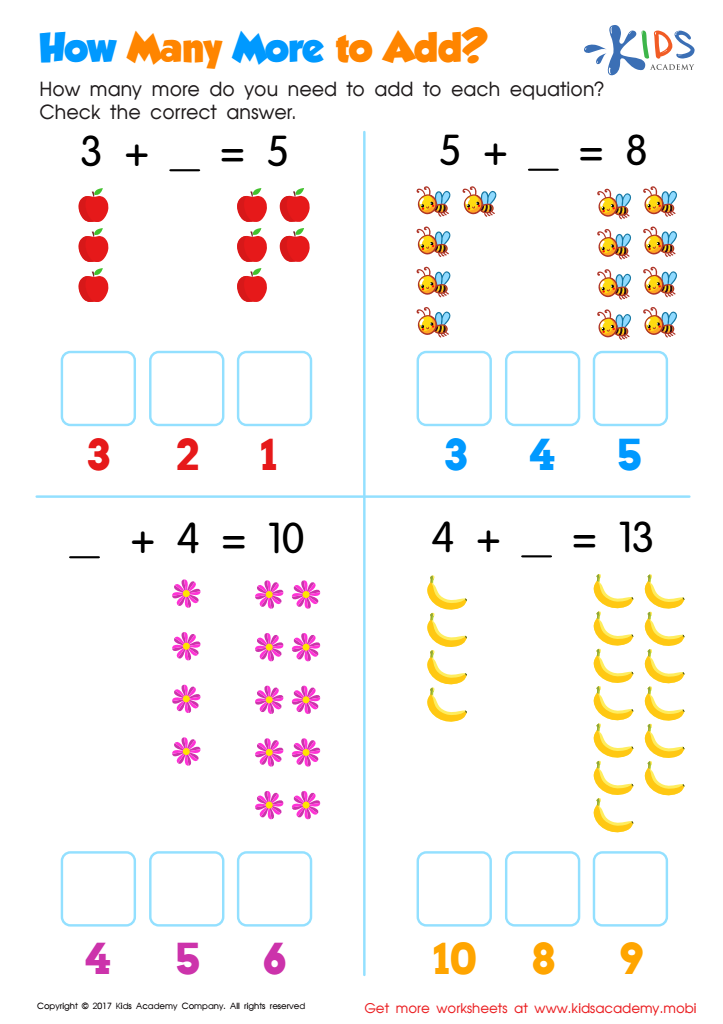

How Many More to Add Worksheet


Fairytale Addition Worksheet
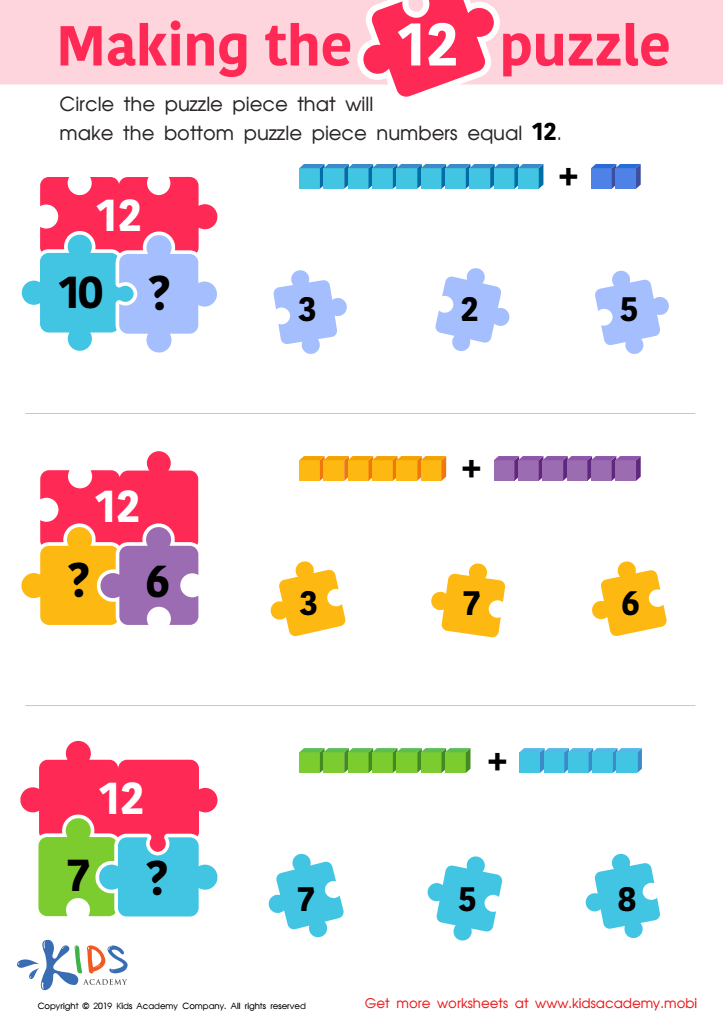

Making the 12 Puzzle Worksheet
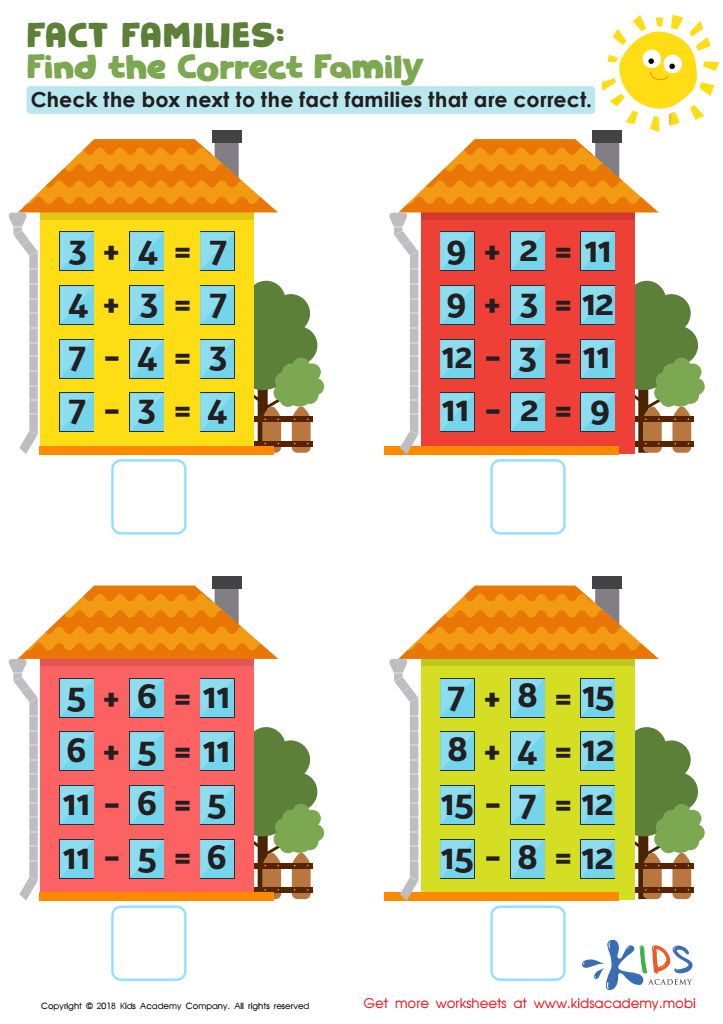

Fact Families: Find Correct Family Worksheet


Dino Addition Worksheet


Addition and Subtraction: Word Problems Worksheet
Problem-solving skills in early childhood, especially those related to addition, play a vital role in a child's cognitive and social development. For children ages 5-6, mastering problem-solving skills goes beyond simply learning how to add numbers; it nurtures critical thinking, perseverance, and creativity. At this age, children are developing foundational math concepts, and effective problem-solving techniques help them understand how numbers interact within real-life contexts.
Parents and teachers should be attentive to fostering these skills because they lay the groundwork for more complex mathematical understanding in later grades. Additionally, children who can think through problems and develop strategies are more likely to succeed in school and beyond. Engaging in problem-solving activities allows children to explore different methods, encouraging them to make mistakes, reflect, and try again, which builds resilience and determination.
Moreover, problem-solving fosters collaboration and communication among peers. When children work together to solve addition problems, they practice sharing ideas and approaches, thereby enhancing their social skills. Overall, supporting the development of problem-solving skills in addition helps prepare children for future academic challenges and equips them with essential life skills that go far beyond the classroom. By investing time and resources in these foundational abilities, adults greatly contribute to a well-rounded education for the youngest learners.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students