Fine Motor Skills Numbers 0–10 Worksheets for Ages 5-7 - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To

Eight Geese Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet

Underwater Adventure Worksheet

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet
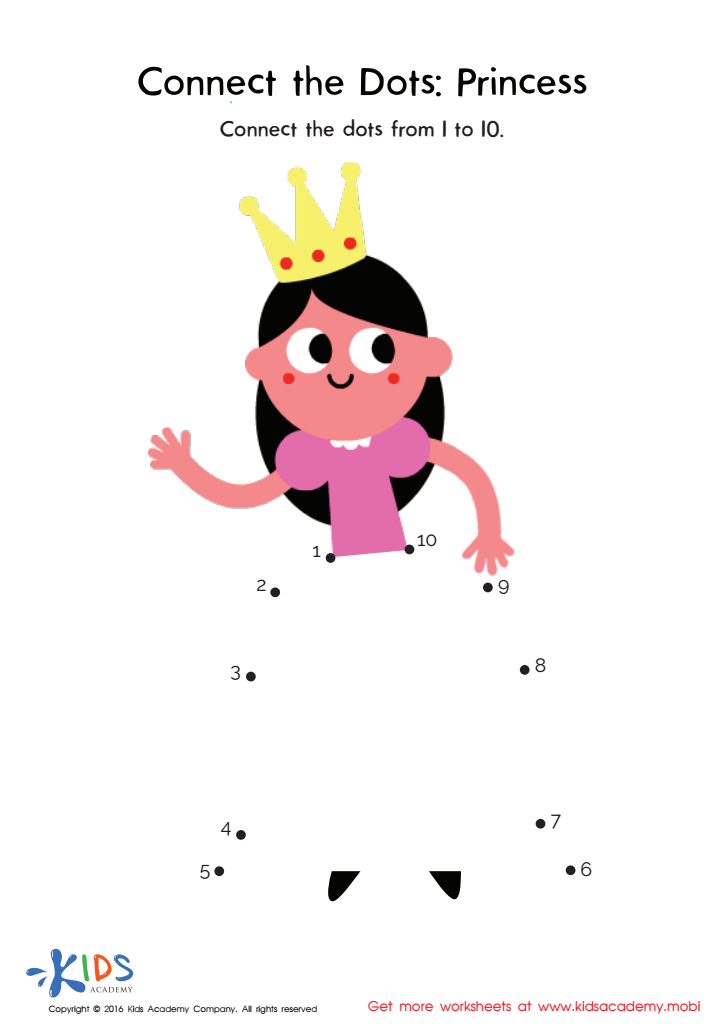


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet


Sloth – Coloring by Numbers
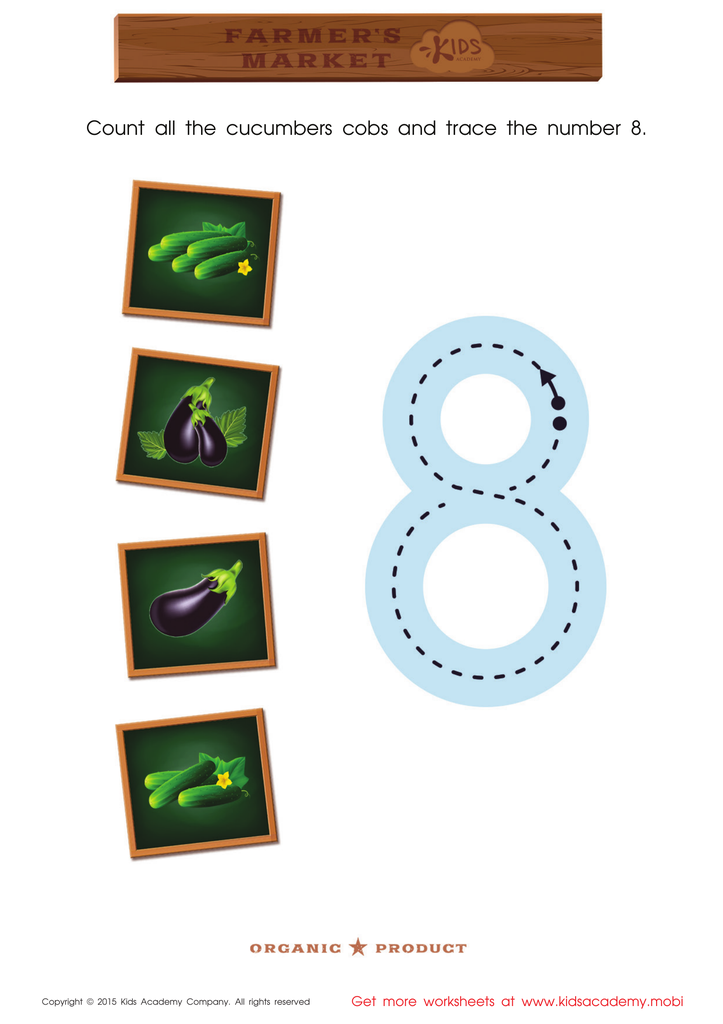


Count the Cucumbers and Trace the Number 8 Printable


Sea Adventure – Coloring by Numbers


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Great Hornbill – Coloring by Numbers


In the Treetops – Coloring Page


Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet


Little Chef – Coloring by Numbers


A Fox and a Bird – Coloring by Numbers


Little Pilot – Coloring by Numbers


Little Red Riding Hood – Coloring by Numbers


In the Garden – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills are the small muscle movements in the fingers, hands, and wrists that enable a child to perform tasks such as writing, cutting, and buttoning a shirt. For children aged 5–7, developing fine motor skills, especially through activities involving numbers 0–10, is crucial for multiple reasons.
First, learning to form numbers helps children grasp the numeric concepts, laying a foundational understanding of mathematics essential for future academic success. Practicing writing numbers improves hand-eye coordination and paves the way for clearer, more legible handwriting, benefiting all areas of a child's education.
Second, activities focused on tracing, coloring, or manipulating objects to represent numbers engage and strengthen these muscles, promoting better control and dexterity. As children develop proficiency, they gain confidence in their abilities, instilling a sense of accomplishment and encouraging a positive attitude towards learning.
Moreover, these skills are significant for daily tasks and self-help activities, fostering independence. Parents and teachers who actively support the development of fine motor skills in early grades not only contribute to academic readiness but also to a child's overall self-sufficiency. The benefits of nurturing these skills are far-reaching, influencing cognitive growth, physical confidence, and emotional well-being. Therefore, investing time in fine motor activities, particularly with a focus on numbers, yields comprehensive developmental advantages for young children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students