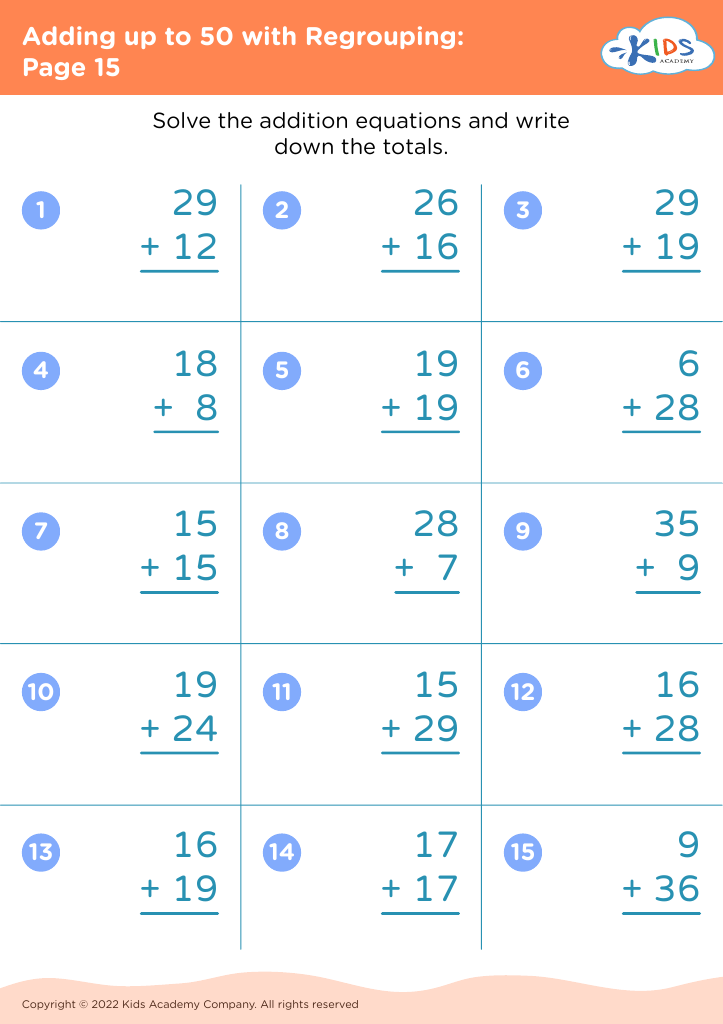
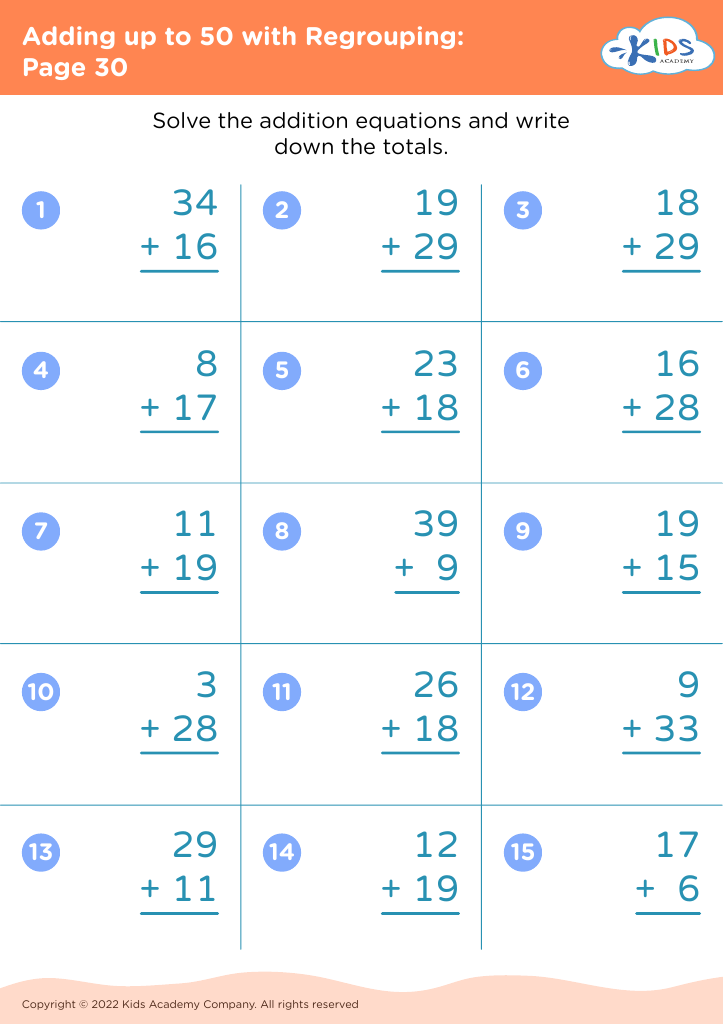
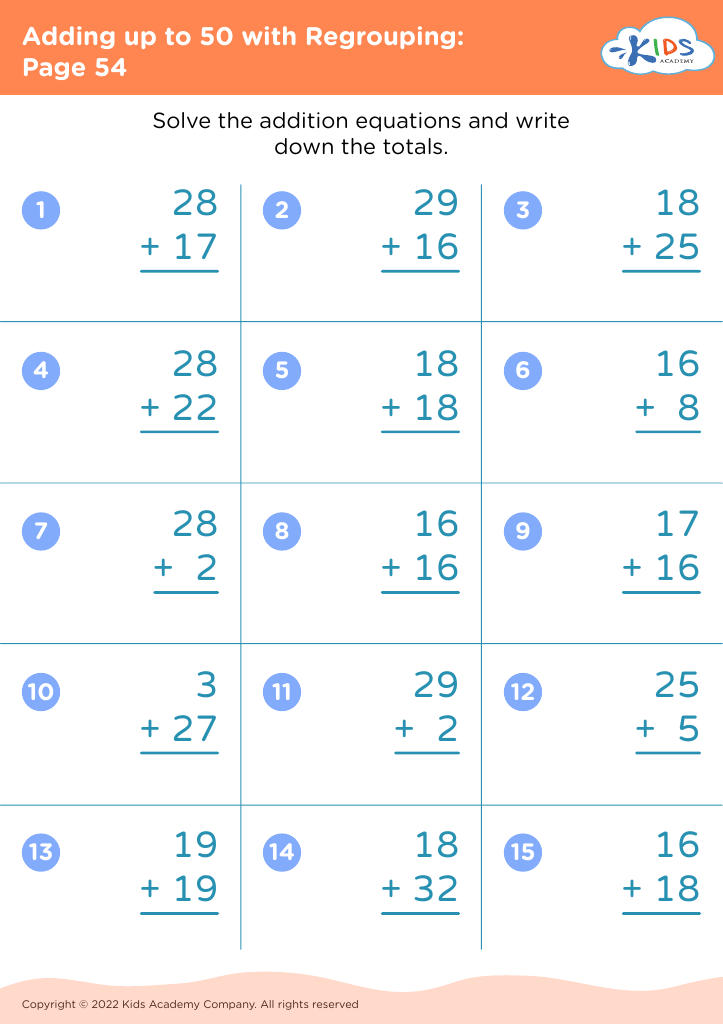
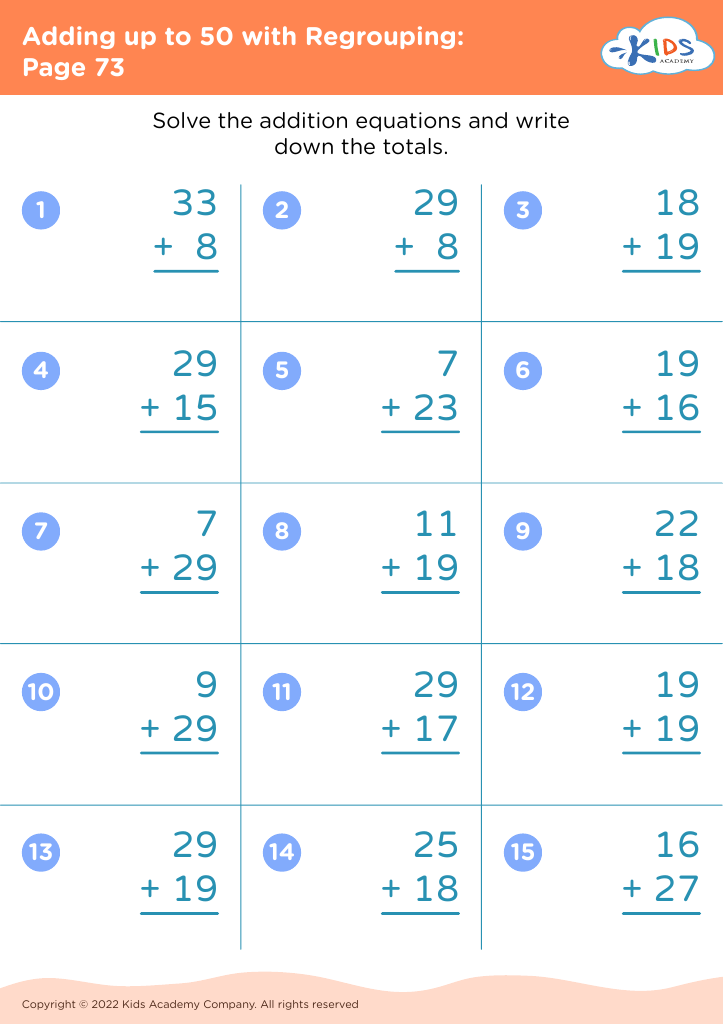
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 50 Worksheets for Ages 8-9
8 filtered results
-
From - To
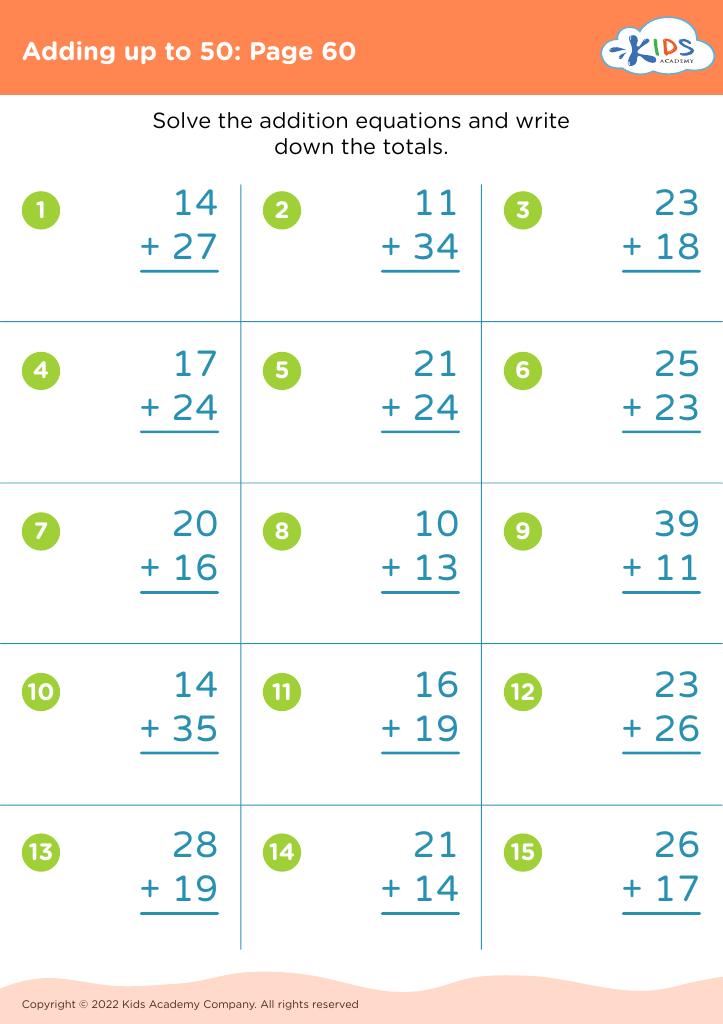
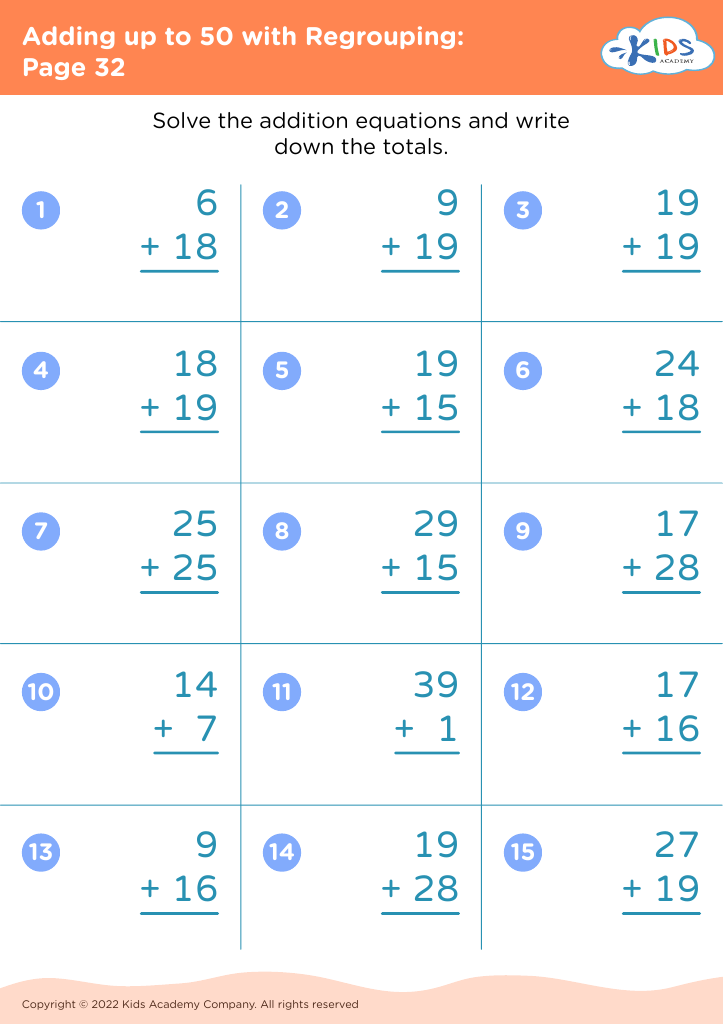
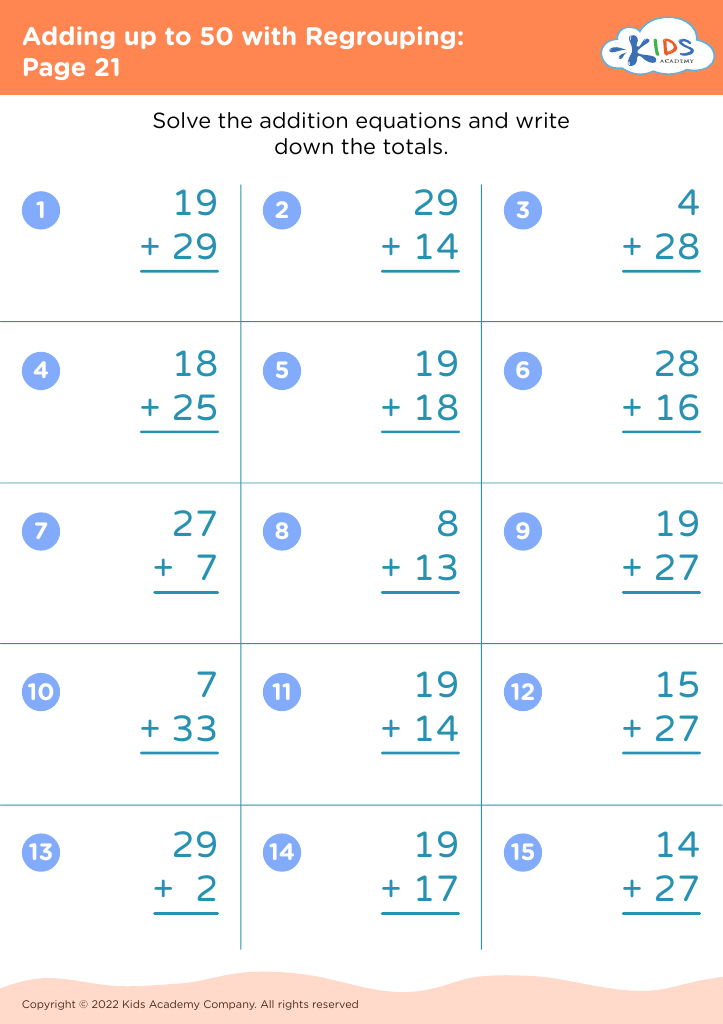
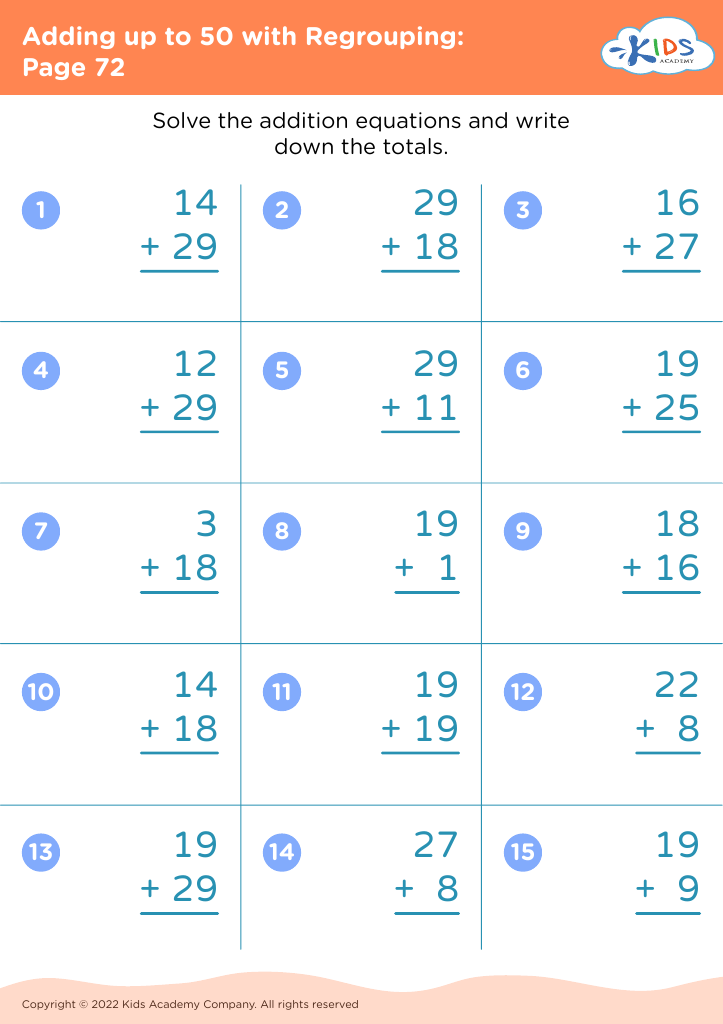
Enhance your child’s learning with our Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 50 Worksheets tailored for ages 8-9. These engaging activities are designed to develop essential math skills while simultaneously strengthening fine motor abilities. Our worksheets feature a variety of exercises that make learning addition up to 50 fun and interactive, including colorful graphics and thoughtful problem sets that captivate young learners. Perfect for reinforcing classroom lessons or extra practice at home, these printable worksheets support holistic development, ensuring children excel in mathematics while improving hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Explore them today to boost your child's confidence and proficiency in math and motor skills!
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 8-9 as they directly support core academic competencies, including achieving proficiency in adding up to 50. These skills involve the small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are necessary for tasks such as writing, cutting, and manipulating small objects. When children develop strong fine motor skills, they are better equipped to write legibly, handle classroom tools, and engage in activities that build mathematical concepts, including addition.
By the age of 8-9, students are often required to perform tasks like solving written math problems, using rulers, and interacting with educational technology—all of which necessitate refined fine motor control. Improved dexterity translates to more efficient and focused participation in math exercises, reducing frustration and enhancing learning experiences.
Furthermore, consistent practice in handwriting, drawing numbers clearly, aligning sums properly, and engaging with tactile tools like manipulatives ensures that these children can focus less on the mechanics and more on the cognitive challenges of math operations. Lastly, strong fine motor skills contribute to a child's self-esteem and independence, providing them the confidence to tackle increasingly complex tasks both in and out of the classroom. Therefore, ensuring children develop fine motor skills corresponding to good handwriting and manipulation lays a significant foundation for mathematical success.