Developing fine motor skills Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Developing Fine Motor Skills Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds" are designed to enhance your child's hand-eye coordination, finger strength, and dexterity through engaging and fun activities. Tailored for young learners, these worksheets include tasks such as cutting, tracing, and writing exercises. Perfect for use at home or at school, they help develop the precision needed for daily activities like writing, tying shoelaces, and crafting. With visually appealing designs and age-appropriate challenges, our worksheets make learning an enjoyable experience while promoting essential motor skills. Unlock your child's potential with our dedicated resources for fine motor skill development.
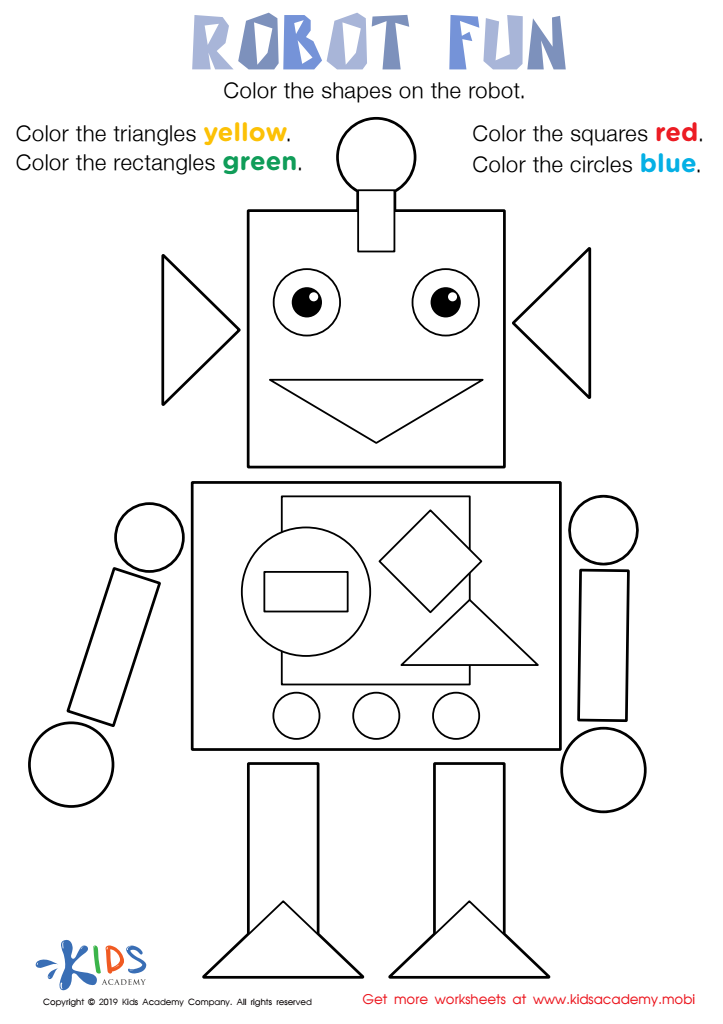

Robot Fun Worksheet
Parents and teachers should place significant emphasis on developing fine motor skills in 8-year-olds because these skills are crucial for numerous aspects of a child's life. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for everyday tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. At eight years old, children are increasingly required to demonstrate precision in their movement. Proficiency in these activities not only contributes to a child's independence but also promotes self-esteem because they can complete tasks confidently.
Additionally, fine motor skills are intrinsically linked to academic success. Children with well-developed fine motor abilities often find it easier to write legibly and quickly, enabling them to complete schoolwork more efficiently and accurately. This can lead to better academic performance and a more positive attitude towards school.
Beyond academics, developing fine motor skills also helps in the cognitive development of children. Engaging in activities like puzzles, drawing, and construction toys enhances problem-solving abilities, hand-eye coordination, and strategic thinking.
Lastly, poor fine motor skills can make children feel frustrated or excluded if they can't participate in the same activities as their peers. Therefore, fostering these skills supports both the child's physical dexterity and their emotional and social well-being, laying a strong foundation for future growth and development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students