Fine Motor Skills Easy Numbers Worksheets for Ages 5-8 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To


Ordering 11–20: Dot–to–dot Seashell Printable


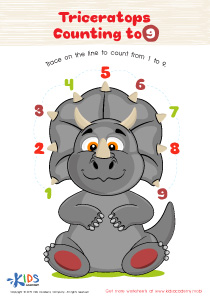
Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


Counting on the City Skyline: Dot-to-Dot Worksheet


Counting Big City Buildings Worksheet


Night Sky Numbers Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for children, especially between the ages of 5 and 8, as they lay the groundwork for various fundamental activities and cognitive development. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. For parents and teachers, focusing on activities that incorporate easy numbers can be particularly beneficial.
At this early age, children are beginning to develop numeracy skills, and combining this learning with fine motor activities can enhance their overall development. Activities that include counting, tracing, or manipulating small objects can simultaneously strengthen fine motor skills and introduce basic math concepts in an engaging way. For example, tasks like coloring numbered sections, connecting dots to form a shape, or stacking blocks to match numeric sequences encourage precision and dexterity, while also reinforcing numerical understanding.
Developing these skills can lead to increased independence and confidence in young children as they become more adept at handling everyday tasks and school assignments. Ignoring the importance of fine motor skills can result in difficulties not only in academics but also in practical life skills. Therefore, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skill development intertwined with number activities to foster well-rounded growth in children during these formative years.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students