Enhancing Counting Skills Normal Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Welcome to our "Enhancing Counting Skills: Normal Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 3-8" page! Designed for young learners, these engaging worksheets provide a fun and interactive way to develop essential counting skills while mastering basic addition and subtraction. Filled with vibrant illustrations and age-appropriate exercises, our resources cater to diverse learning styles. With a focus on hands-on practice, children will gain confidence in their math abilities and develop a solid foundation for more advanced concepts. Start your child's mathematical journey today with our thoughtfully crafted worksheets that make learning fun and effective! Explore now and watch them thrive!


Addition: Space Math Worksheet


Garage Sale Less Than Worksheet
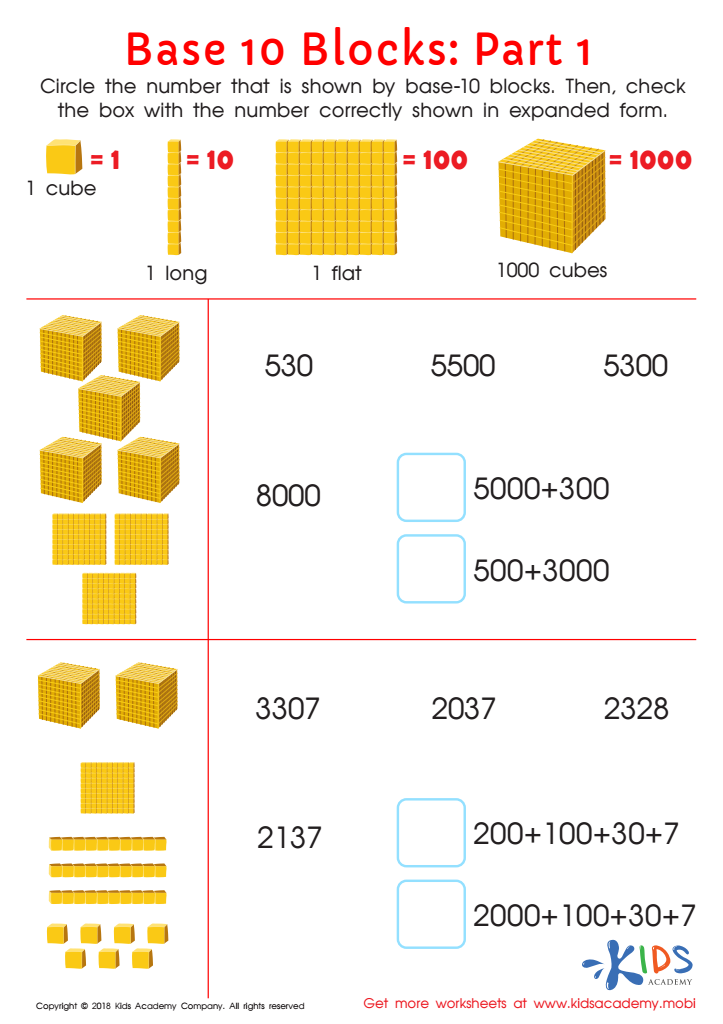

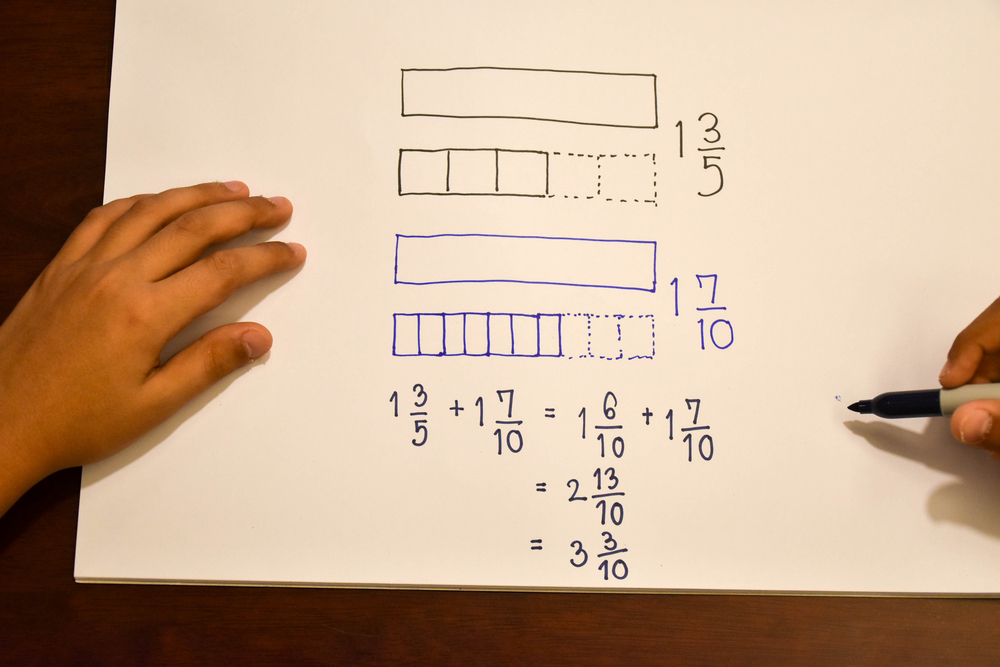
Base 10 Blocks Worksheet: Part 1
Enhancing counting skills and early addition and subtraction abilities for children aged 3-8 is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, these foundational math skills are vital for cognitive development and problem-solving, allowing children to develop logical reasoning and critical thinking. When children grasp counting, addition, and subtraction, they build confidence in their ability to tackle more complex mathematics as they grow.
Secondly, early math proficiency has a significant impact on academic success. Research shows that children who develop strong math skills in their early years are more likely to excel in school, leading to better opportunities in higher education and future career paths. This foundational knowledge also supports children's ability to cope with everyday situations involving numbers, such as managing money or measuring ingredients in cooking.
Finally, fostering counting and arithmetic skills encourages positive parental and teacher involvement. Engaging children in fun, interactive math games and activities strengthens the bond between caregivers and children and creates a supportive learning environment. By prioritizing the enhancement of counting and early arithmetic skills, parents and teachers are setting the stage for overall growth, self-esteem, and readiness for lifelong learning in children.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students