Rhyming skills development Normal Worksheets for Ages 4-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Rhyming Skills Development Worksheets designed specifically for children ages 4 to 9. These expertly crafted resources aim to enhance young learners' phonemic awareness and language skills through fun and interactive rhyming activities. Our worksheets include a variety of exercises, such as matching rhyming pairs, filling in the blanks, and creating original rhymes. By encouraging playful learning, these worksheets help strengthen vocabulary, reading fluency, and auditory discrimination. Ideal for both classroom settings and at-home learning, they cater to diverse learning styles, ensuring every child can thrive. Unlock your child's potential with our dynamic resources today!


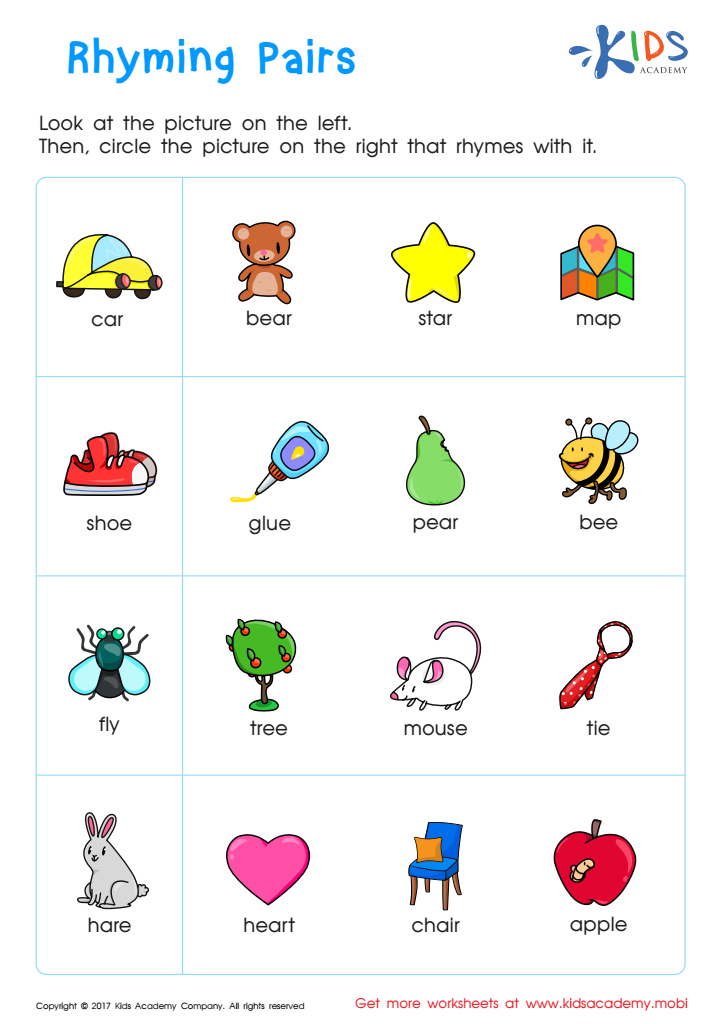
Rhyming Words Rhyming Worksheet


Rhyming Bells Worksheet


First Words: Picture Rhymes Worksheet
Rhyming skills development is a crucial aspect of early literacy for children aged 4-9. First, it enhances phonemic awareness, the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate sounds in language. This foundational skill is essential for reading and spelling since it helps children decode words and understand their structure. When children can recognize and produce rhymes, they become more adept at identifying similar sounds, which increases their reading fluency.
Additionally, rhyming boosts vocabulary development. Engaging with rhymes introduces youngsters to new words and promotes language play, making learning fun and memorable. This playful interaction fosters a positive attitude towards reading and books, which is vital for lifelong literacy.
Furthermore, rhyming cultivates cognitive skills such as memory and creativity. The rhythmic and repetitive nature of rhymes makes them easier to remember, aiding in language retention and recall. When children experiment with creating their own rhymes, they exercise their imaginations and enhance their problem-solving skills.
In summary, fostering rhyming skills in young learners builds essential foundations for reading, vocabulary, and cognitive abilities, setting them on a path to academic success and instilling a love for language and literacy. Thus, parents and teachers should prioritize this developmental aspect in their educational approaches.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students





.jpg)








