Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 5-6
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Unlock the world of critical thinking for your little ones with our Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets designed for ages 5-6! These engaging worksheets introduce young learners to the basics of chess while enhancing their logical reasoning and decision-making abilities. With fun, interactive activities tailored to capture their attention, children will enjoy exploring various chess scenarios that promote strategic thinking. Ideal for early education settings and at-home learning, our worksheets provide a delightful way to develop essential problem-solving skills. Help your child build confidence and cognitive skills while nurturing a lifelong love for the game of chess!
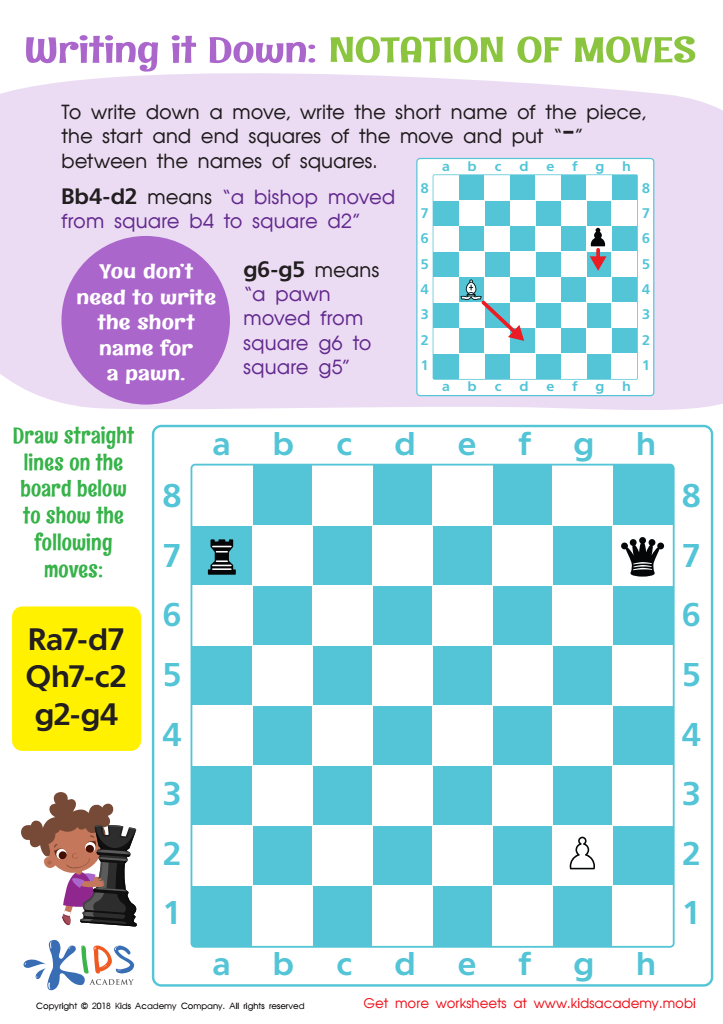

Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
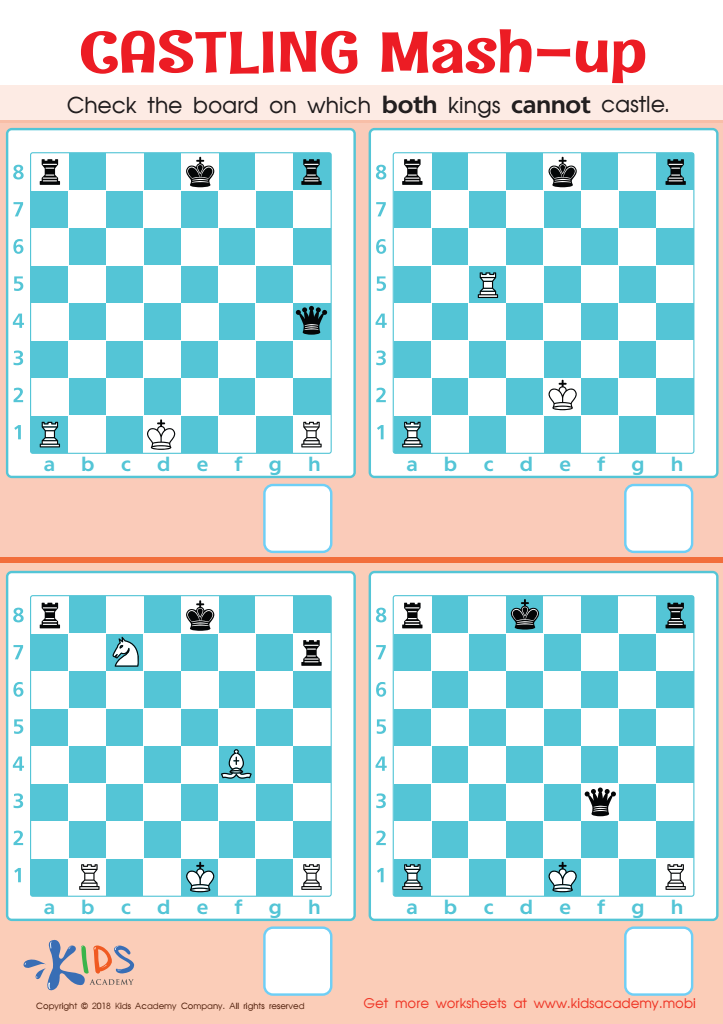

Castling Mash–up Worksheet
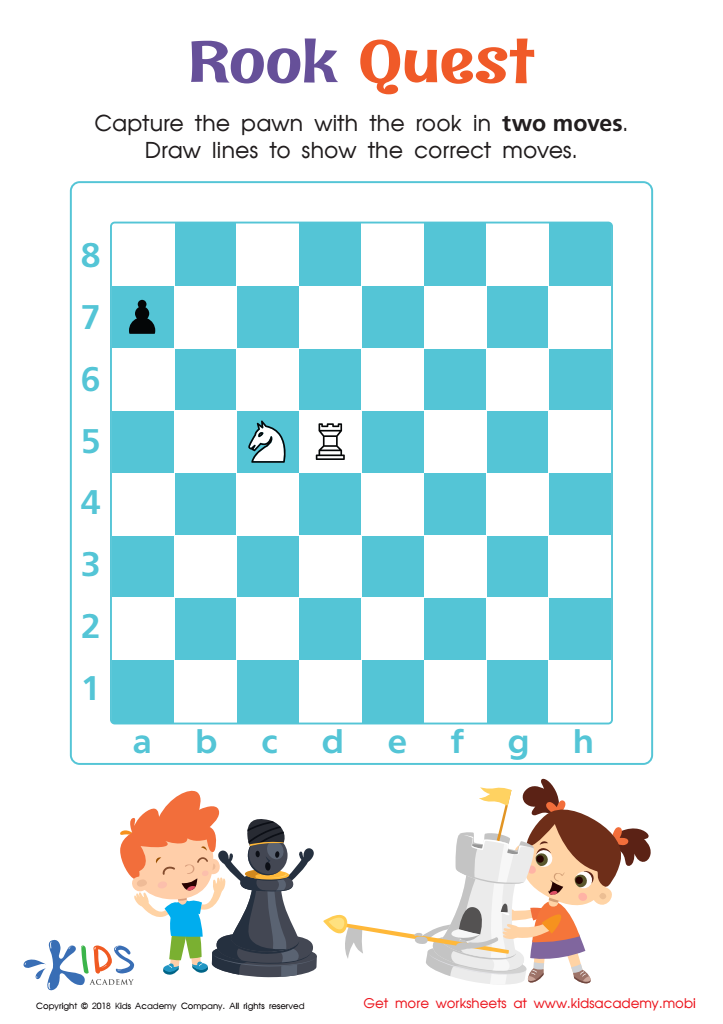

Rook Quest Worksheet
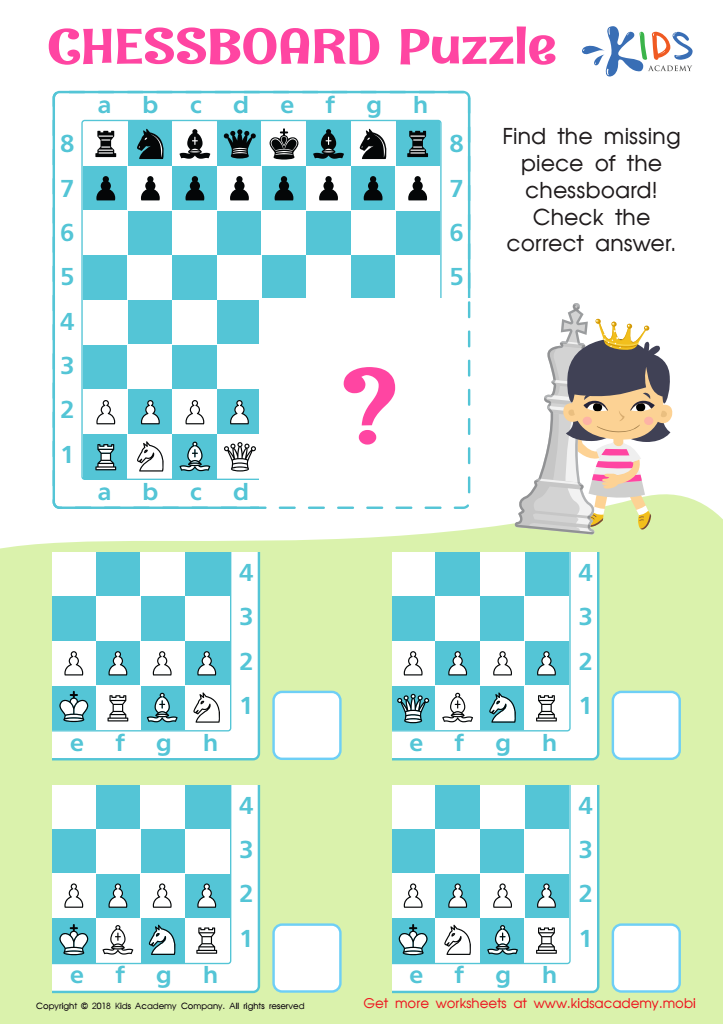

Chessboard Puzzle Worksheet
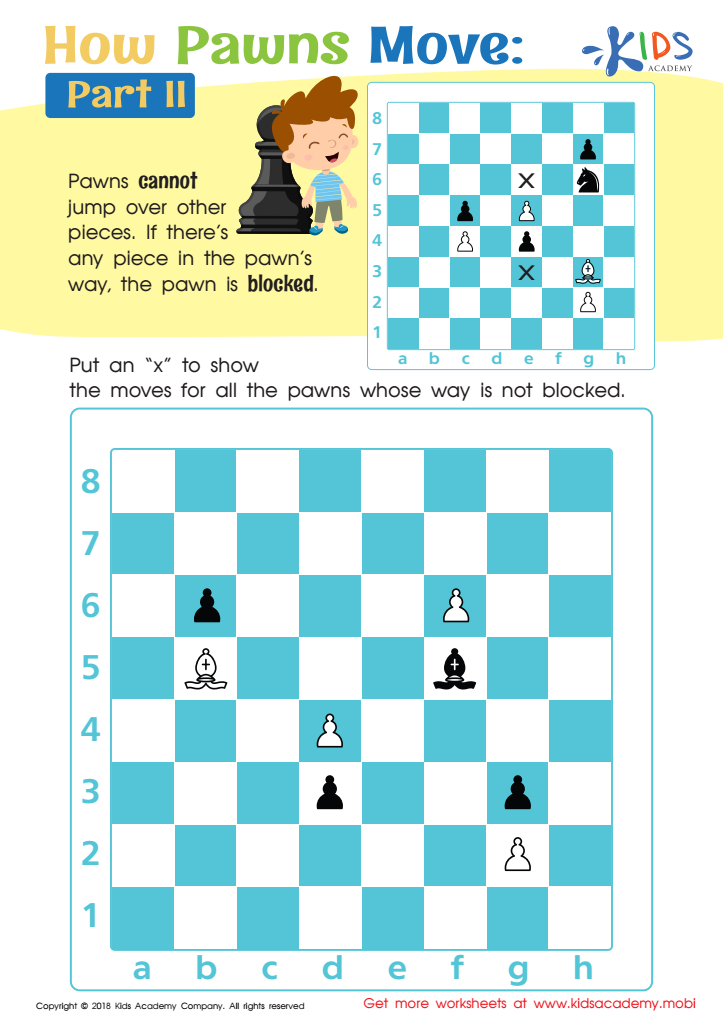

How Pawns Move: Part II Worksheet
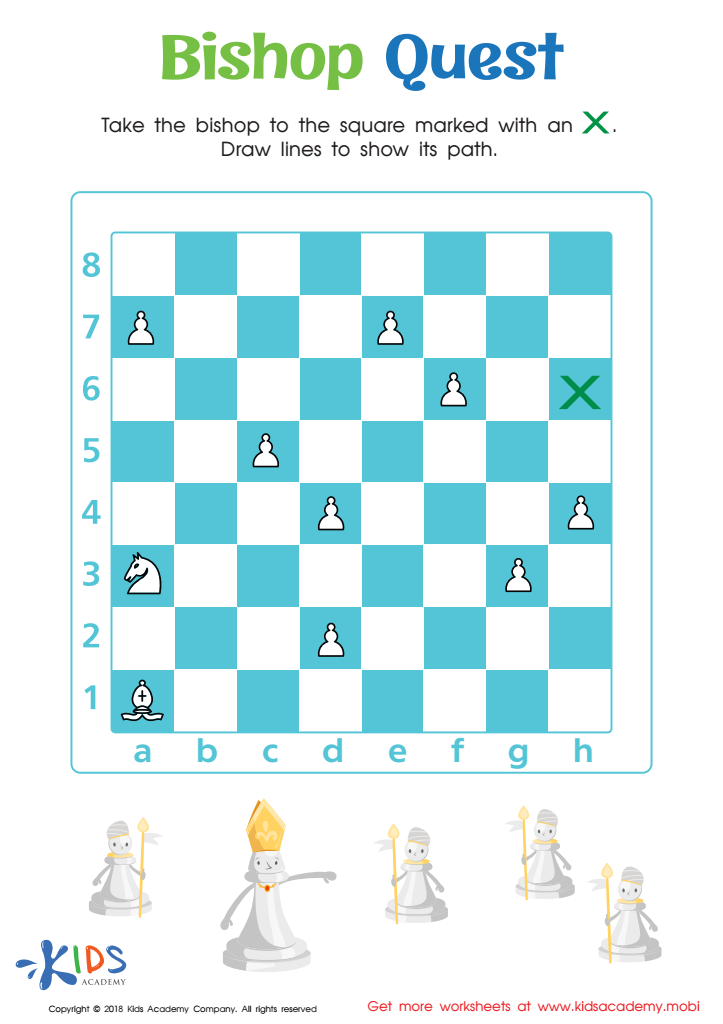

Bishop Quest Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize developing problem-solving skills through normal chess for children aged 5-6 for several compelling reasons. First, chess promotes critical thinking and strategic planning. At such a young age, introducing them to the game encourages children to analyze situations, foresee outcomes, and make informed decisions. These cognitive skills extend far beyond the chessboard, enhancing academic performance across subjects such as math and reading.
Additionally, chess fosters patience and perseverance. Children learn that success requires practice and understanding that not every move yields an immediate reward. This intrinsic resilience is vital as they face challenges in their educational journey and in life.
Moreover, engaging in normal chess nurtures social skills. Playing with peers teaches cooperation, respect for opponents, and the importance of good sportsmanship. It builds confidence as they navigate wins and losses, helping them manage emotions effectively.
Finally, introducing chess at this early age is a wonderful bonding opportunity for parents and children or teachers and students, enhancing relationships through enjoyable, shared experiences. Overall, incorporating problem-solving skills through chess lays a strong foundation for lifelong learning, cognitive development, and social interaction.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students