Addition Practice Normal Worksheets for Ages 5-9 - Page 2
39 filtered results
-
From - To
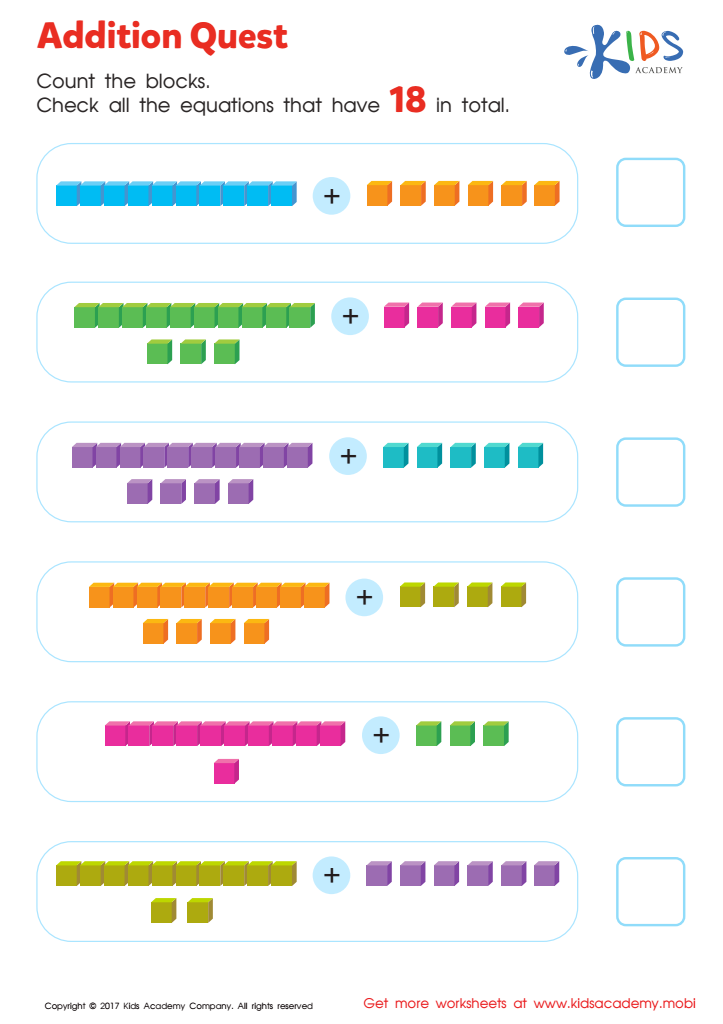

Addition Quest Worksheet: Part 2
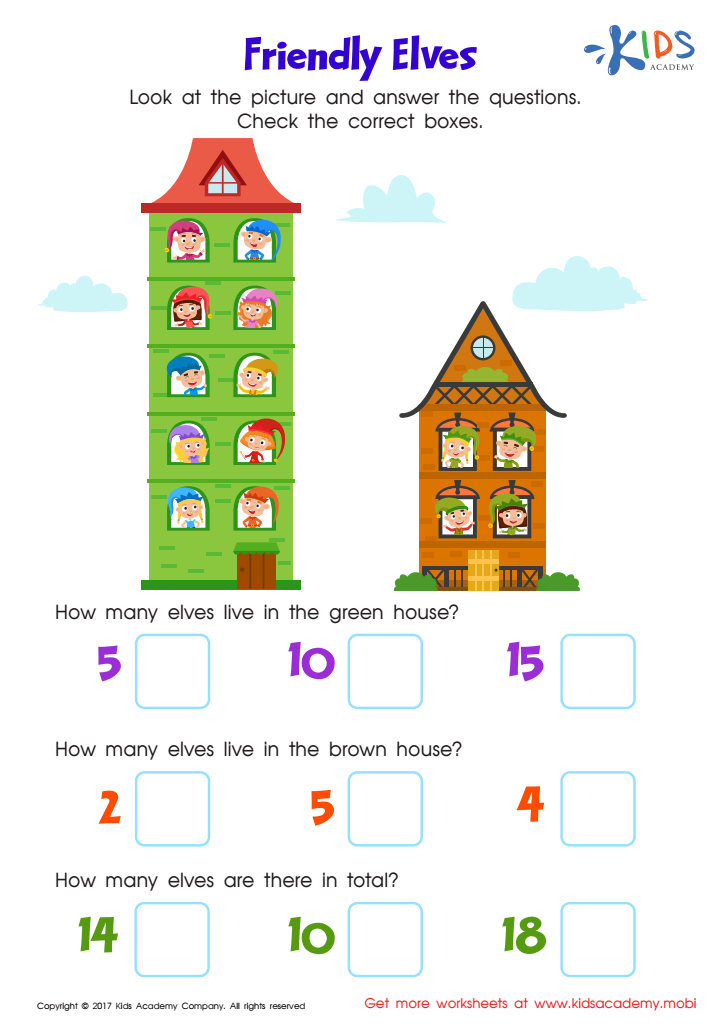

Place Value: Friendly Elves Worksheet


Building with 10 Worksheet


Clothes Math: Bar Graph Word Problems Worksheet
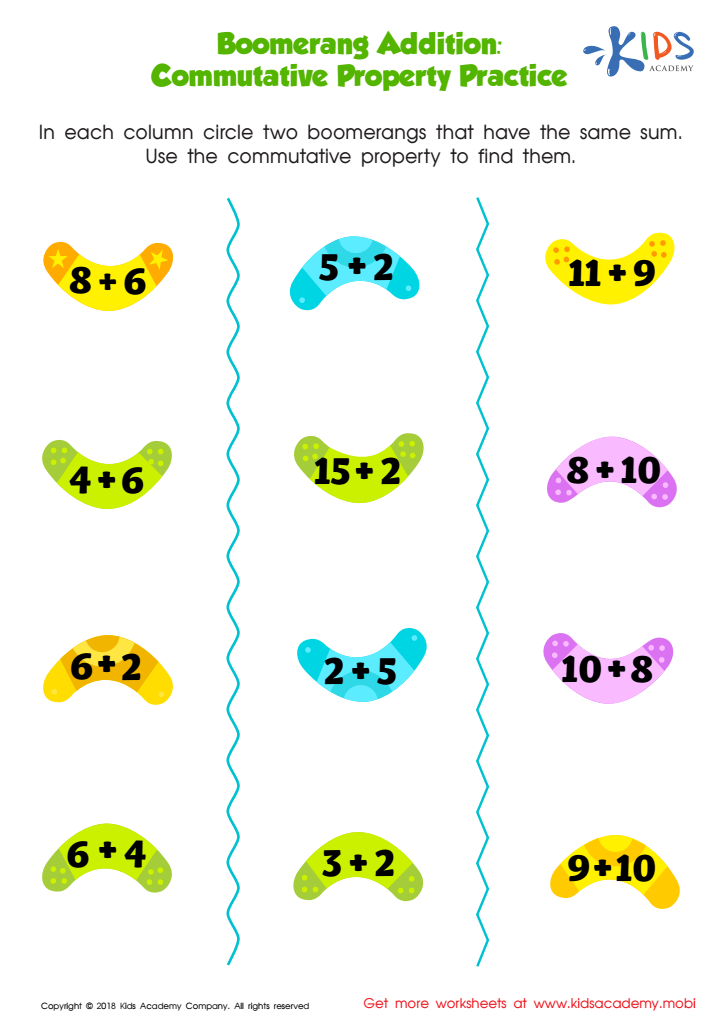

Boomerang Addition Worksheet
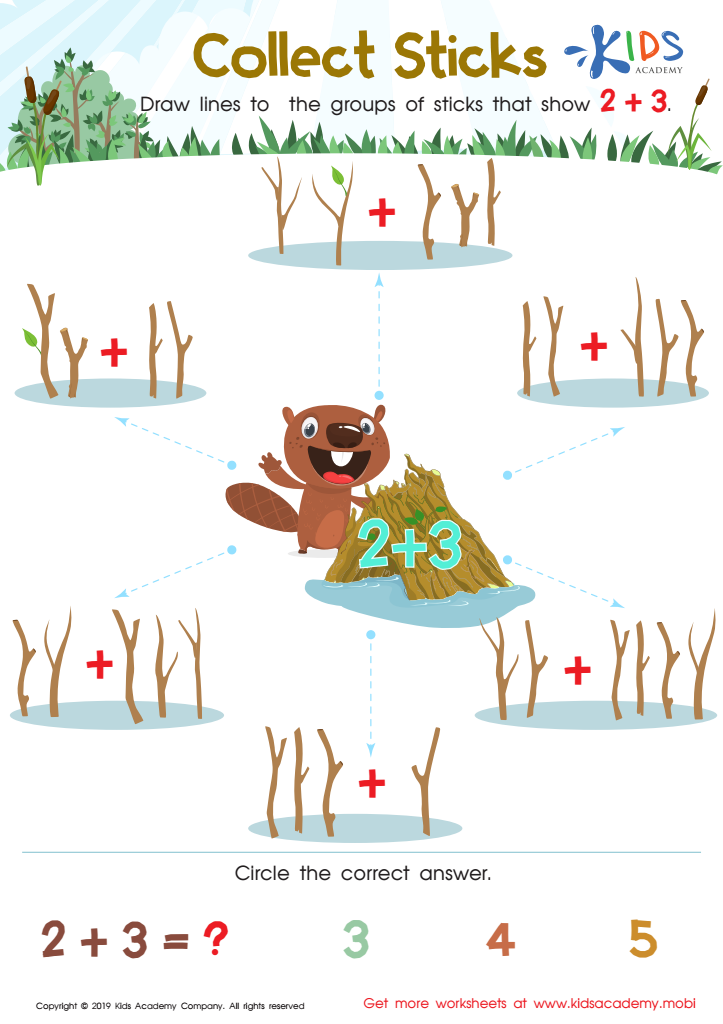


Collect Sticks Worksheet


Undersea Math Worksheet
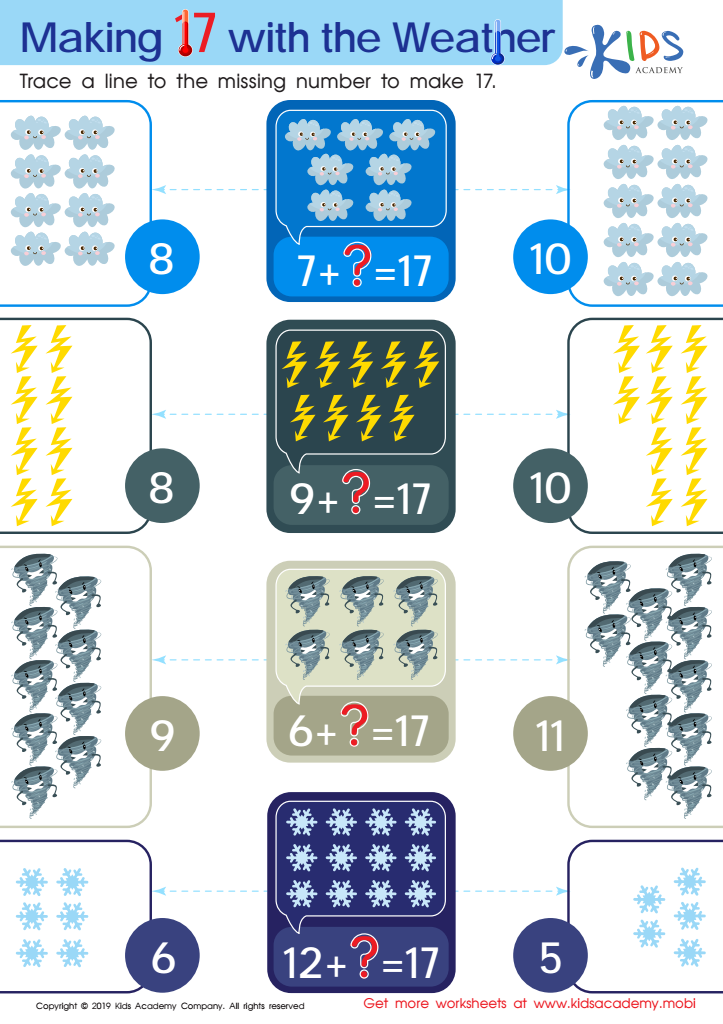

Making 17 with the Weather Worksheet


Pirate Ship Addition Worksheet
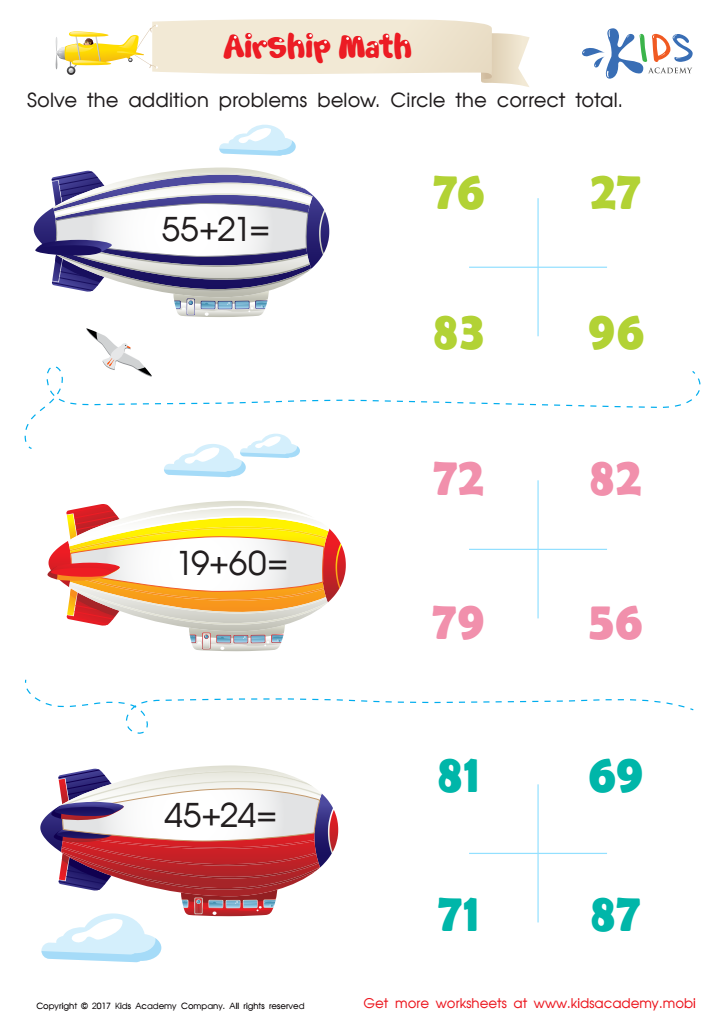

Airship Math Addition Printable
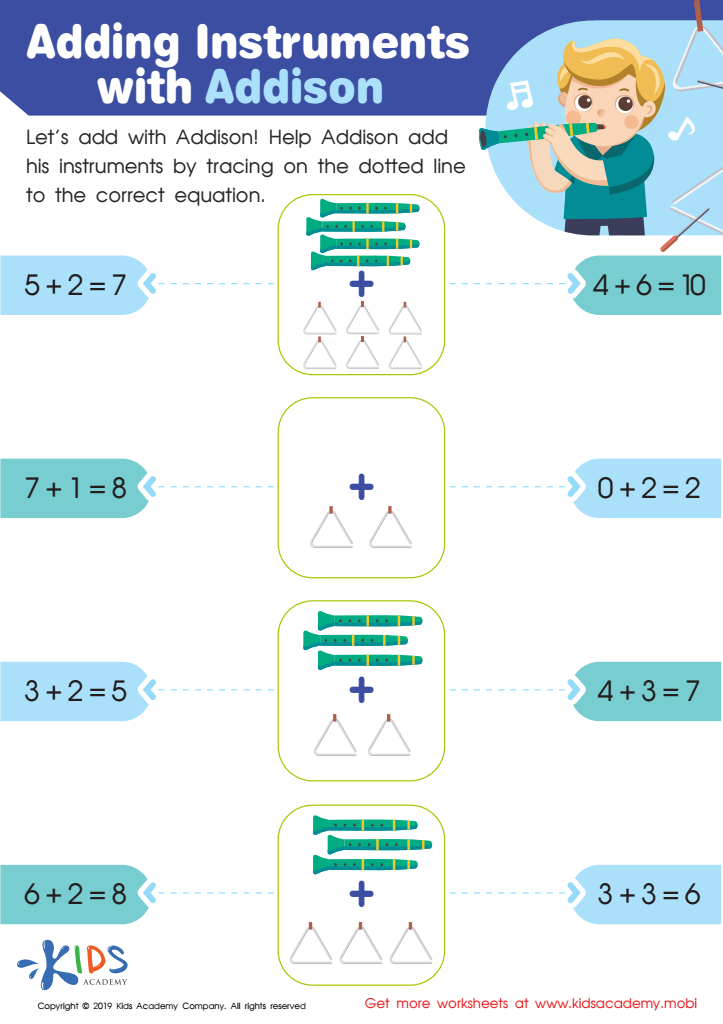

Adding Instruments with Addison Worksheet
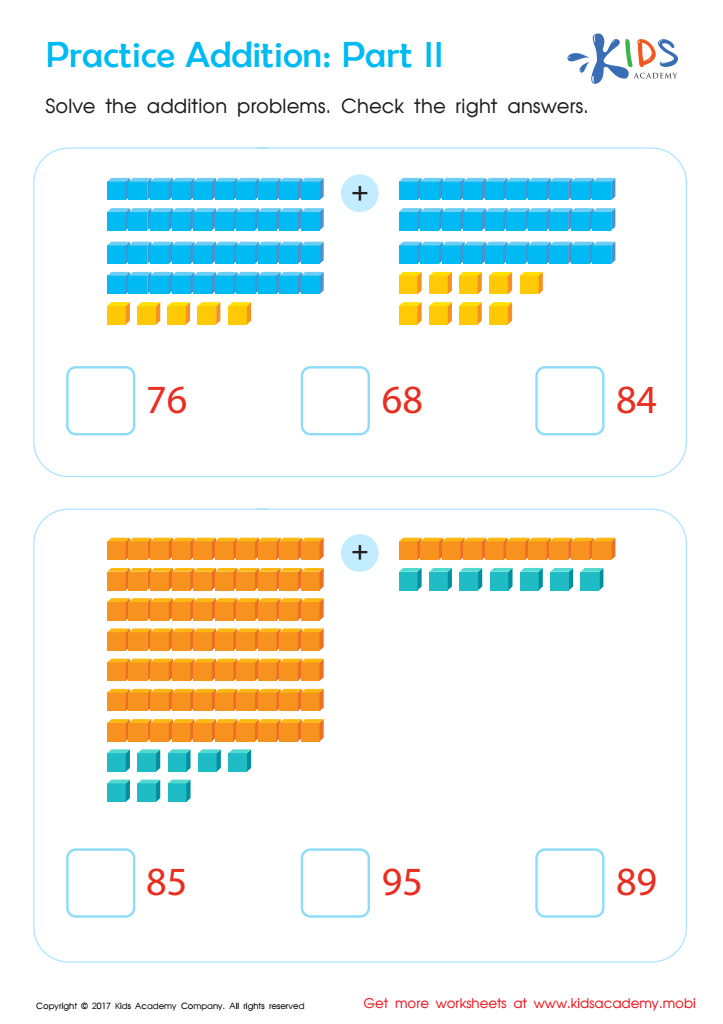

Practice Addition: Part 2 Worksheet

Falling Leaves Worksheet

Pyramid Math to Make 11 Worksheet

Number Line Fun Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize addition practice for children aged 5-9 because these early years are crucial for building a strong mathematical foundation. Learning addition at this age helps develop number sense, a fundamental skill that underpins all future math learning. Through understanding addition, children learn to recognize patterns, understand relationships between numbers, and develop problem-solving skills.
Addition practice also supports cognitive development. It enhances memory, logic, and decision-making abilities. Repeated practice enables children to perform calculations automatically, freeing cognitive resources for more complex problem-solving.
Additionally, consistent practice builds confidence. Mastery of addition allows children to feel more competent and self-assured in their abilities, fostering a positive attitude towards math and learning in general. When children struggle with basic math concepts, it can lead to anxiety and avoidance of math-related subjects later in life.
Moreover, math is not just essential for academic success but also for everyday activities. Skills acquired through addition are commonly used in daily life, such as managing money, understanding time, and measuring ingredients in cooking. Instilling these skills at a young age sets children up for practical problem-solving in real-life situations.
Therefore, prioritizing addition practice in early childhood equips children with essential tools for both academic and real-world success, laying a solid groundwork for future learning and everyday applications.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students