Basic Addition Skills Normal Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 5-9
8 filtered results
-
From - To
Welcome to our "Basic Addition Skills" worksheets page, designed for children ages 5-9! Here, you'll find engaging and colorful printable worksheets focused on normal addition and subtraction techniques. Our resources help young learners develop essential math skills through fun exercises that build confidence and understanding. Each worksheet is designed to cater to different learning levels, ensuring that every child can practice at a pace that suits them. With a variety of interactive activities, your child will enjoy mastering fundamental addition and subtraction concepts. Start fostering a love for math today with our carefully crafted worksheets that make learning enjoyable and effective!
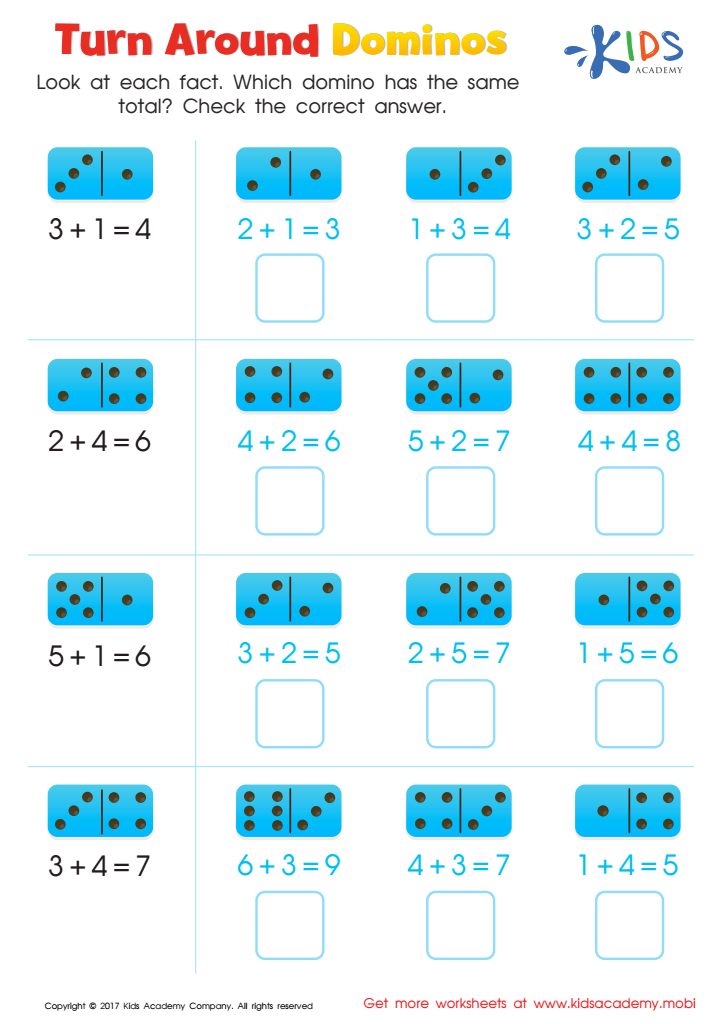

Turn Around Dominos Worksheet
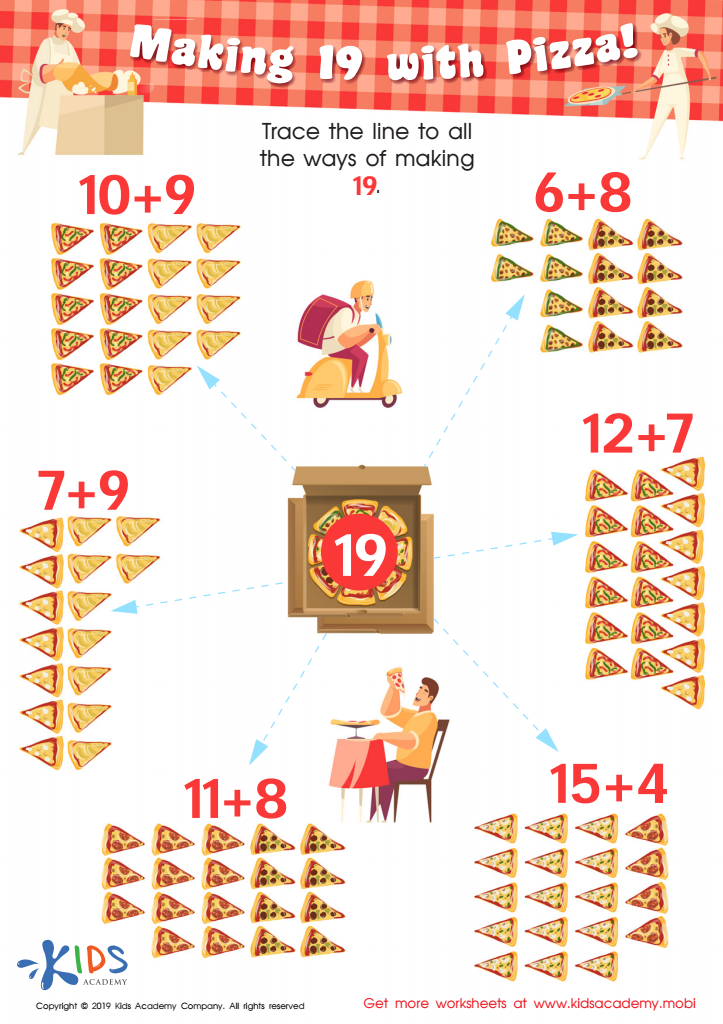

Making 19 with Pizza! Worksheet
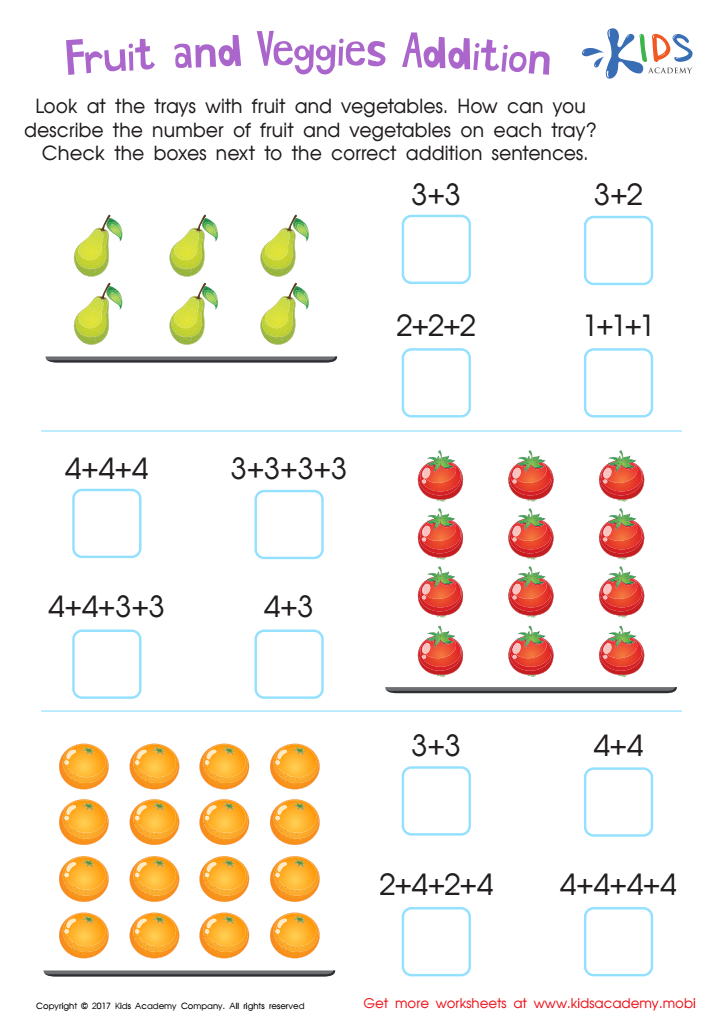

Fruit and Veggies Worksheet
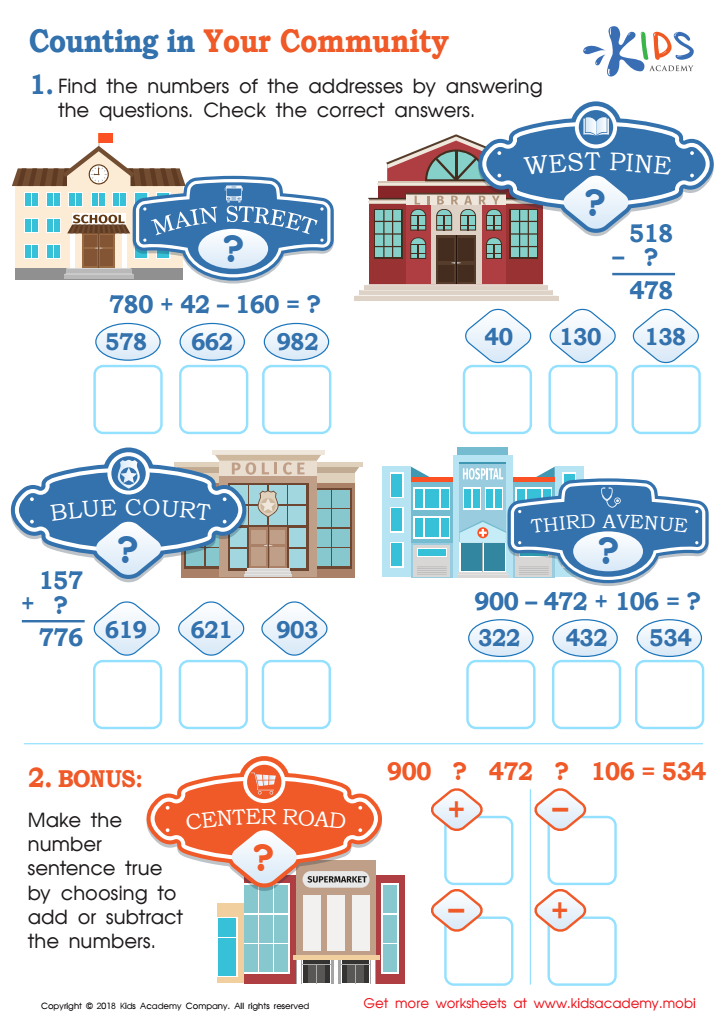

Counting in Your Community Worksheet


Adding Numbers: What Country Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet
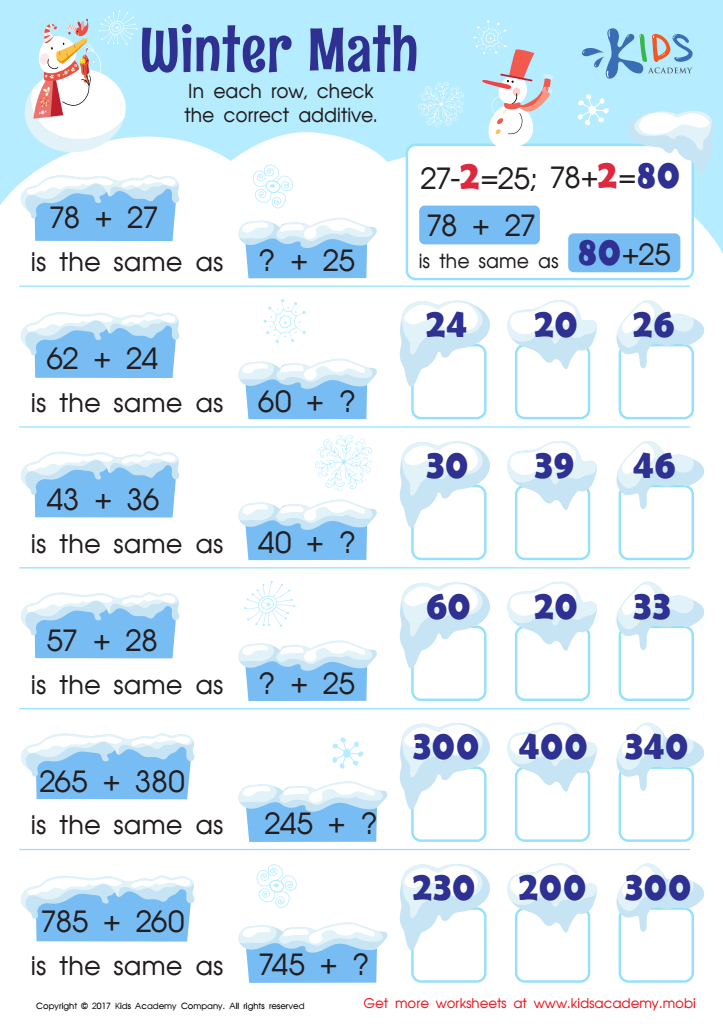

Free Addition Worksheet
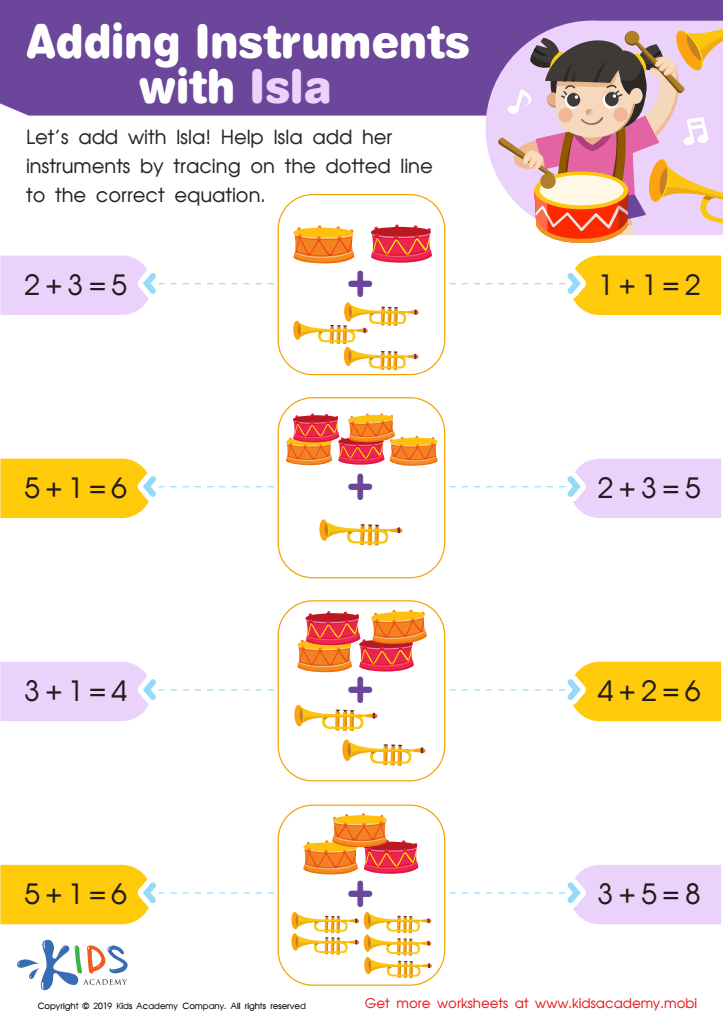

Adding Instruments with Isla Worksheet
Basic addition and subtraction skills are foundational to a child's overall mathematical understanding and development, particularly for ages 5-9. This crucial period lays the groundwork for all future learning in math. A solid grasp of these skills fosters problem-solving abilities, logical thinking, and boosts self-confidence in young learners.
Parents and teachers should care about these skills because they are essential not only for academic success but also for everyday life. Simple tasks such as counting change, managing time, or sharing items require a basic understanding of addition and subtraction. Early proficiency can help prevent future learning gaps and anxiety surrounding math as children progress through school.
Moreover, these skills support critical thinking and reasoning, encouraging students to make connections between different concepts. Engaging children in fun, contextual learning activities can stimulate their interest and make math enjoyable. When parents and educators collaboratively promote numerical fluency through games, songs, or hands-on activities, children are more likely to develop a positive attitude towards math.
Ultimately, fostering basic addition and subtraction skills equips children with the tools necessary for academic enrichment and lifelong learning. Thus, ensuring that they are confident and competent in their mathematical abilities should be a priority for both parents and teachers.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students