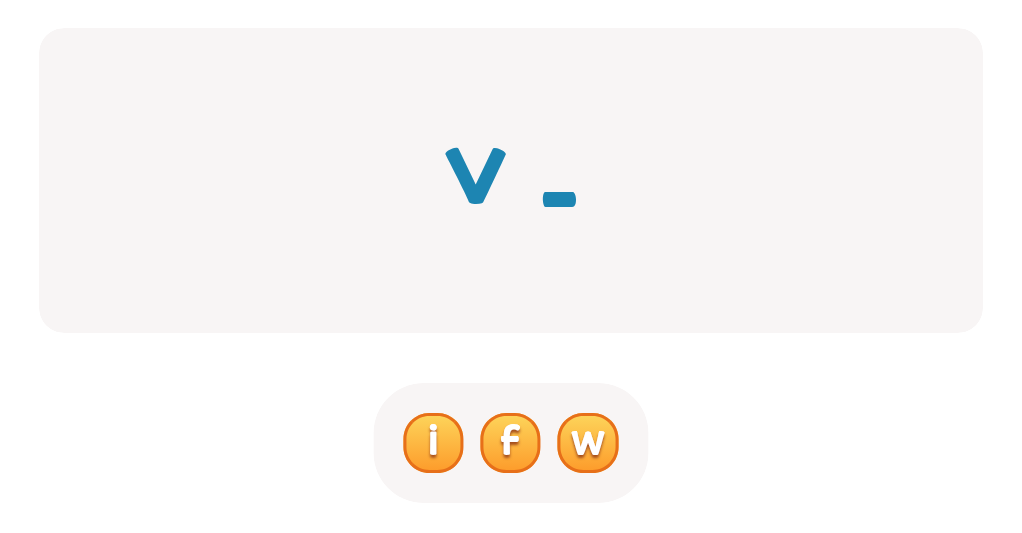
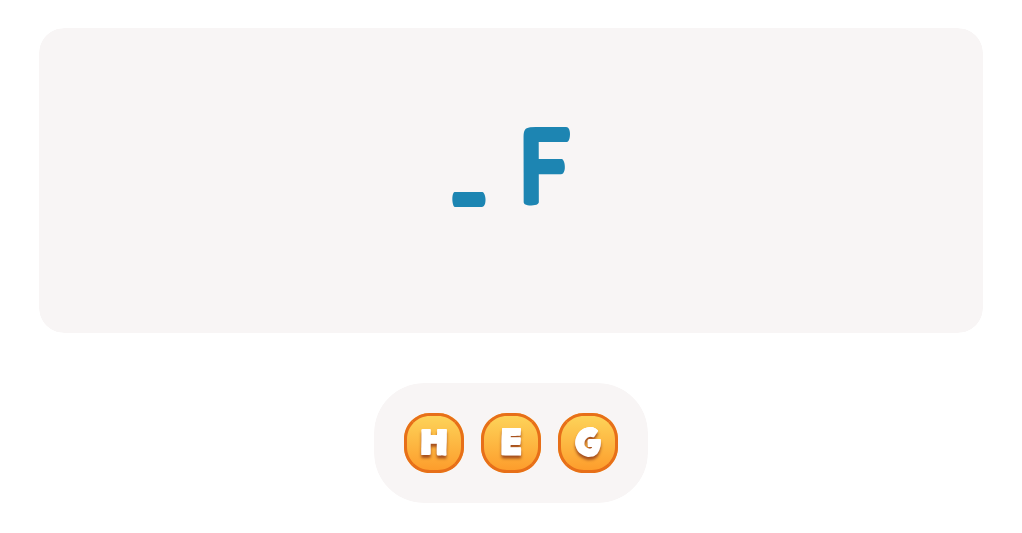
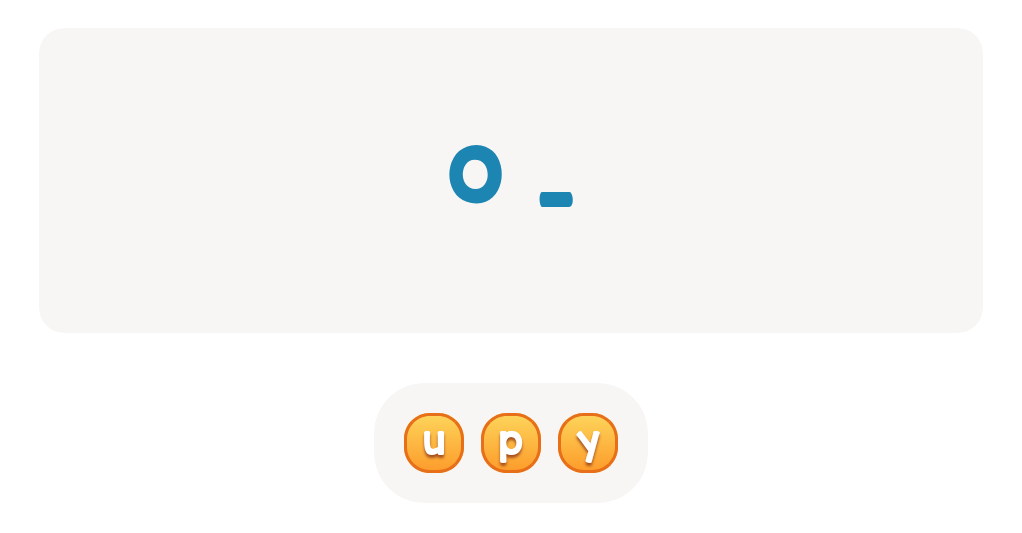
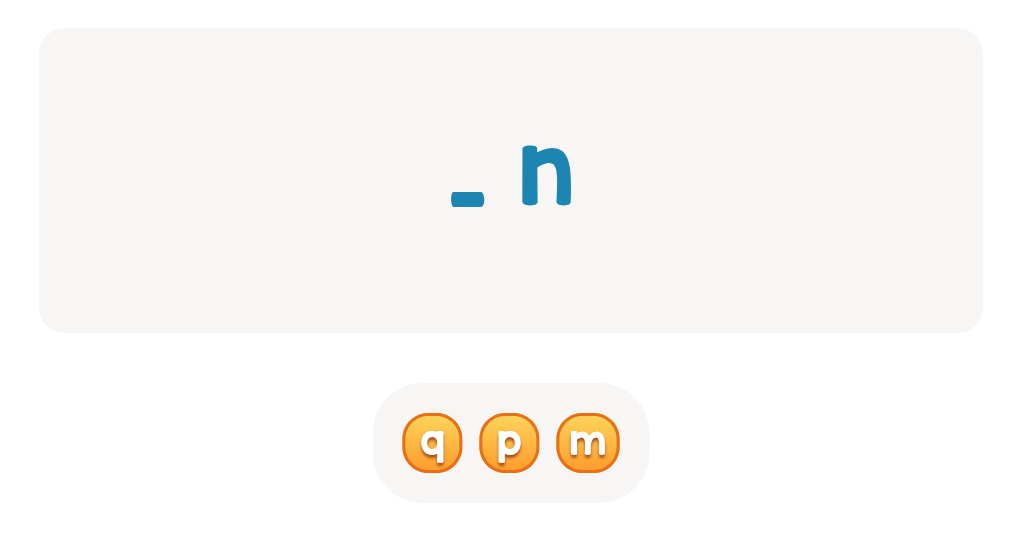
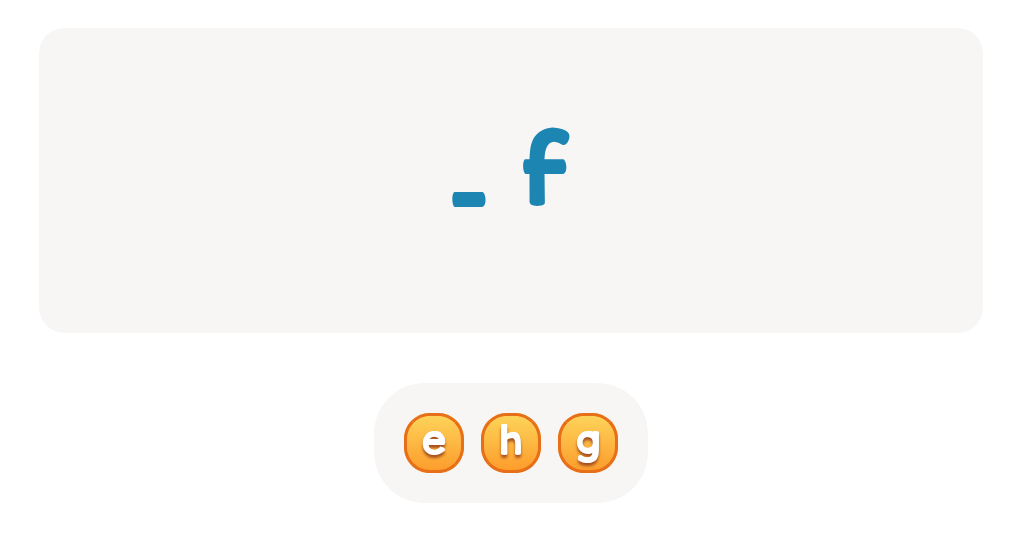
Letter recognition Normal ABC Order Worksheets for Ages 6-7
8 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Letter Recognition Normal ABC Order Worksheets" for ages 6-7 are designed to make learning the alphabet engaging and effective. These colorful and fun printable worksheets help young learners master the order of the alphabet while enhancing their letter recognition skills. Perfect for both classroom and at-home practice, each worksheet presents activities that challenge and delight children, building a strong foundation for reading and writing. Watch your child's confidence grow as they correctly sequence the letters from A to Z with enthusiasm and ease. Equip your little one with essential literacy skills through enjoyable educational exercises. Dive into alphabet adventure today!

Letter P Tracing Page


Letter Q Tracing Page

Letter H Tracing Page


Letter G Tracing Page

Letter L Tracing Page


Letter K Tracing Page


Letter F Tracing Page


Letter D Tracing Page
Letter recognition in normal ABC order is foundational for children ages 6-7. At this age, understanding the correct sequence of the alphabet serves as a crucial building block for developing literacy skills. For parents and teachers, fostering this knowledge aids the transition from simple letter recognition to more complex tasks like reading and writing.
Firstly, recognizing letters in order enables children to efficiently locate them in various contexts—be it in an alphabet chart or a dictionary. This familiarity promotes confidence and independence in young learners. Additionally, knowing the correct sequence enhances their ability to follow along in alphabetical lists, comprehend classroom materials, and organize information logically.
Moreover, mastering the ABC order lays the groundwork for alphabetic principle comprehension, where children connect letters with sounds. This understanding is pivotal for phonemic awareness, an essential component of reading proficiency and overall language acquisition. Without a clear grasp of the ABC order, children may struggle to decode words, hindering their reading and academic progress.
Finally, early mastery of letter recognition can instill a joy for learning. It enables children to play educational games, enjoy alphabet-centered activities, and participate actively in classroom tasks. Thus, prioritizing this skill benefits overall linguistic development, setting up learners for long-term success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students