Alphabet Recognition Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 2
64 filtered results
-
From - To


Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet
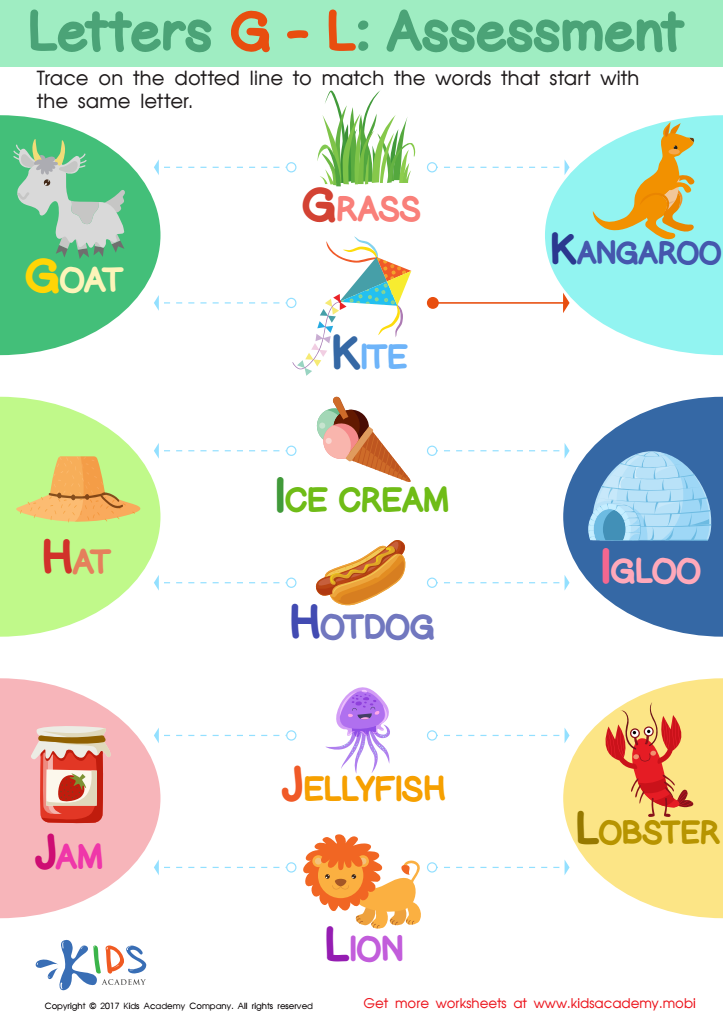

Letters G-L Worksheet
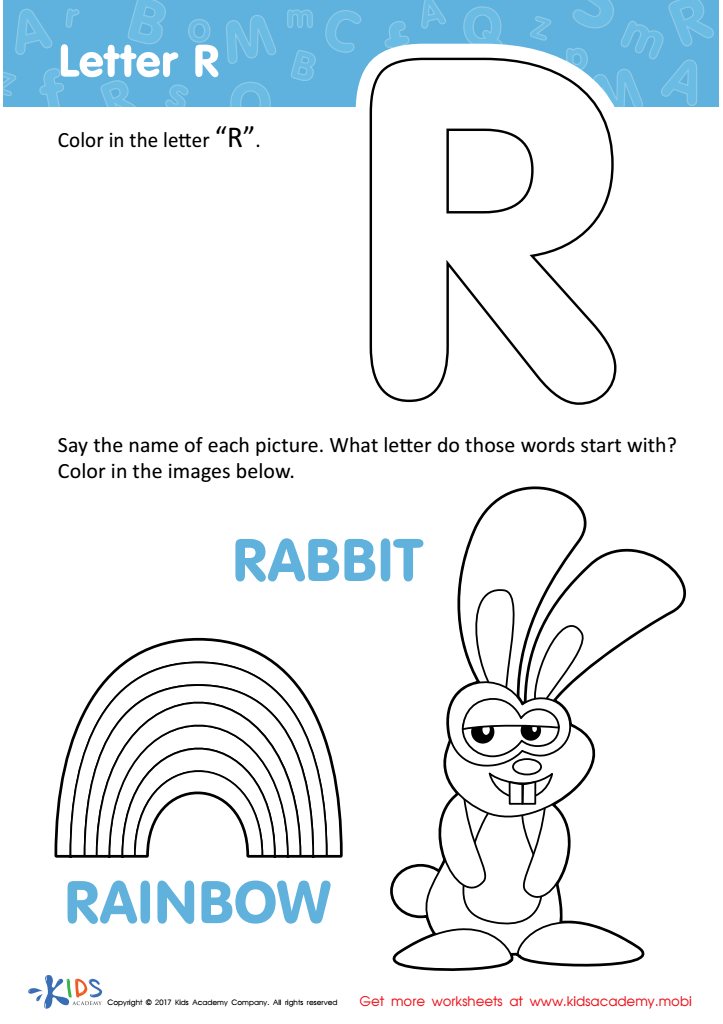

Letter R Coloring Sheet
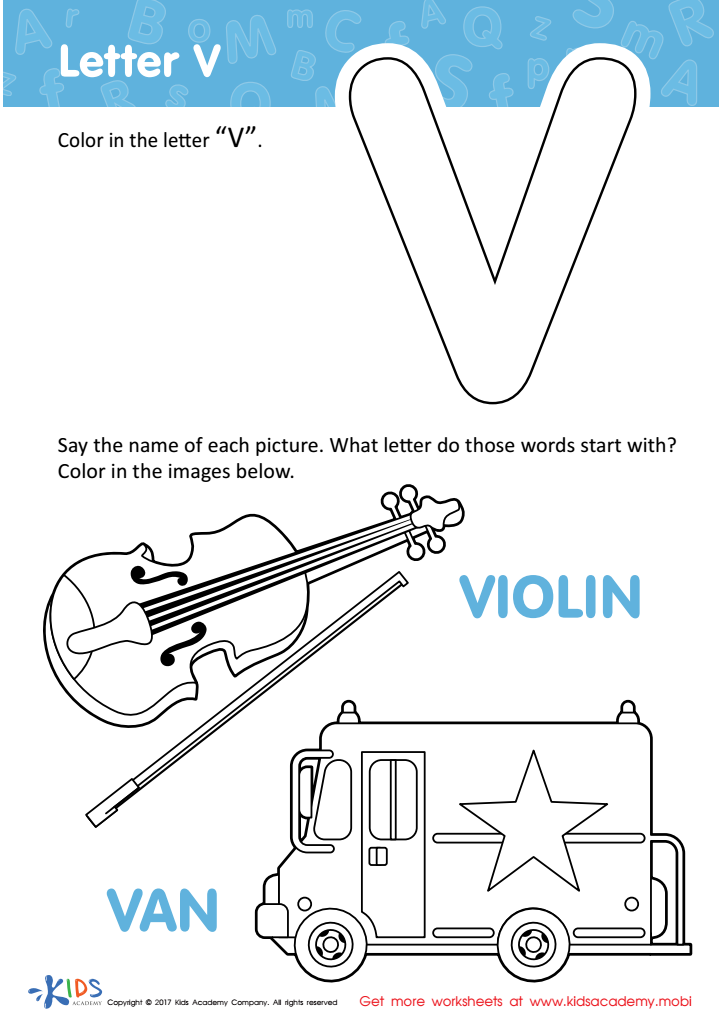

Letter V Coloring Sheet


Letter C Coloring Sheet
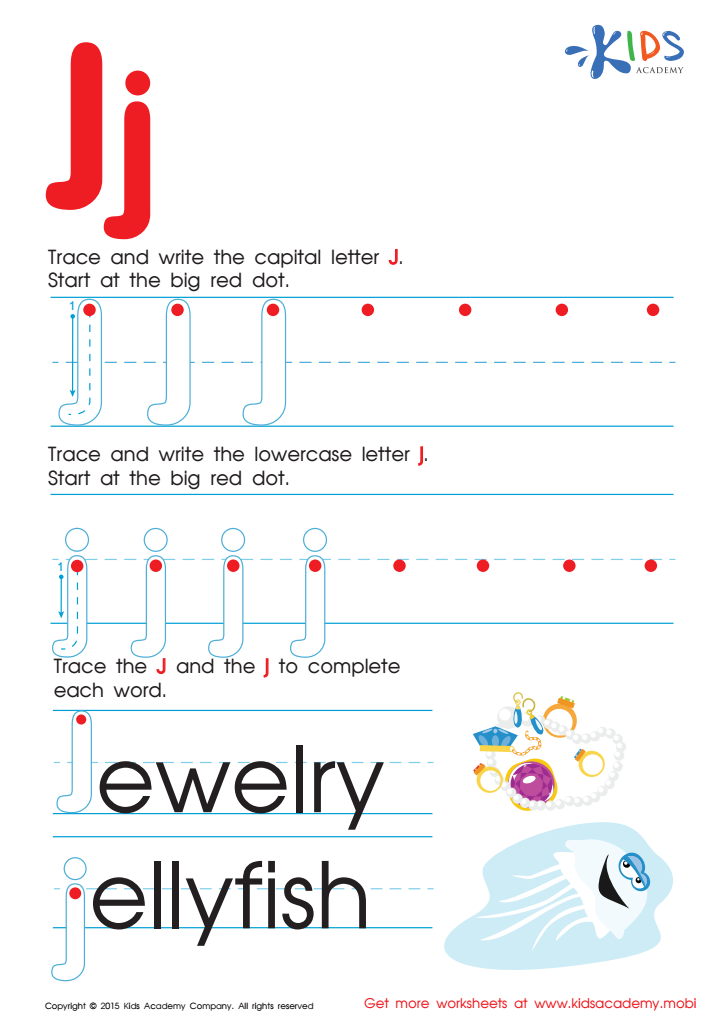

Letter J Tracing Page
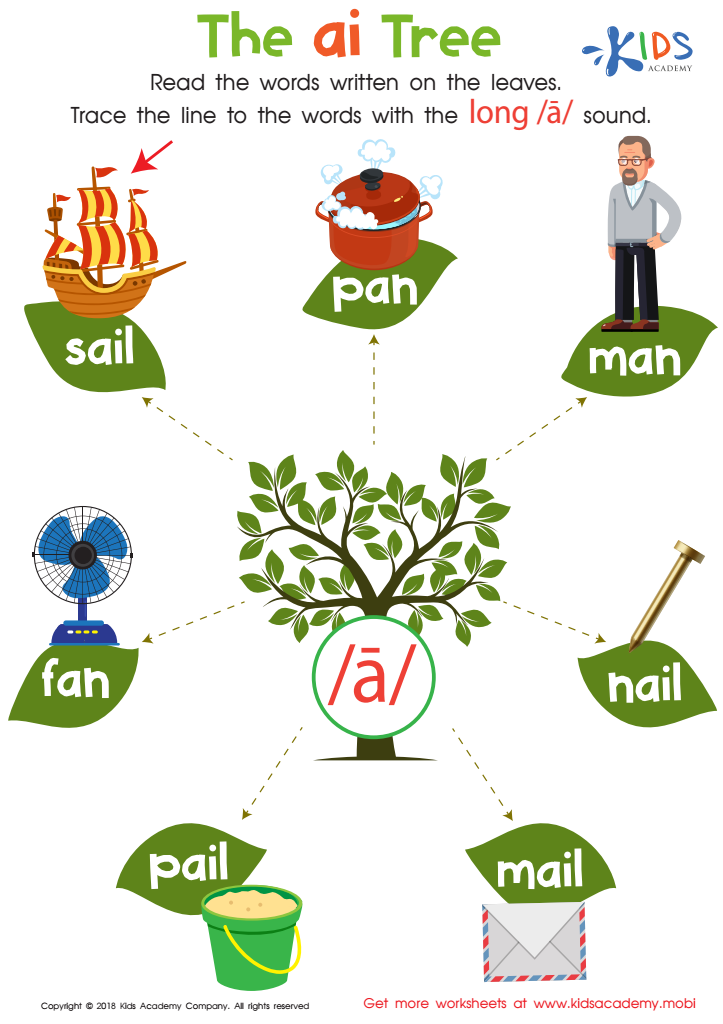

The AI Tree Worksheet


Find Uppercase Letters P, Q, and R Worksheet
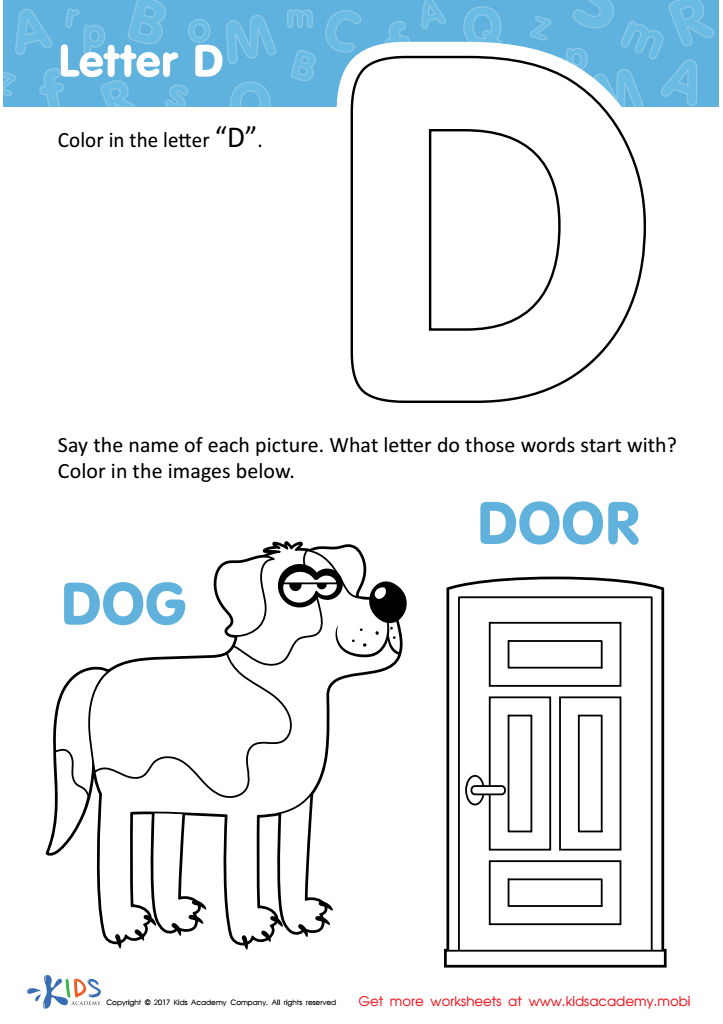

Letter D Coloring Sheet


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet
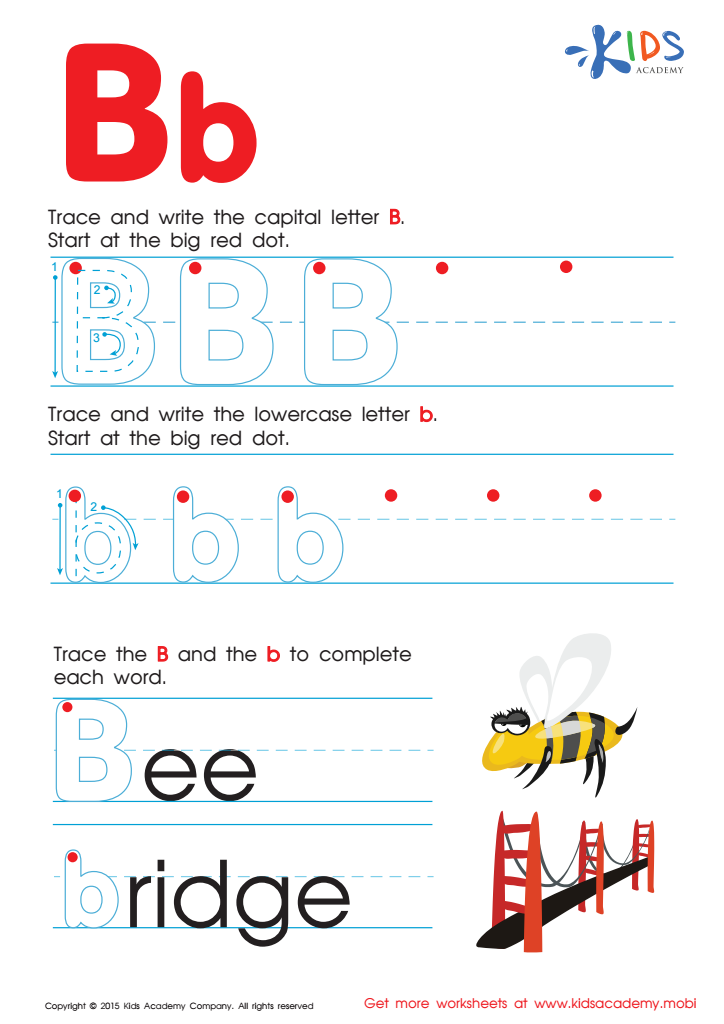

Letter B Tracing Page
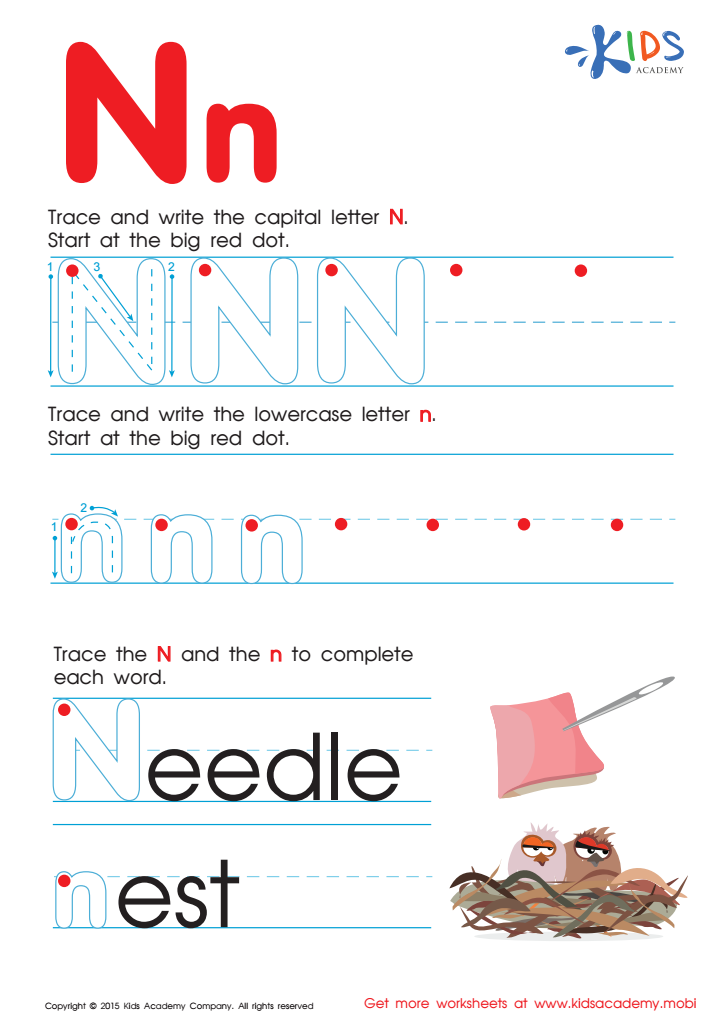

Letter N Tracing Page


Lowercase Letters d e f Worksheet


Uppercase Letters P, Q, and R Worksheet
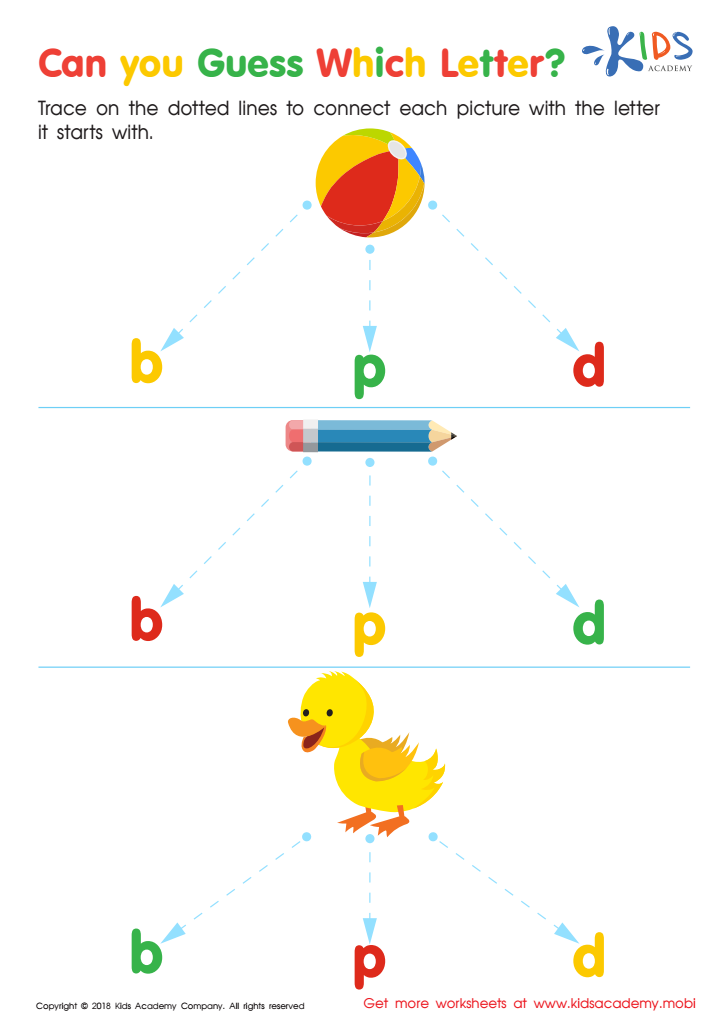

Can you Guess Which Letter? Worksheet
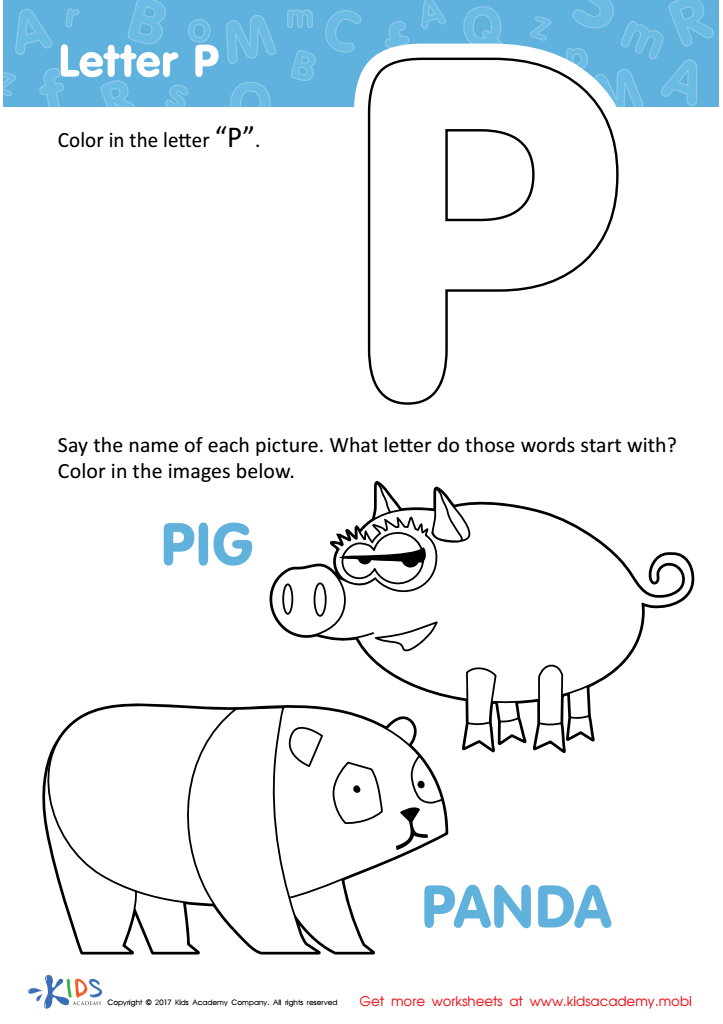

Letter P Coloring Sheet
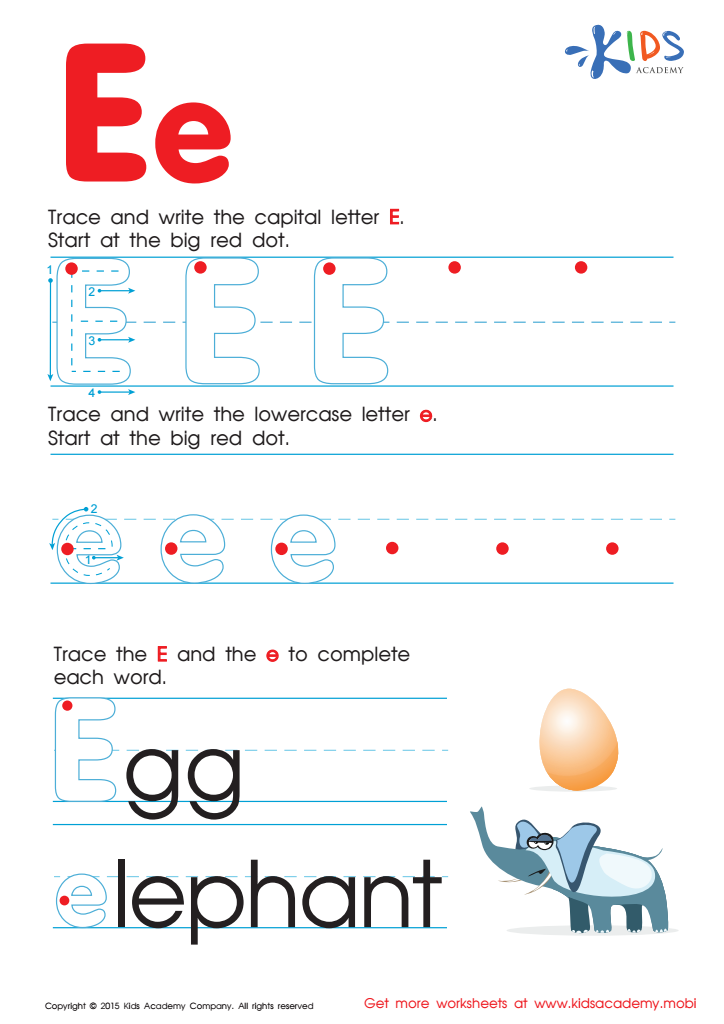

Letter E Tracing Page


Pick the Letter Worksheet


Identifying Uppercase Letters Worksheet


Letter H Coloring Sheet
Alphabet recognition in children aged 3-7 is vital as it forms the foundation of successful reading and writing skills. During these formative years, a child's brain is exceptionally receptive to learning basic literacy fundamentals. Recognizing the alphabet is the first step towards phonemic awareness, where children learn to connect specific sounds with individual letters and combinations. This knowledge aids in decoding words, an essential skill for effective reading.
When children are confident in recognizing the alphabet, they are more prepared to engage in more advanced literacy activities, such as sounding out words, spelling, and eventually comprehending text. Additionally, alphabet recognition enhances fine motor skills, as children learn to write letters and words. This foundational understanding of language systems promotes cognitive development, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities.
Moreover, proficiency in alphabet recognition contributes to social and emotional growth. As children master this skill, they experience a sense of achievement and build self-esteem. It enables smoother transitions into formal schooling environments, encouraging active participation and fostering a positive attitude toward learning. By prioritizing alphabet recognition, parents and teachers set the stage for a child's lifelong educational journey, ensuring they develop strong, robust literacy skills indispensable for all areas of learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students















