Fine Motor Skills Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 3
86 filtered results
-
From - To
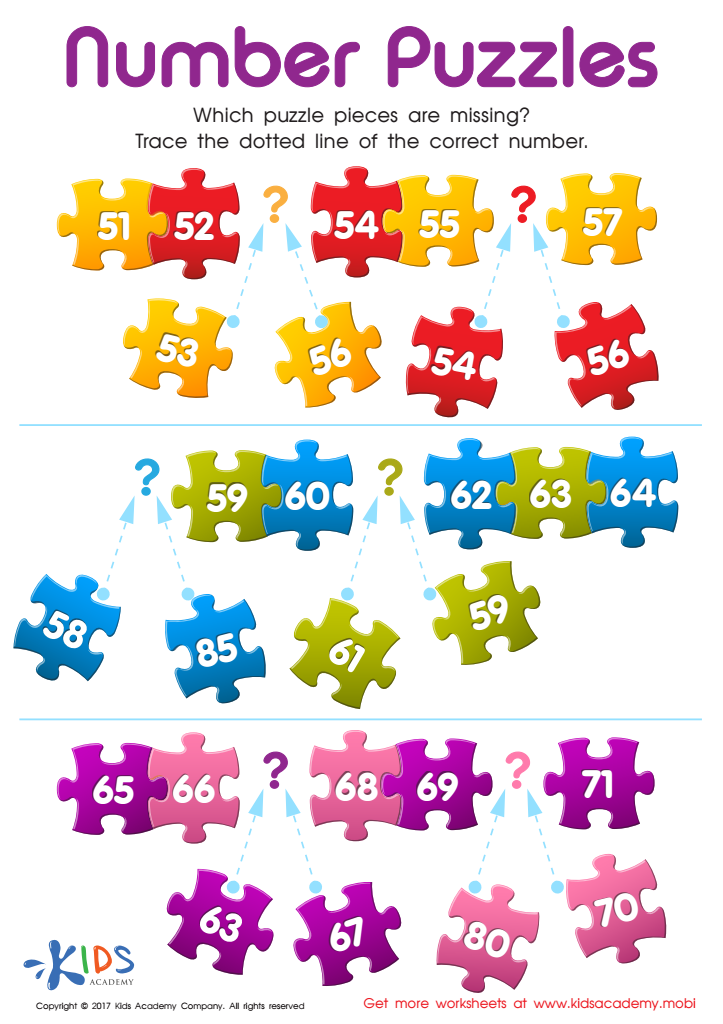

Number Puzzles Worksheet
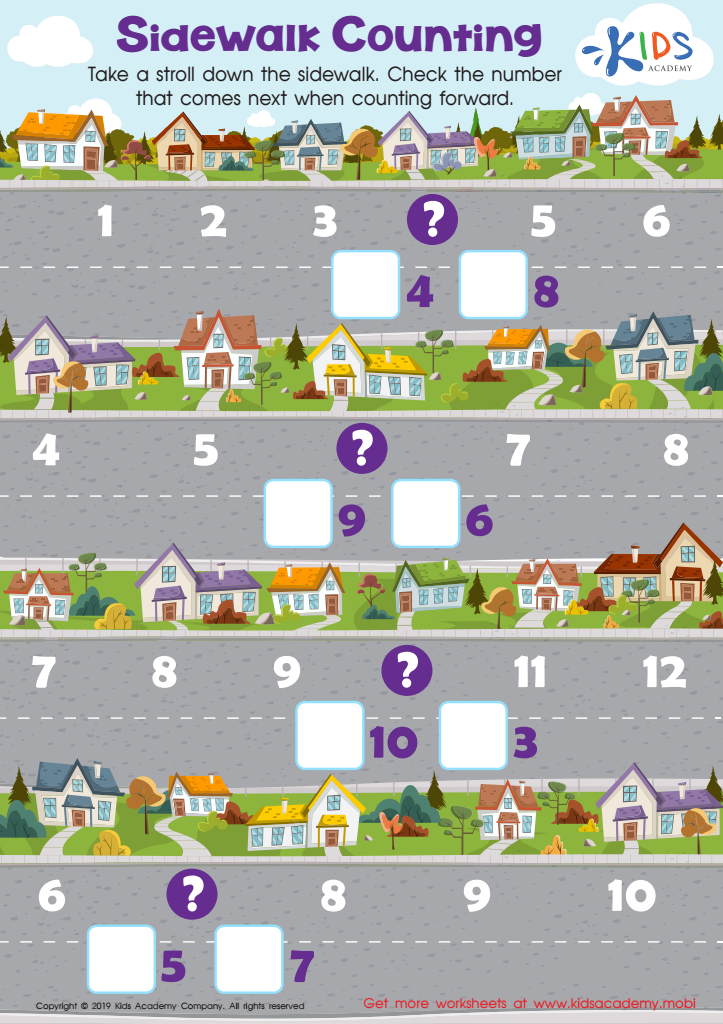

Sidewalk Counting Worksheet
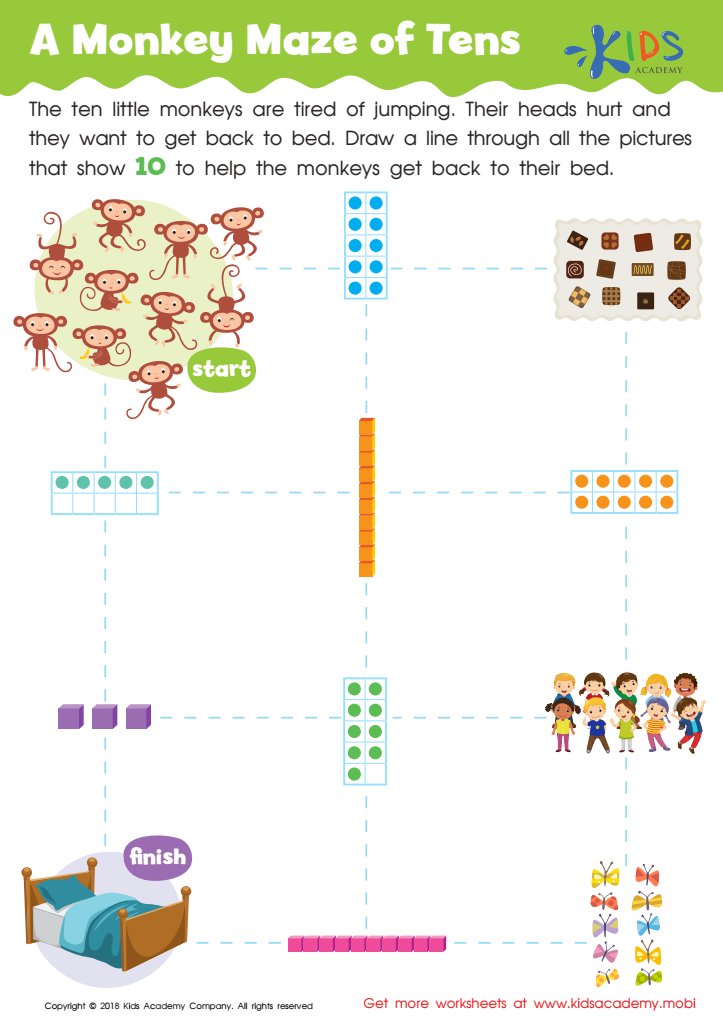

A Monkey Maze of Tens Worksheet
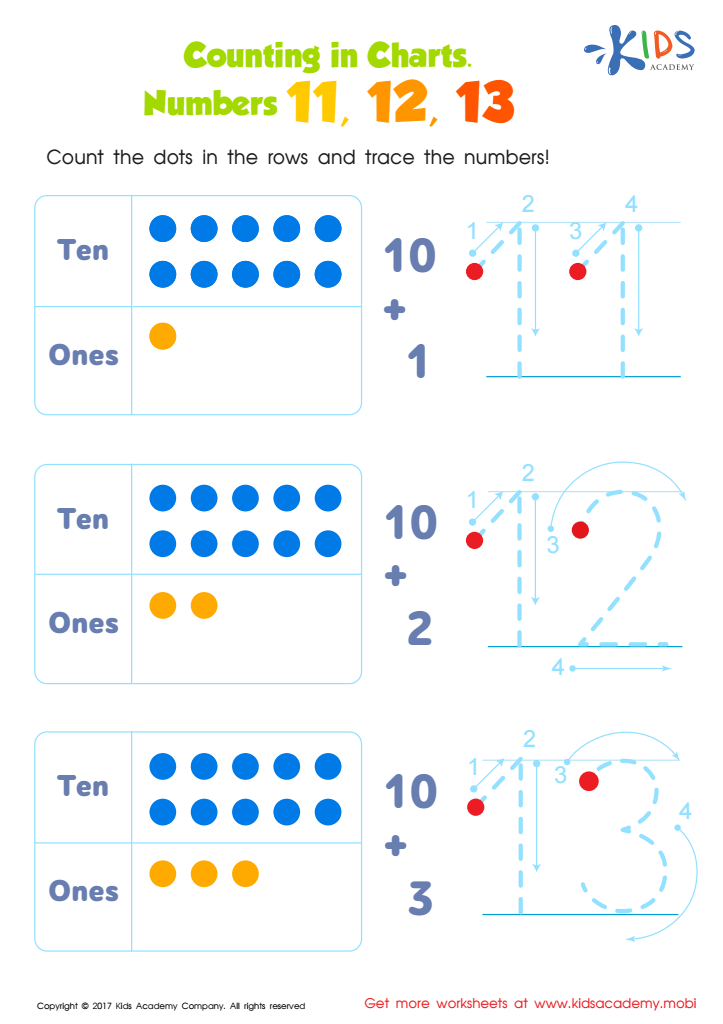

Number Tracing Worksheet For Kindergarten


Frog Countdown Worksheet
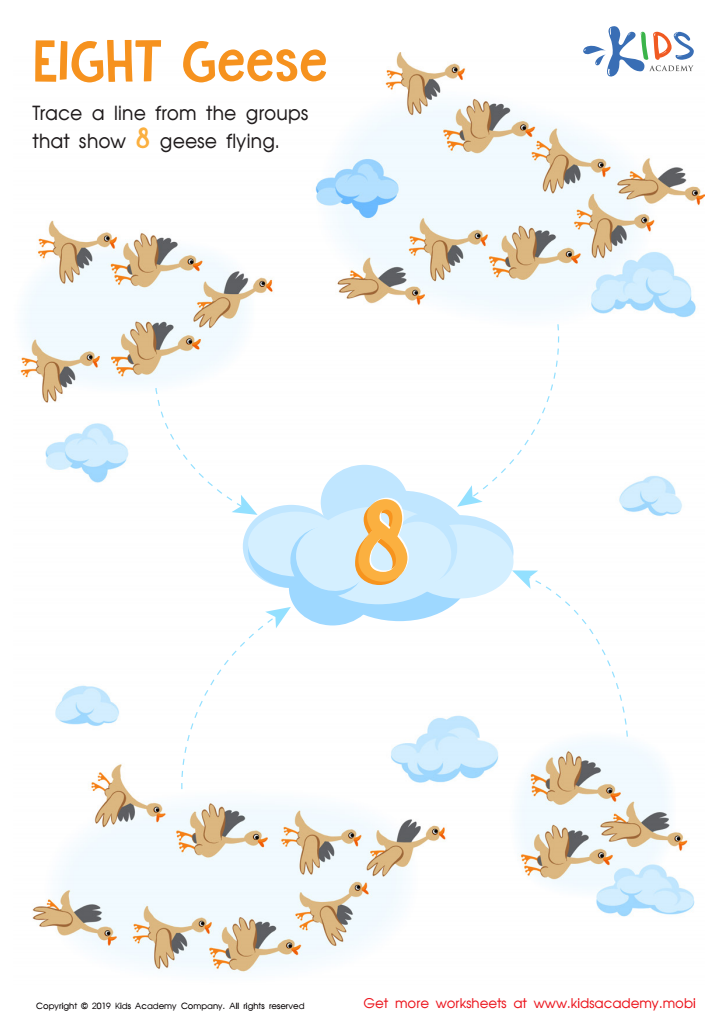

Eight Geese Worksheet


Pirate Ship Connect Dots Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet
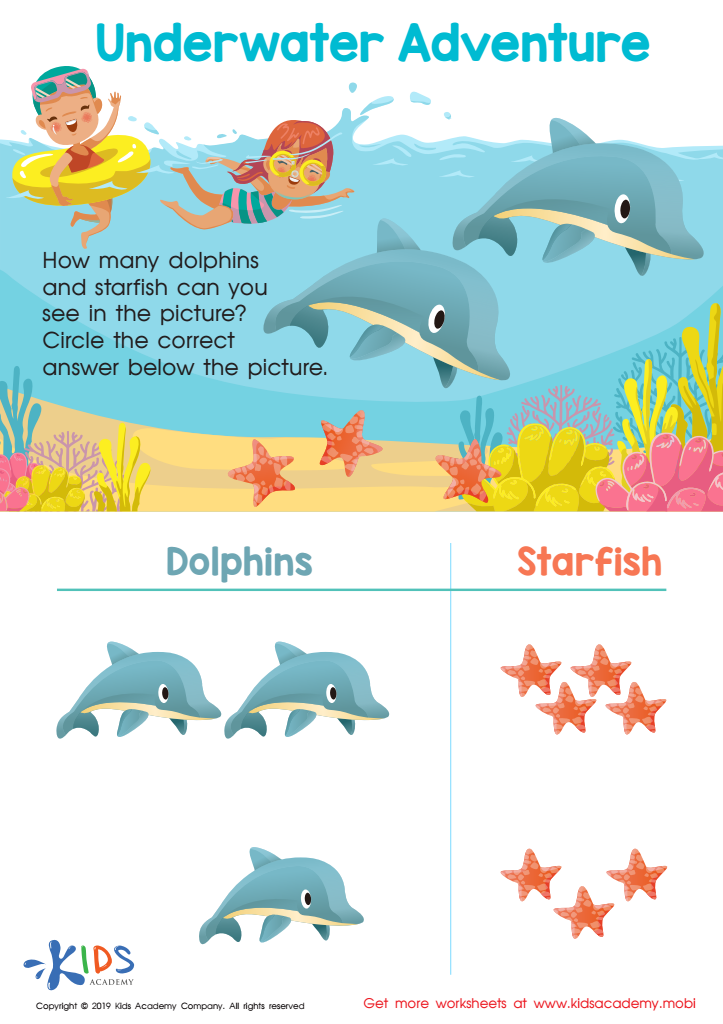

Underwater Adventure Worksheet

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet


Bubble Matching Fun Worksheet


Build with 9 Worksheet


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet

Scottish Sewing Part 2 Worksheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet


Sloth – Coloring by Numbers


Count the Cucumbers and Trace the Number 8 Printable


Cursive Numbers: 3 Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Dot–to–dot Seashell Printable


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Sea Adventure – Coloring by Numbers


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet
Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, like those in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for performing tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using scissors. For children aged 3-8, the development of these skills is fundamental as they enter and progress through their formative educational years.
Firstly, strong fine motor skills are directly linked to success in academic activities. Learning to write letters and numbers clearly relies on the ability to hold and control a pencil. This forms the basis for literacy and numeracy skills, setting the foundation for future academic achievement. Children with well-developed fine motor skills can more easily manage tasks like cutting with scissors or pasting objects, which are often part of creative and practical class exercises.
Secondly, these skills promote independence. Children gain confidence as they master buttoning shirts, tying shoelaces, and taking care of personal belongings. This sense of independence is significant for boosting self-esteem and overall emotional development.
Lastly, fine motor skills development encourages cognitive growth. Activities that hone these skills often require following sequences, solving spatial problems, and developing hand-eye coordination, all of which stimulate the brain. For parents and teachers, paying attention to these skills means supporting a child’s holistic growth, ensuring they have the foundational tools required for lifelong learning and independence.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students