Handwriting practice Alphabet Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
55 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet
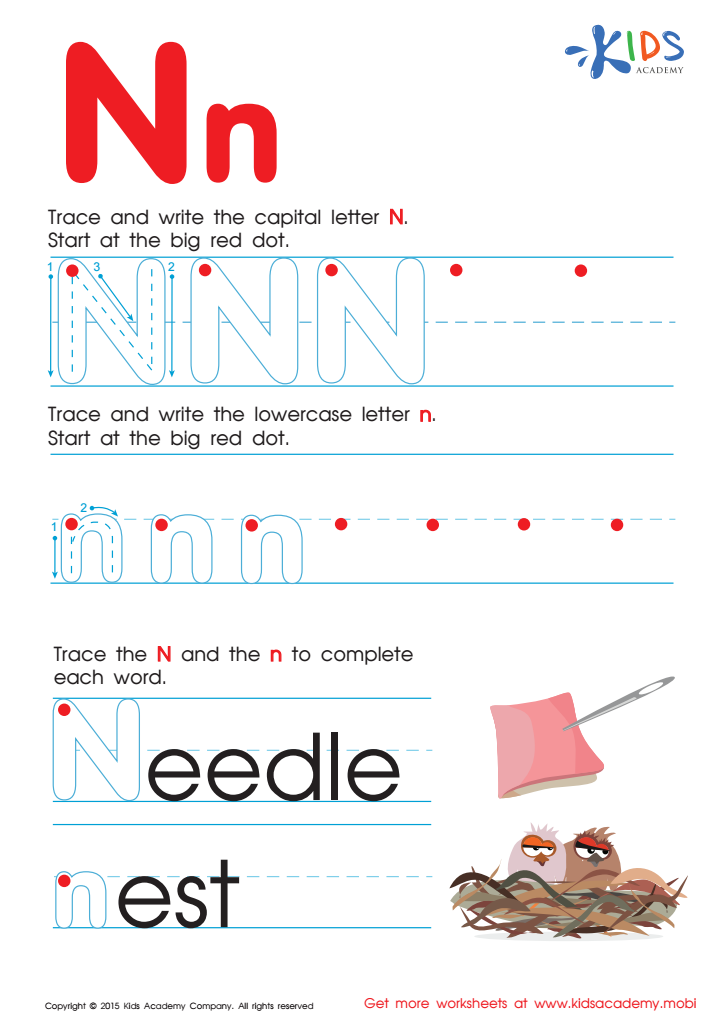

Letter N Tracing Page


Lowercase Letters d e f Worksheet


Letter V Tracing Page


Letters M and S Tracing Worksheet


Letter A Tracing Worksheet


Letter G Coloring Sheet


Letters H and V Tracing Worksheet


Letter Z Coloring Sheet


Letter J Coloring Sheet


Letter H Coloring Sheet
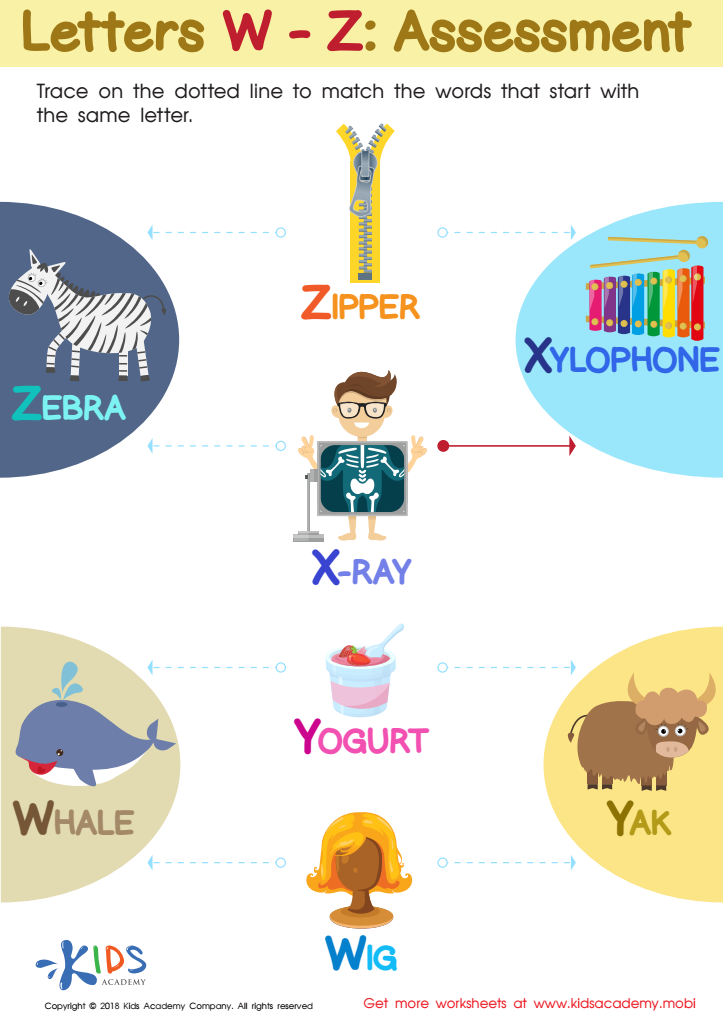

Letters W–Z Tracing Worksheet


Letter Y Tracing Worksheet


Lowercase Letters s t u Worksheet


Uppercase Letters D, E, and F Worksheet
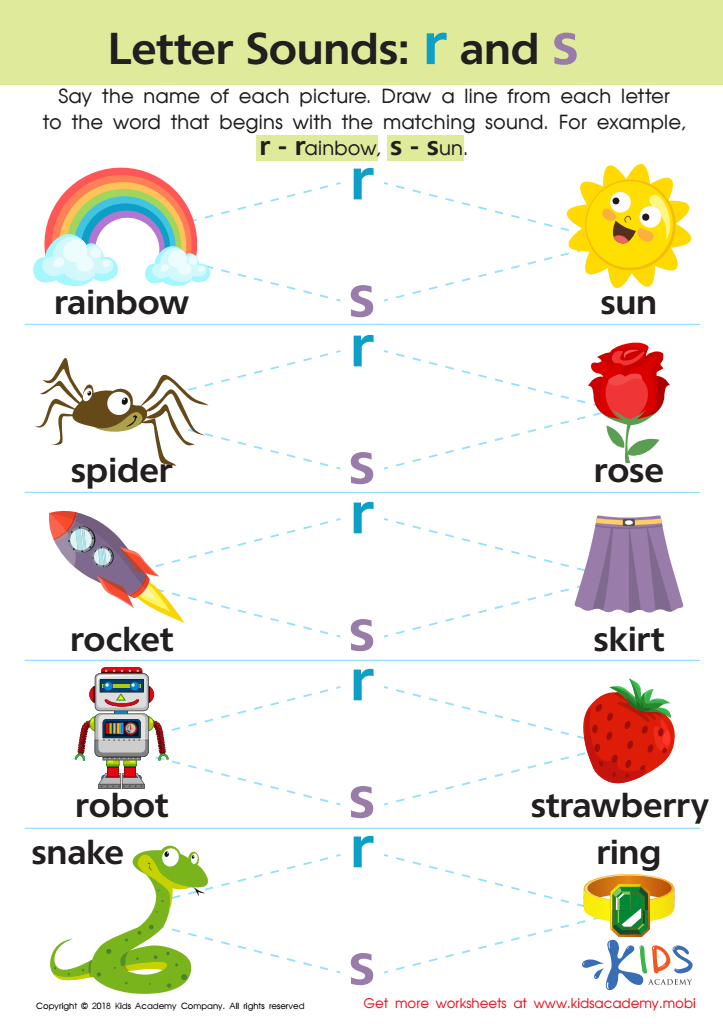

Letter R and S Sounds Worksheet


Letter K Coloring Sheet


Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet
Handwriting practice for children ages 4-5 is vital for several reasons. First, it plays a fundamental role in developing fine motor skills, which are crucial for overall dexterity. As children manipulate writing tools, they build the hand-eye coordination necessary for various tasks throughout life, such as typing or using scissors.
Moreover, early handwriting practice promotes cognitive development. Learning to form letters helps children associate sounds with symbols, laying the groundwork for reading and literacy. Mastering the alphabet not only enriches their vocabulary but also enhances their ability to communicate effectively.
Additionally, handwriting fosters a sense of accomplishment and boosts self-esteem. When young learners see their progress in letters and words, they gain confidence in their abilities, which is essential during this formative stage.
Socially, handwriting encourages collaborative learning opportunities. Children often engage with peers or adults for guidance and feedback, enhancing their communication skills and fostering relationships.
Finally, investing time in handwriting practice nurtures creativity and self-expression. It allows young learners to share their thoughts, stories, and ideas through written words. Thus, parents and teachers should prioritize handwriting practice to lay a strong foundation for future educational success and personal development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students















