Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 3
137 filtered results
-
From - To
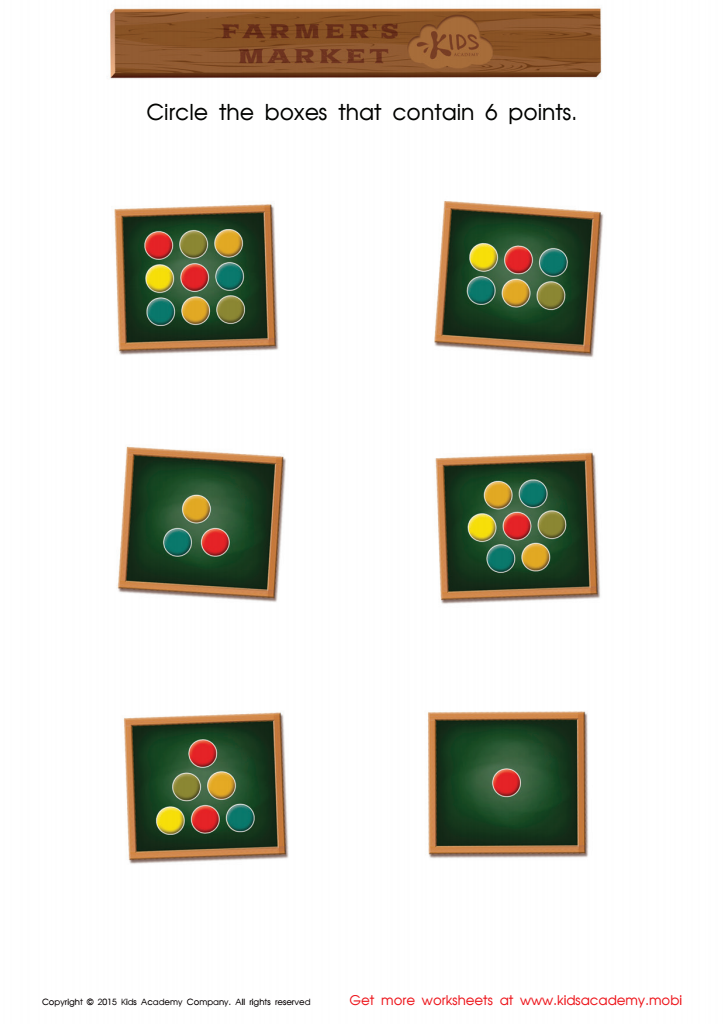

Count and Match Points 6 Math Worksheet
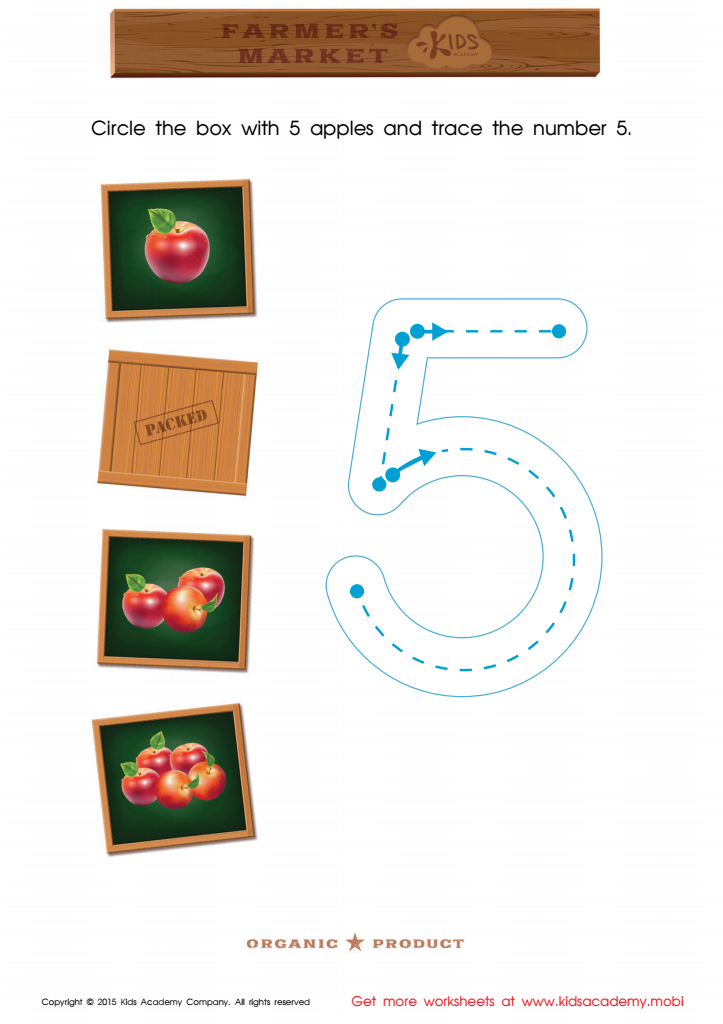

Count the Apples and Trace the Number 5 Printable
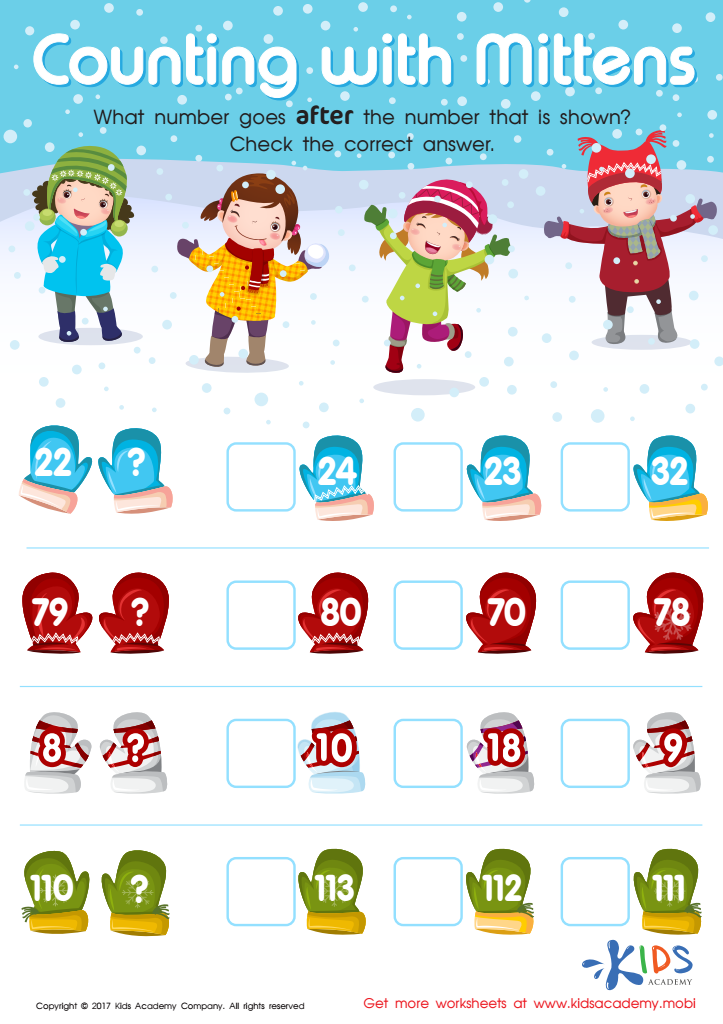

Counting with Mittens Worksheet
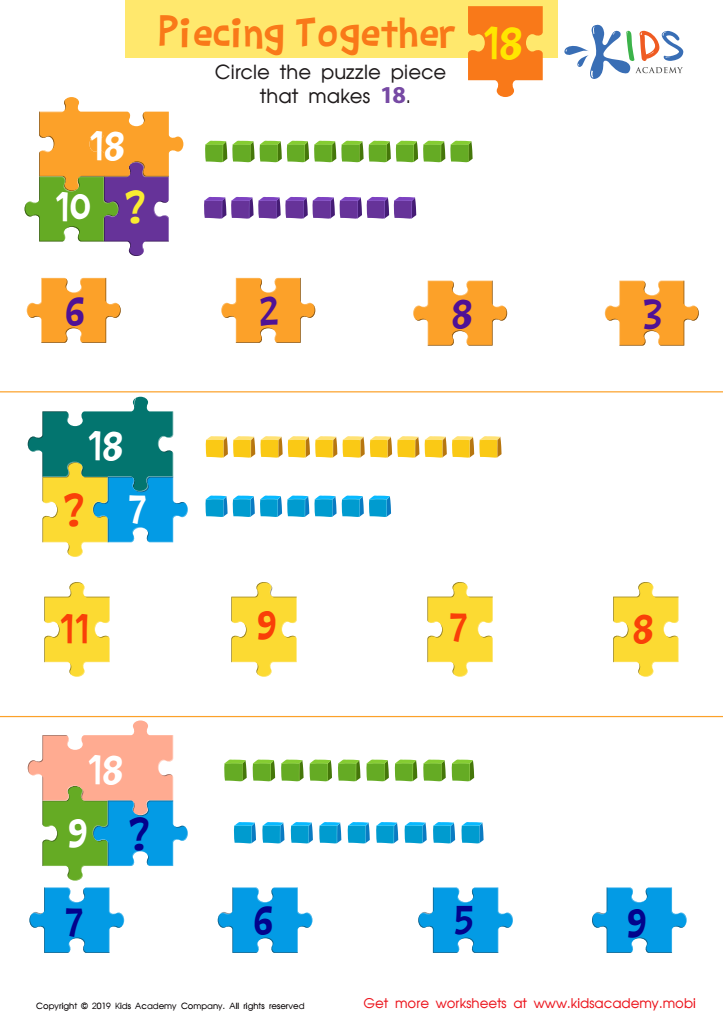

Piecing Together 18 Worksheet

Ordering 11–20: Halloween Counting Worksheet

Counting Eggs Worksheet
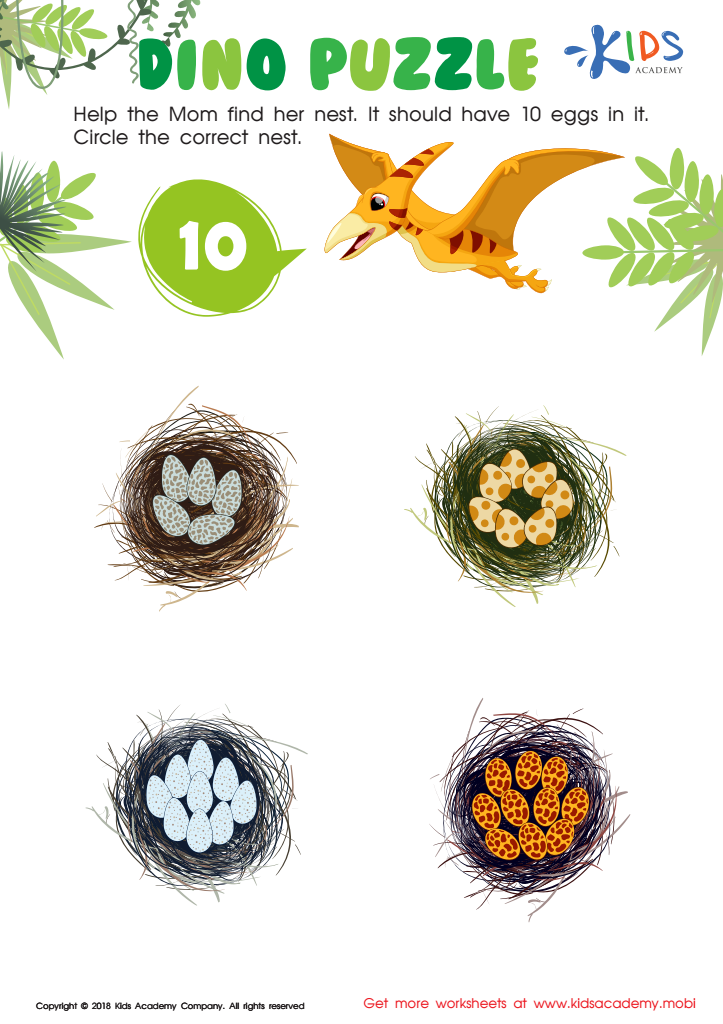


Learn Number For Kindergarten Worksheet

Count and Match Points 9 Math Worksheet

6 Parrots Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet
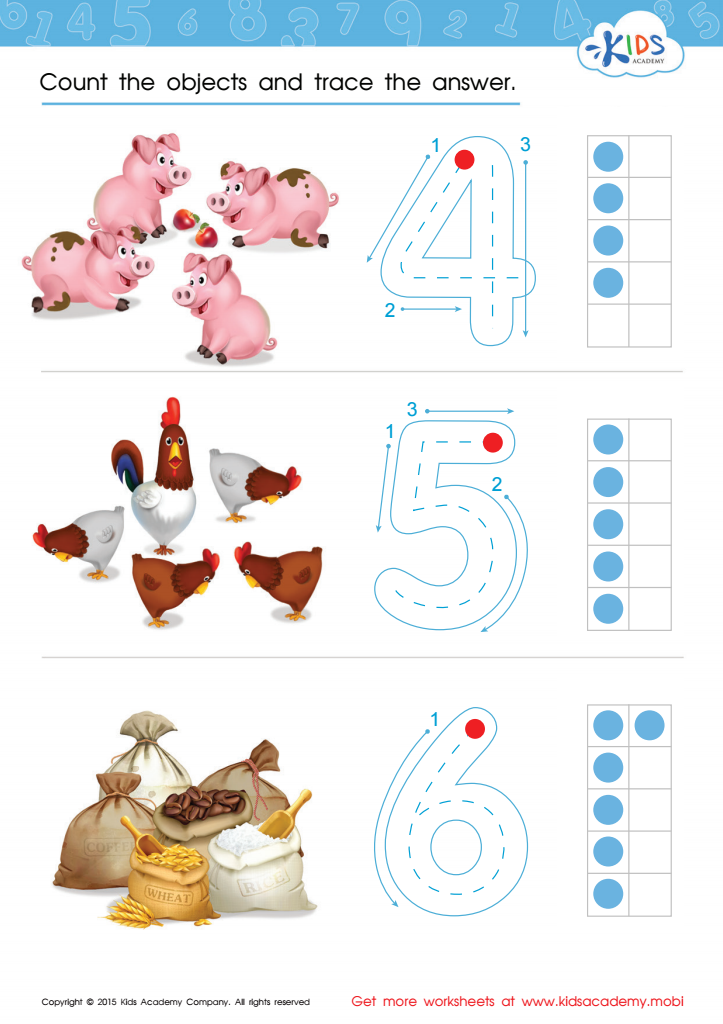

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet


Count the Stegosaurus's Spikes Worksheet
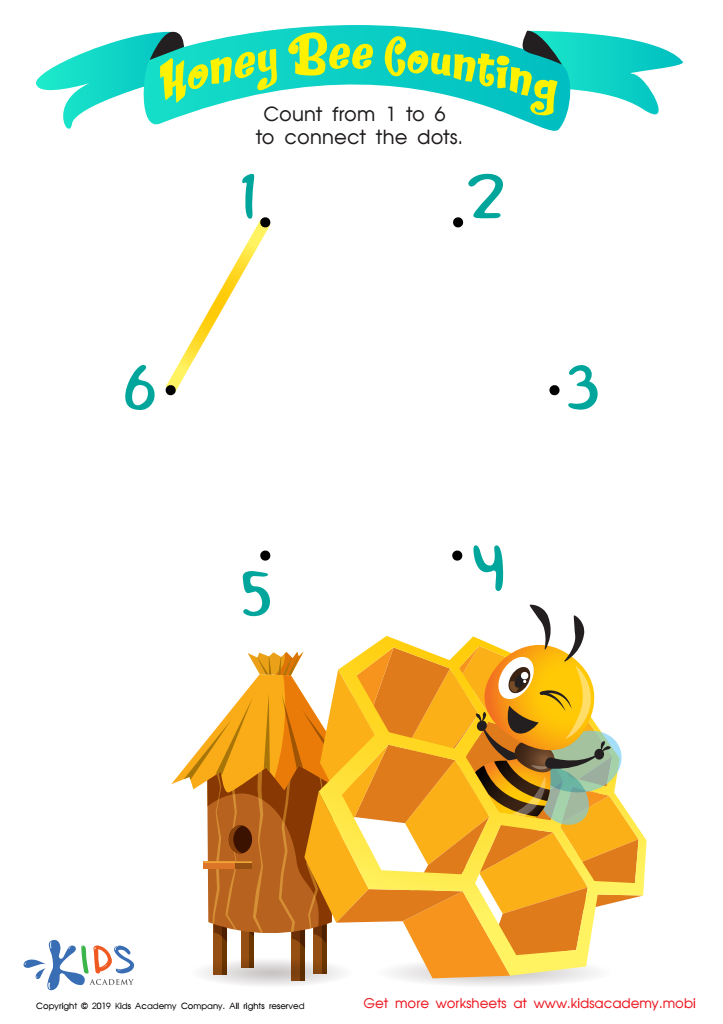


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet
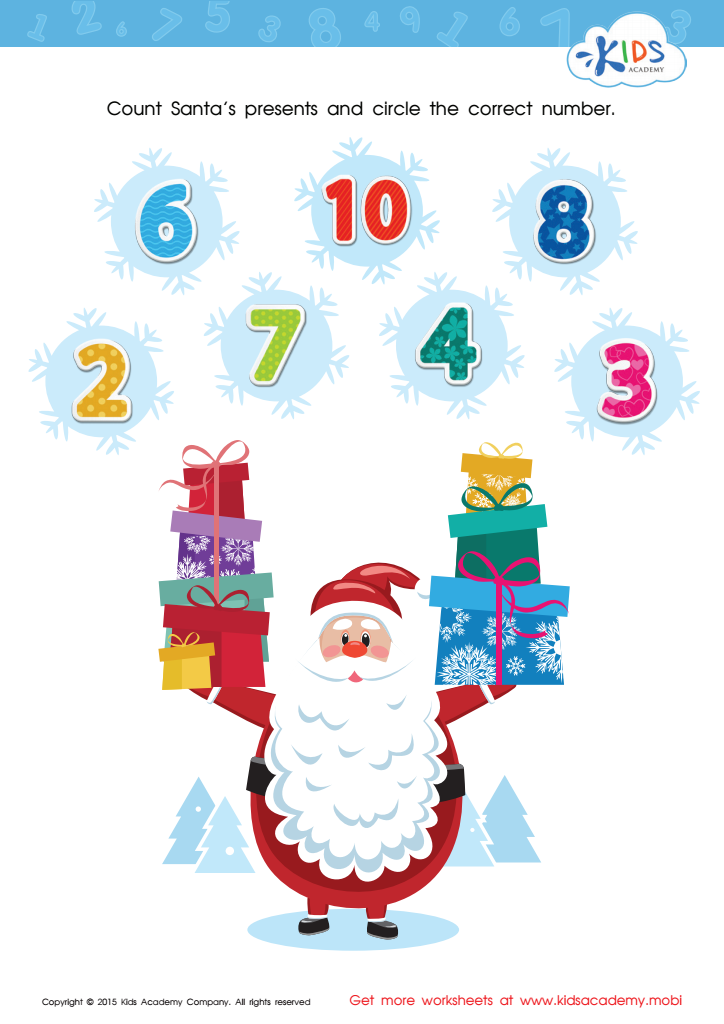


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet
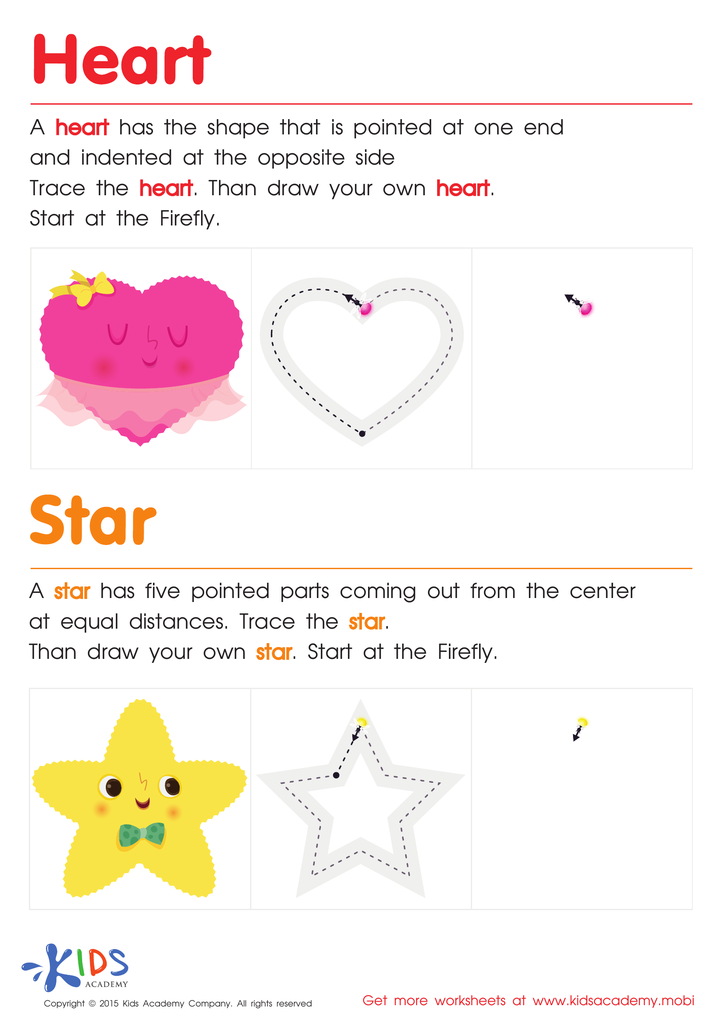

Let's Learn to Draw Hearts And Stars Printable
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children's development, particularly in the context of math for ages 4-5. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which play a significant role in a child’s ability to perform everyday tasks. For young learners, fine motor skills lay the foundation for math concepts by enabling them to manipulate tools and materials effectively.
Engaging in activities that strengthen fine motor skills, such as cutting paper, threading beads, or using counters, directly supports mathematical understanding. For instance, when children grasp and move objects, they work on essential pre-math skills such as counting and sorting. This tactile manipulation aids in the conceptualization of numbers and quantities while enhancing hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
Moreover, encouraging proficiency in fine motor skills helps boost children’s confidence and independence, making them more willing to engage in math-related activities. As students of this age begin their educational journey, investing in these skills will pay dividends not just in math but across a range of subjects. Therefore, parents and teachers must prioritize activities that promote fine motor skills, ensuring a strong foundation for future learning and success in school.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students























