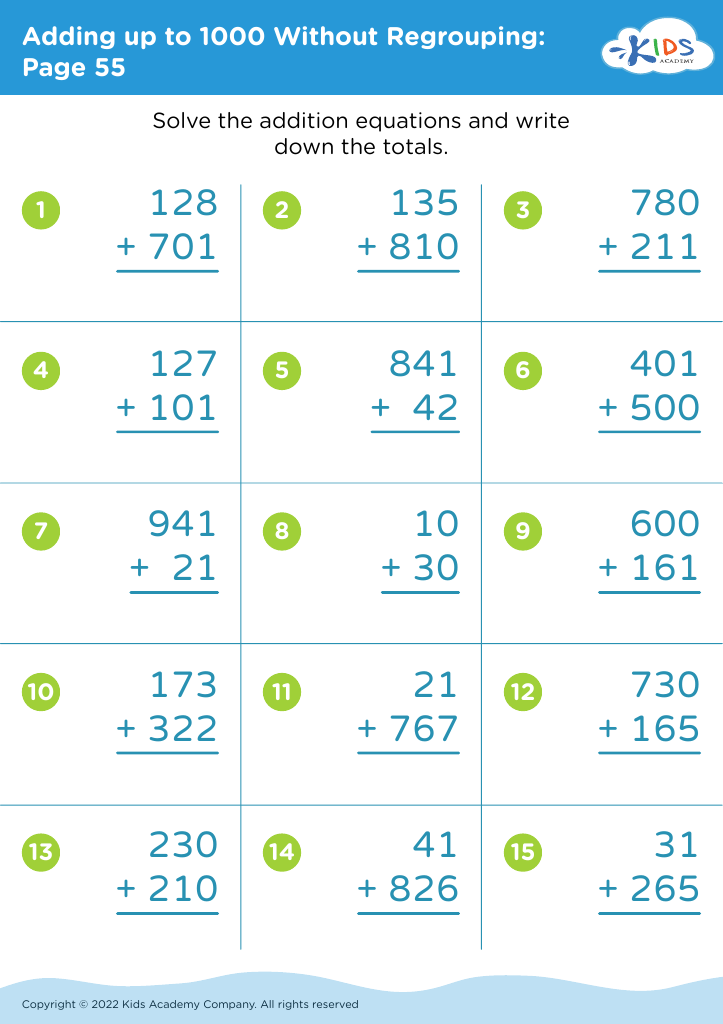
Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 4-7 - Page 2
96 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter U Coloring Sheet


Italian Word Tracing: Ciao Worksheet


Yellow Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet

Letter C Tracing Page

Letter S Coloring Sheet


English Word Tracing: Hello Worksheet


Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


Letter G Tracing Page


The Presidential Symbol Worksheet


Pink Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Teachers Community Helpers Worksheet

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable

Letter D Coloring Sheet


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet


Bat Rhyming Words Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Spanish Word Tracing: Hola Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet
Handwriting practice is critically important for children aged 4-7, and both parents and teachers should prioritize it for several reasons. Firstly, handwriting is foundational to effective written communication. As children learn to form letters and words legibly, they gain an essential skill for academic success and everyday life.
Secondly, handwriting practice promotes fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination. When young children engage in writing activities, they develop the small muscle movements necessary for tasks such as tying shoes, buttoning shirts, and using utensils.
Additionally, handwriting has been linked to cognitive development. Learning to write involves memorizing shapes, practicing sequences, and understanding spatial organization, which stimulates brain activity and enhances memory retention.
Socially and emotionally, mastering handwriting can boost a child's confidence and self-esteem. Being able to write letters and numbers competently allows children to participate fully in class activities and express themselves independently.
Finally, research shows that handwriting practice can improve reading and spelling skills. The motor activity of writing letters helps to solidify the understanding of phonics, letter recognition, and word formation, which are crucial components of early literacy.
Considering the wide-ranging benefits, investing time in handwriting practice for children aged 4-7 sets the stage for broad developmental gains and academic achievement.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students