Problem-Solving Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 7-9 - Page 5
102 filtered results
-
From - To
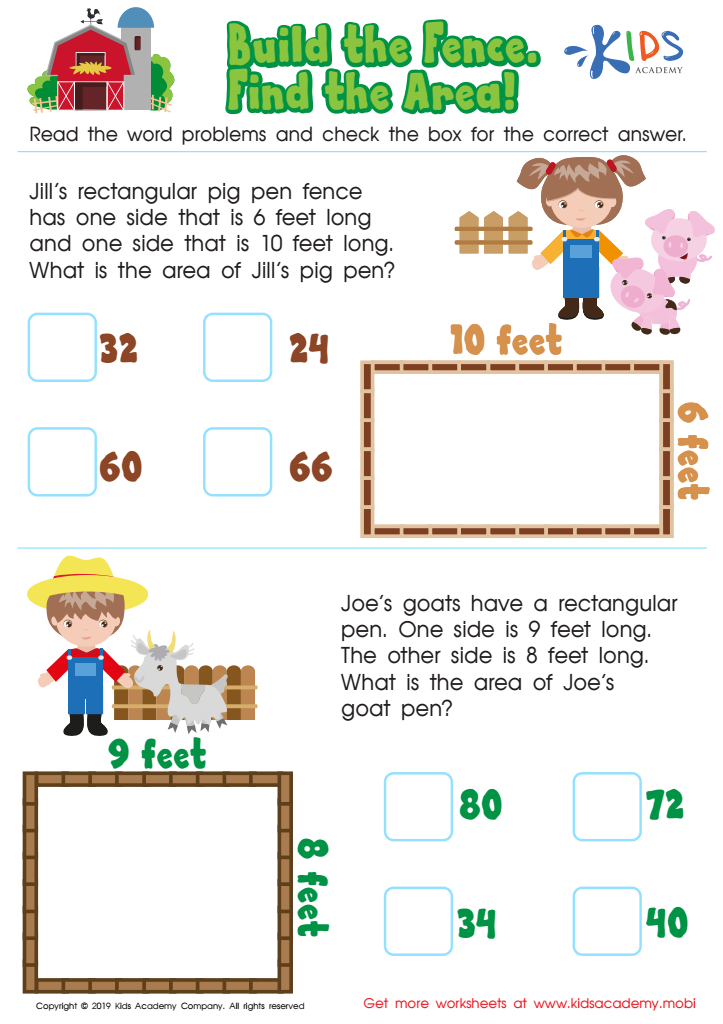

Build the Fence, Find the Area Worksheet
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of problem-solving skills in children aged 7-9, particularly in the context of addition, because these skills lay the foundation for critical thinking and mathematics proficiency. At this age, children are transitioning from concrete understanding of numbers to more abstract reasoning. Cultivating problem-solving skills helps them recognize patterns, make connections between concepts, and approach challenges with confidence.
Furthermore, strong problem-solving abilities are essential for academic success across various subjects, as they foster analytical thinking, creativity, and perseverance. When children learn to approach addition problems using different strategies—such as visualization, breaking down numbers, and estimation—they not only improve their calculation skills, but also enhance their overall cognitive flexibility.
Encouraging children to engage with addition problems collaboratively allows them to communicate their thought processes, learn from peers, and develop interpersonal skills. This hands-on approach makes math more accessible and enjoyable while reducing anxiety around numeracy.
Ultimately, equipping young learners with effective problem-solving skills in addition empowers them to face not just math challenges, but any problems they encounter in their academic journey and daily life, fostering a love for learning and a growth mindset as they mature.
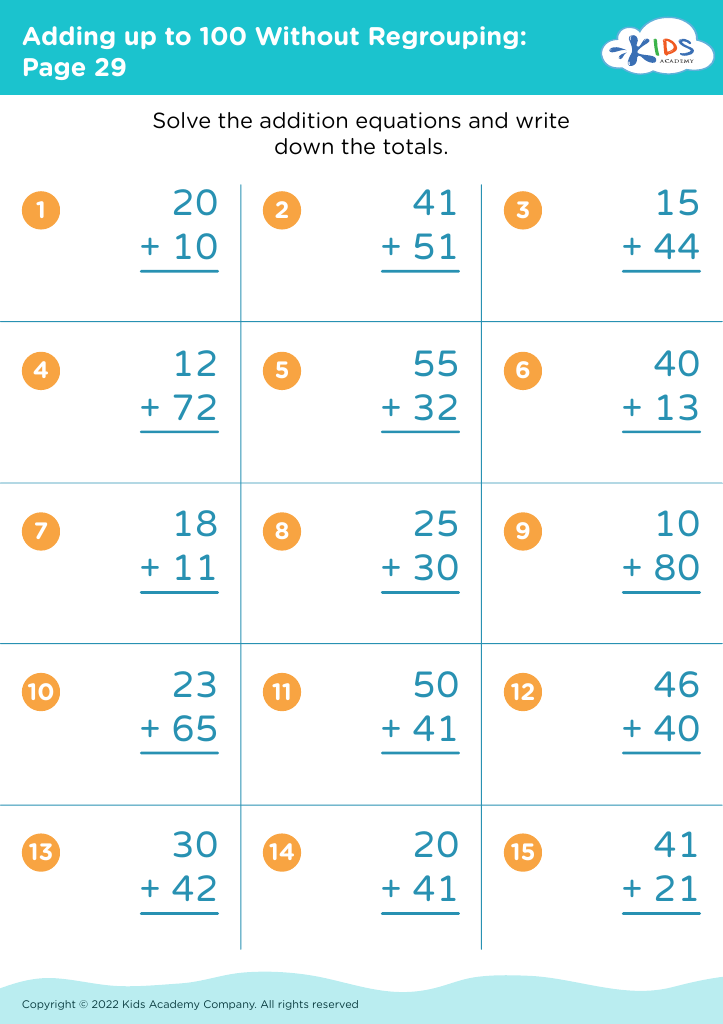
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
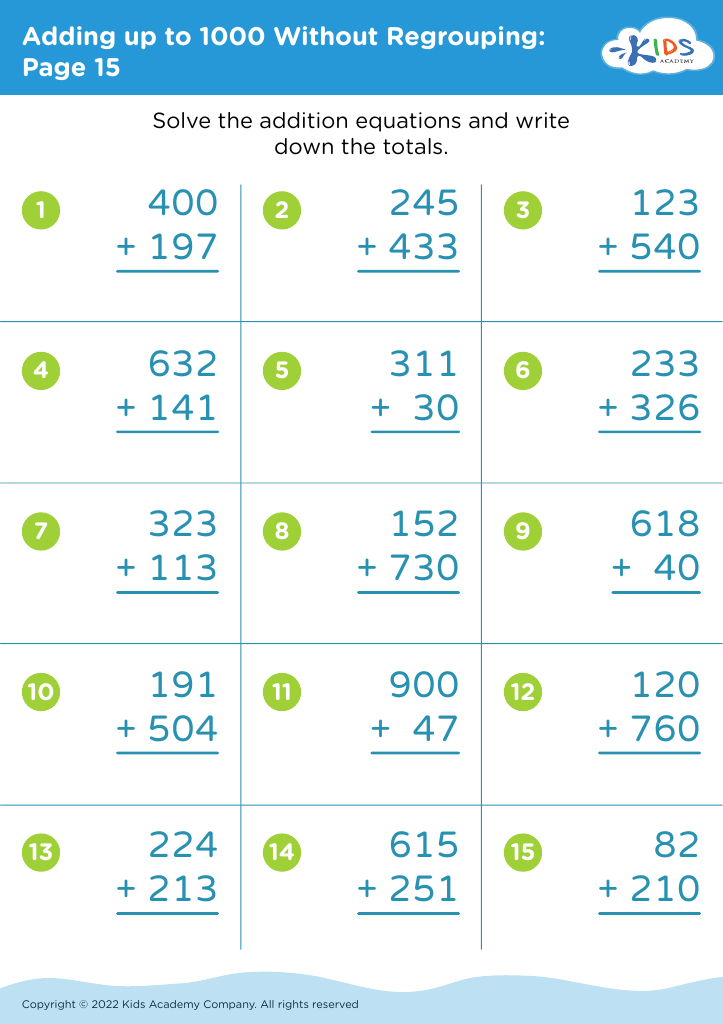




.jpg)
.jpg)










