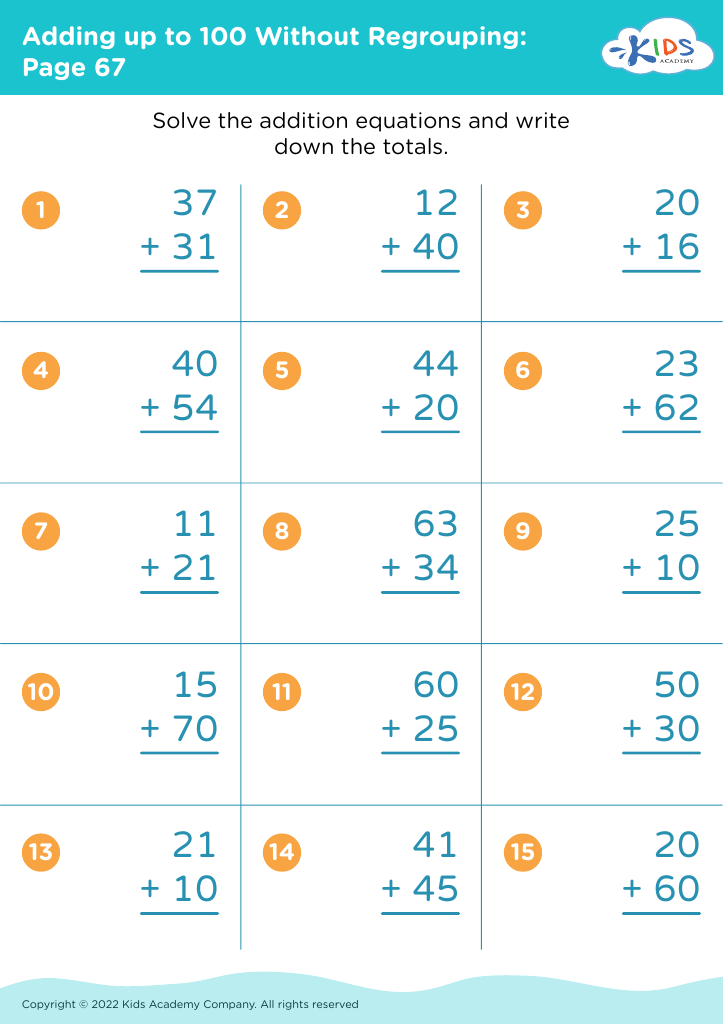
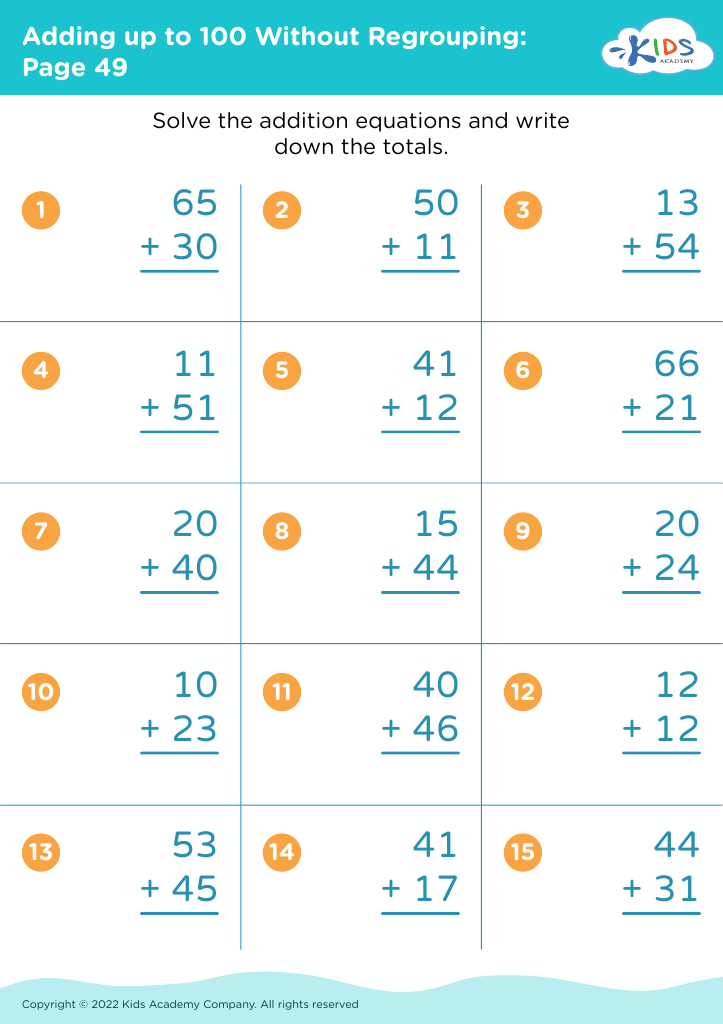
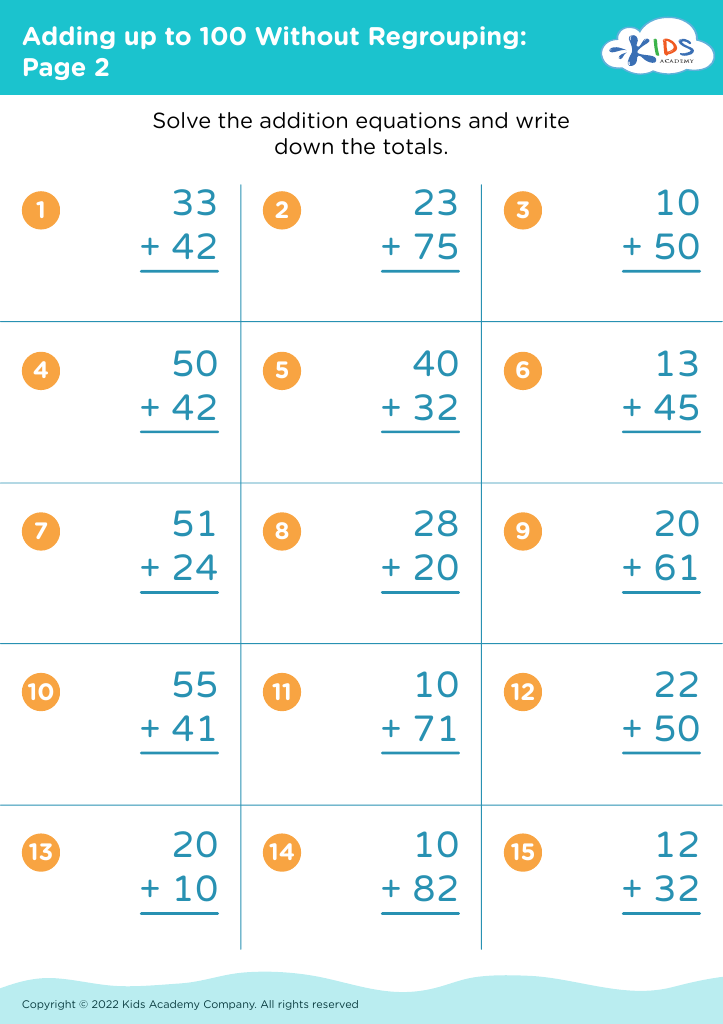
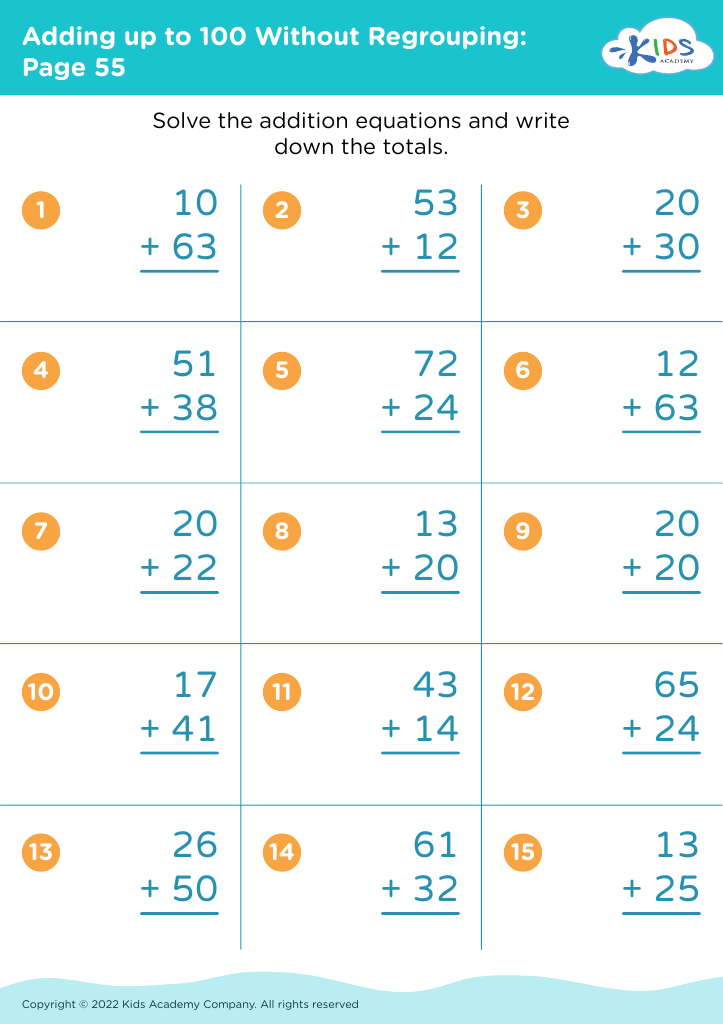
Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Fine Motor Skills Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds" are designed to strengthen your child’s addition and fine motor skills simultaneously. Each engaging worksheet features a variety of addition problems crafted to help children practice summing numbers up to 100 without regrouping. As kids write out answers, they refine their hand-eye coordination, pencil control, and fine motor skills essential for writing. These worksheets not only enhance mathematical understanding but also support overall developmental skills needed for classroom success. Ideal for both classroom and at-home practice, they make learning math enjoyable and productive. Suitable for ages 8 and up!
Fine motor skills and the ability to add up to 100 without regrouping are critical benchmarks for 8-year-olds and warrant considerable attention from both parents and teachers. Fine motor skills involve the use of small muscles in the hands and fingers, integral for activities such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using scissors; these skills are foundational for academic tasks and everyday functions. Development in this area promotes hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and precision, essential for activities like playing musical instruments and manipulating objects in science experiments.
When it comes to mathematics, specifically adding up to 100 without regrouping, this skill forms a cornerstone for higher-level math concepts, supporting numerical fluency and mental math agility. Mastering this capability illustrates a child's understanding of number sense, sequencing, and the base-ten system, all crucial for arithmetic and problem-solving processes encountered in later grades.
Fostering these competencies controls a more holistic developmental path, building confidence and self-esteem in learners. Teachers and parents who prioritize these areas not only bolster academic skills but also prepare children for a smoother transition to more complex tasks and concepts. Overall, placing emphasis on fine motor development and foundational math skills encourages a balanced growth that underpins future learning success.