Vowel Diphthongs Worksheets for Ages 4-6
6 filtered results
Difficulty Level
Grade
Age
-
From - To
Subject
Activity
Standards
Favorites
With answer key
Interactive


The AI Vowel Pair Worksheet
Vowel pairs make different sounds than individual letters. The 'ai' combination often forms the long /a/ sound, like in 'brain' and 'strain'. Get your kids to look at the pictures in the worksheet, identify each and say the name aloud. Help them circle the words with the long /a/ sound.
The AI Vowel Pair Worksheet
Worksheet


Which's the OA Word? Worksheet
Encourage your kids to complete this fun worksheet. Ask them to identify the animals and objects in the pictures. Read the incomplete sentences aloud, and then find the correct word to finish the sentence. Check their work.
Which's the OA Word? Worksheet
Worksheet


Is It EE, EA, or AY? Worksheet
When 'ee', 'ea' and 'ay' are in words, they usually make the long /e/ and /a/ sounds. Examples of words with 'ee' are "sheep", 'beach' and 'seat' with 'ea', and 'clay' and 'play' with 'ay'. Check this colourful worksheet with your kids; help them find the words that make the long /e/ sound like 'sheep'.
Is It EE, EA, or AY? Worksheet
Worksheet


What Sounds Like Float? Worksheet
Help your kids practice the long /o/ sound with words such as 'boat', 'goat' and 'float'. Ask them to identify and circle the images in the worksheet that have the same sound. Award bonus points if they come up with more words with 'oa' spelling!
What Sounds Like Float? Worksheet
Worksheet
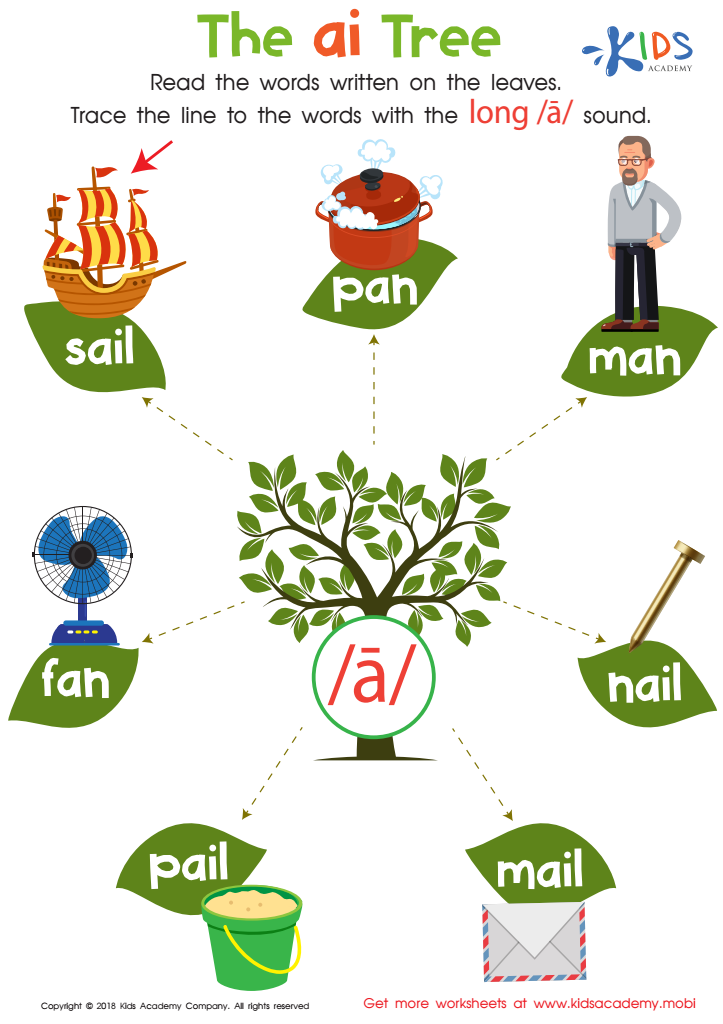

The AI Tree Worksheet
Help your kids learn to read better with this worksheet! Introduce the vowel pair 'ai' and give them familiar examples. Ask them to give you some in return. Then, have them read the words on the leaves and help them trace the ones with the long /a/ sound.
The AI Tree Worksheet
Worksheet


Hungry Caterpillar Maze Worksheet
Remind the kids that caterpillars turn into butterflies! This worksheet helps them practice their vowel sounds. They must trace the path of words that sound like ‘lie’ to help the caterpillar reach the finish line. It's a fun way to learn and explore!
Hungry Caterpillar Maze Worksheet
Worksheet

 Assign to the classroom
Assign to the classroom