Fine Motor Skills Extra Challenge Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 2
46 filtered results
-
From - To
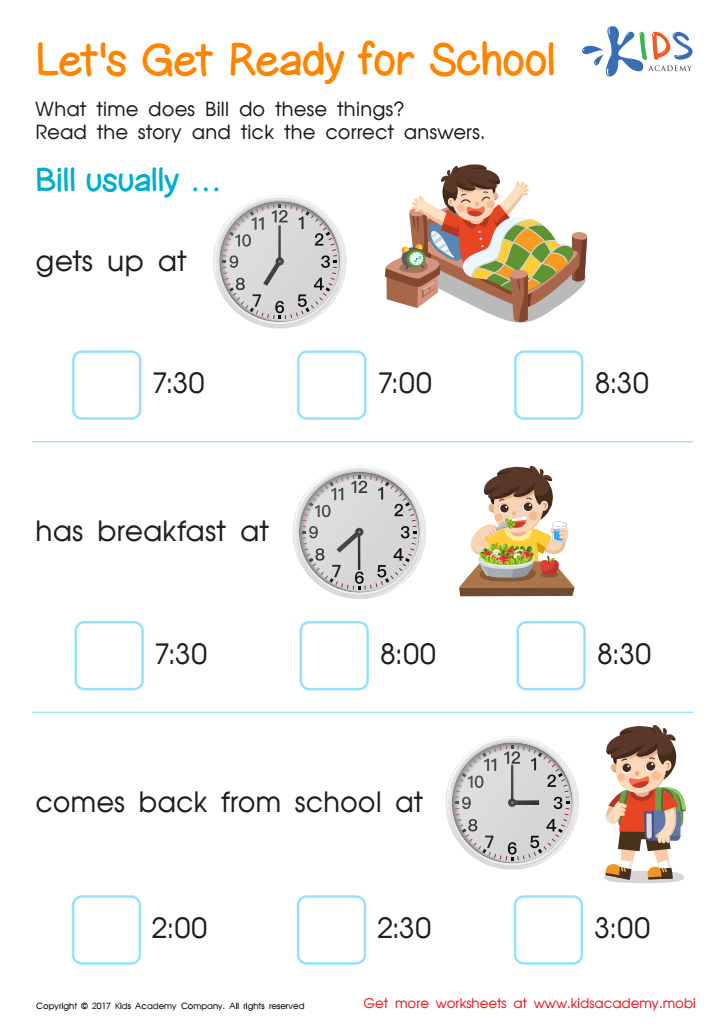

Lets Get Ready For School Time Printable


Woodpecker and Triangles Worksheet
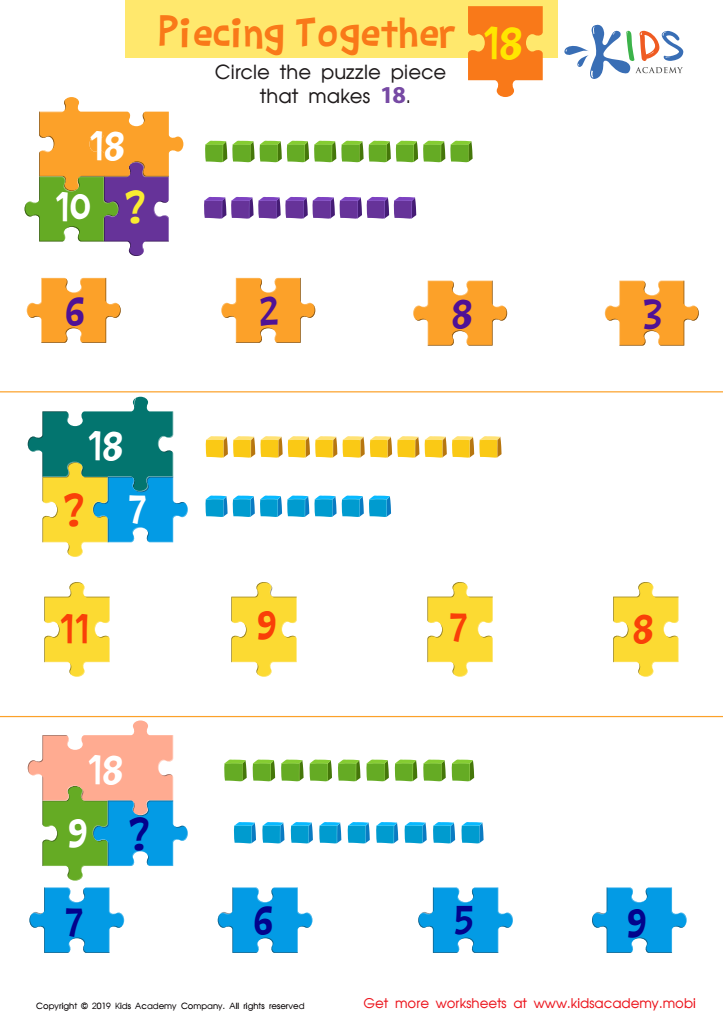

Piecing Together 18 Worksheet
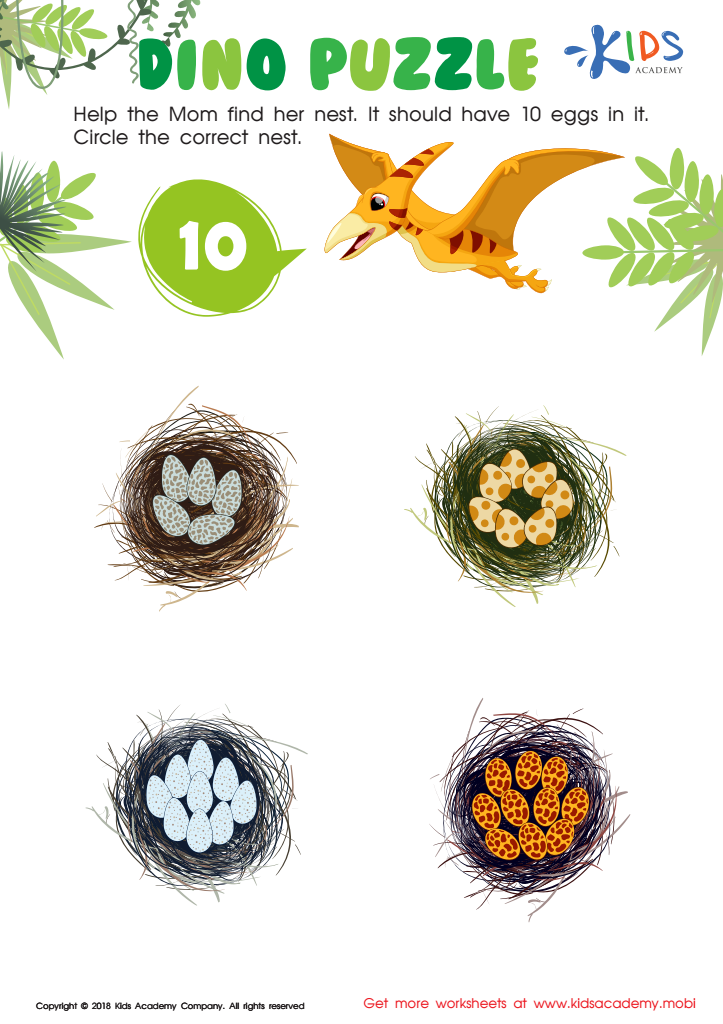


Learn Number For Kindergarten Worksheet
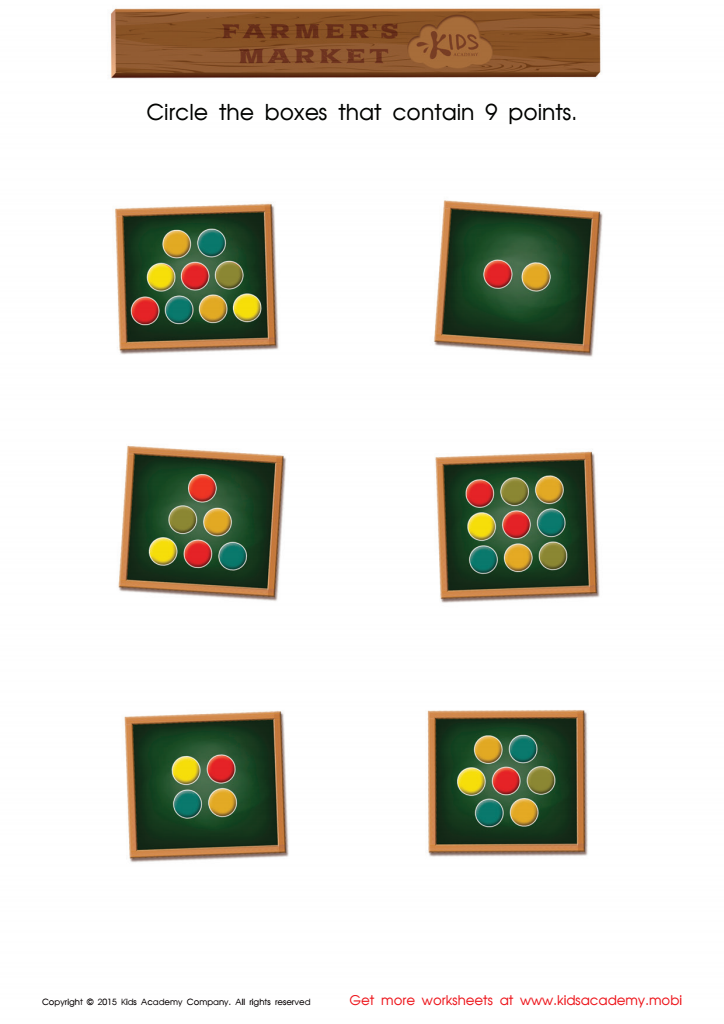

Count and Match Points 9 Math Worksheet
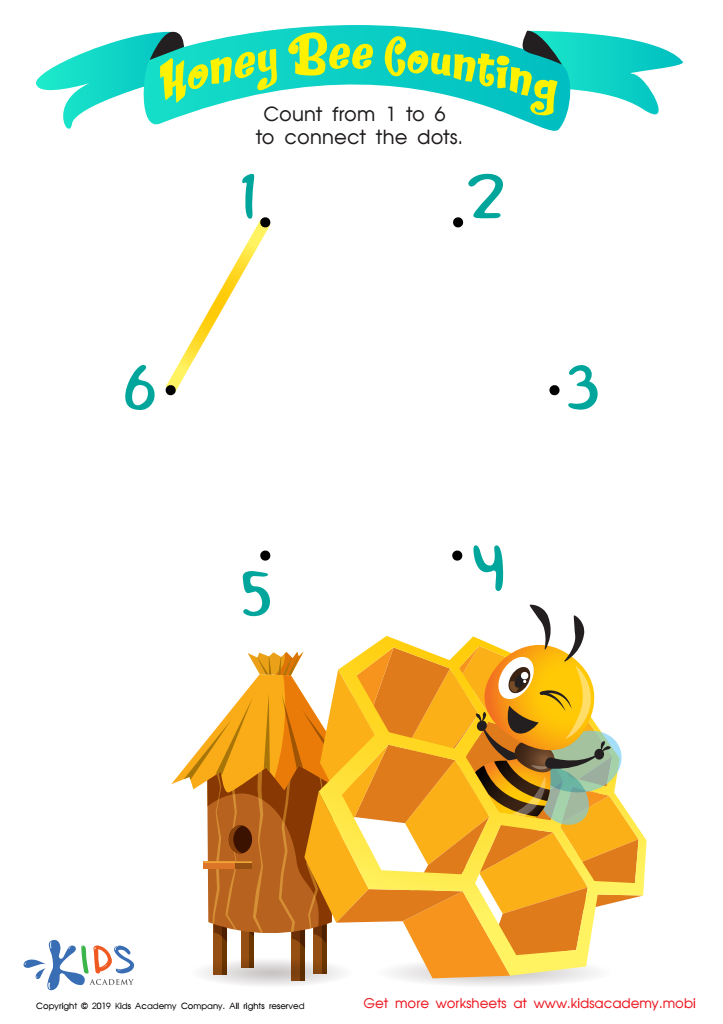


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet

Trace and Draw More Shapes Worksheet


Letter V Tracing Page


Counting Butterflies Worksheet


The Circle Maze Worksheet


Santa Claus Tracing Winter Words Worksheet


Pirate Ship Connect Dots Worksheet


Pilgrim Maze Worksheet


Find Words Mouse Maze Worksheet


Three Little Piggies Printable Coloring Page


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet

Letter T Tracing Page

Big Bad Wolf Printable Coloring Page




Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet
Parents and teachers should pay close attention to fine motor skills development in children ages 3-7, because these skills are foundational for many important aspects of daily life and academic success. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, with the eyes, enabling children to perform tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. These activities enhance cognitive development, hand-eye coordination, and overall dexterity.
In the early years, children are at a critical stage of developing their fine motor skills. Without proper development, a child might struggle with basic tasks, potentially leading to frustration and a lack of confidence. For example, delayed fine motor skills can slow down a child's ability to learn to write effectively, impacting their educational growth. Additionally, fine motor skills are connected to self-care independence, allowing children to dress themselves and manage personal tasks.
Structured challenge exercises, such as puzzles, playdough manipulation, or drawing, offer engaging ways to strengthen these skills. Emphasizing fine motor skill development within this age group prepares children for future academic challenges and daily tasks, promoting independence and boosting their self-esteem. Thus, parents and teachers play a crucial role in providing opportunities and support for enhancing these essential skills.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students






.jpg)