Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 3-7
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's critical thinking abilities with our Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets designed for ages 3-7. These engaging activities introduce young learners to the fundamentals of chess, fostering their logic and strategic planning skills. Through a variety of fun puzzles and scenarios, children will learn to analyze different positions, make thoughtful decisions, and anticipate consequences. Perfect for both beginners and those looking to sharpen their cognitive abilities, our worksheets provide a structured yet enjoyable way to develop problem-solving competencies that will benefit them academically and socially. Make learning chess an adventure with these kid-friendly, expertly crafted resources.
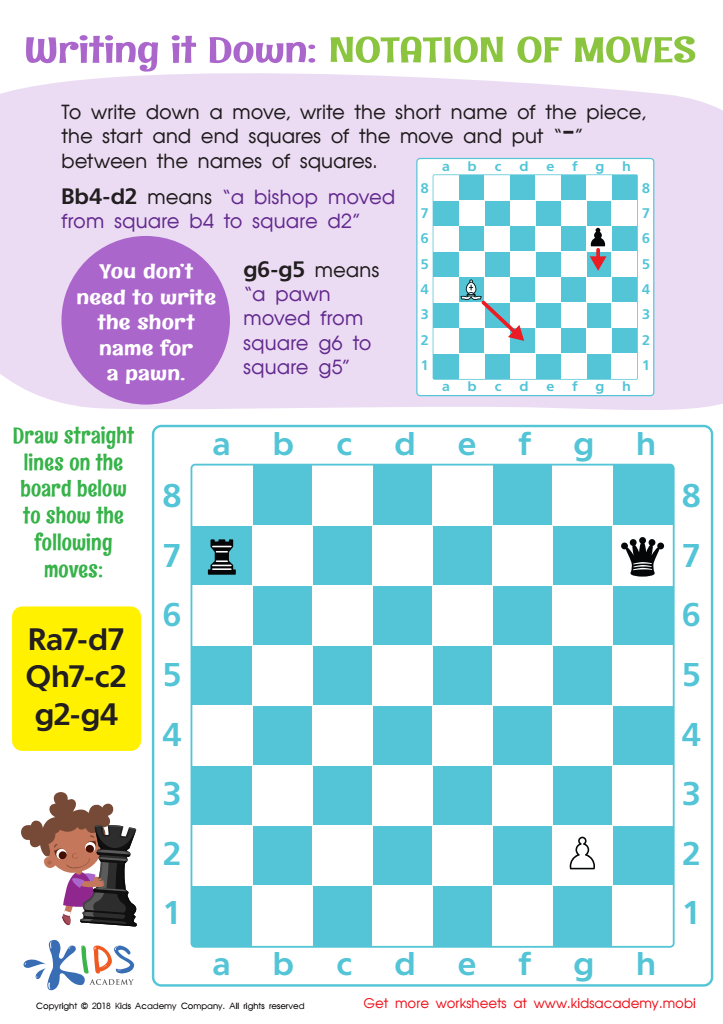

Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
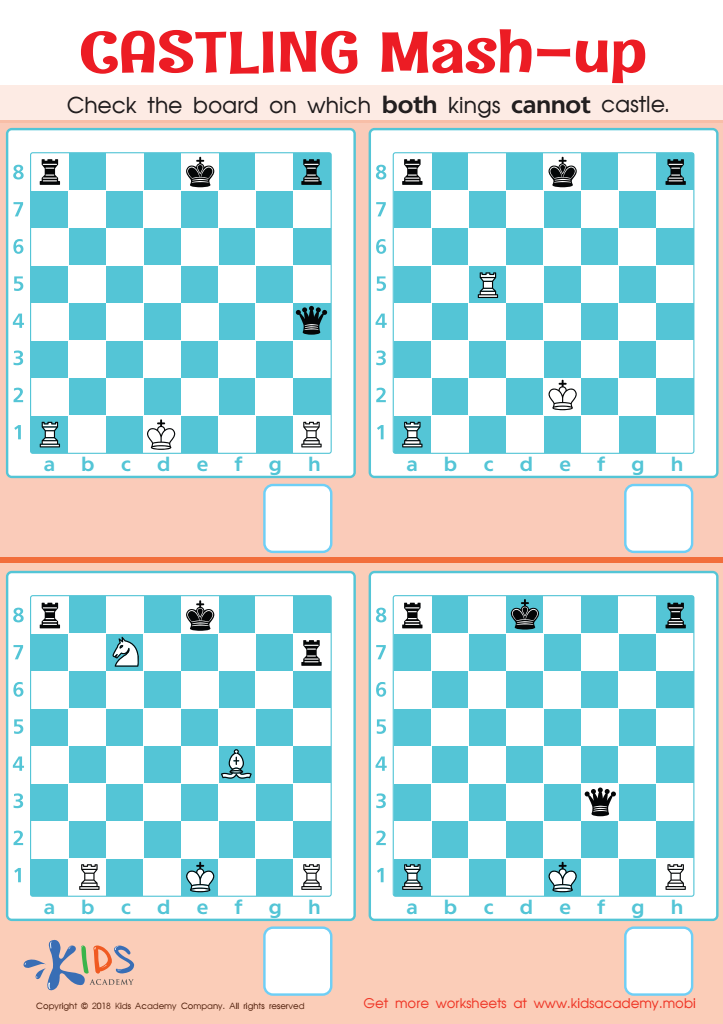

Castling Mash–up Worksheet
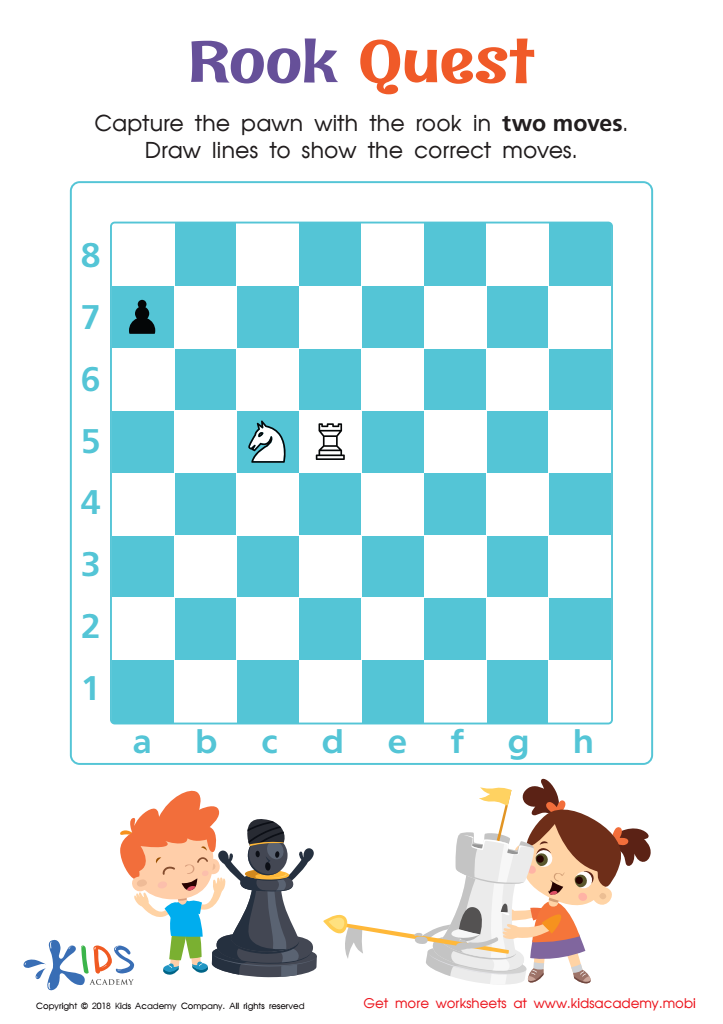

Rook Quest Worksheet
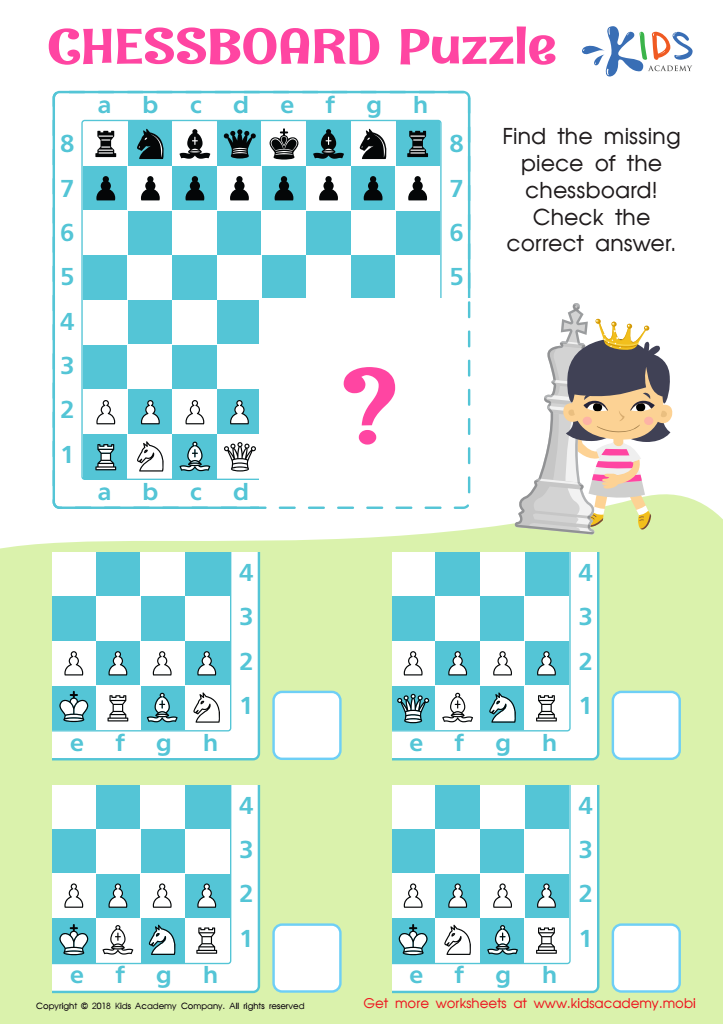

Chessboard Puzzle Worksheet
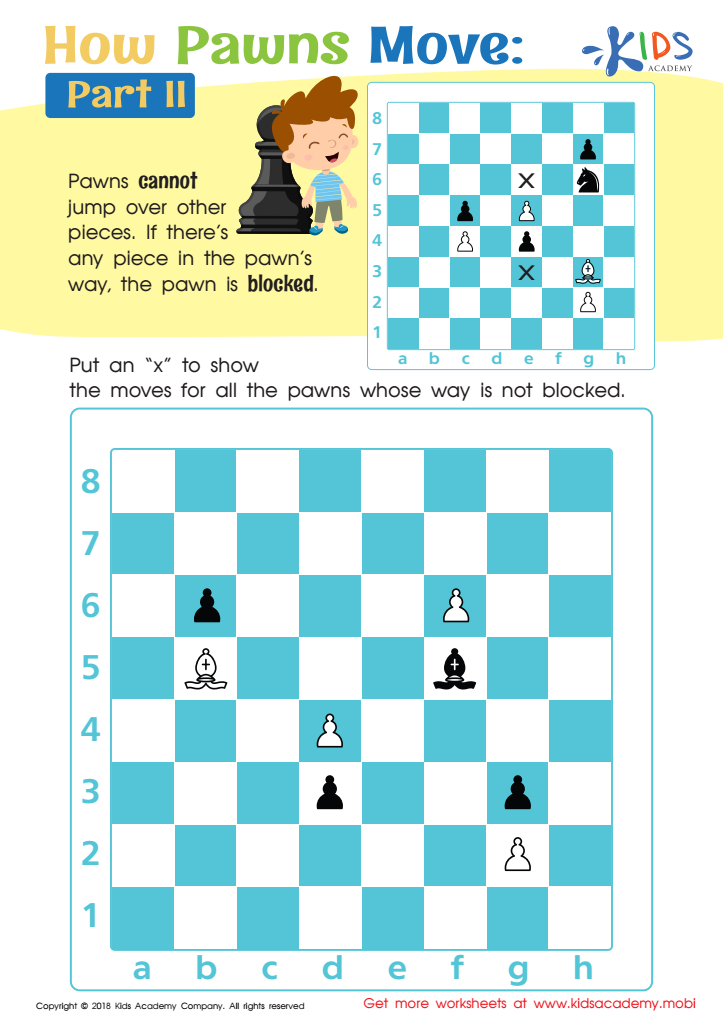

How Pawns Move: Part II Worksheet
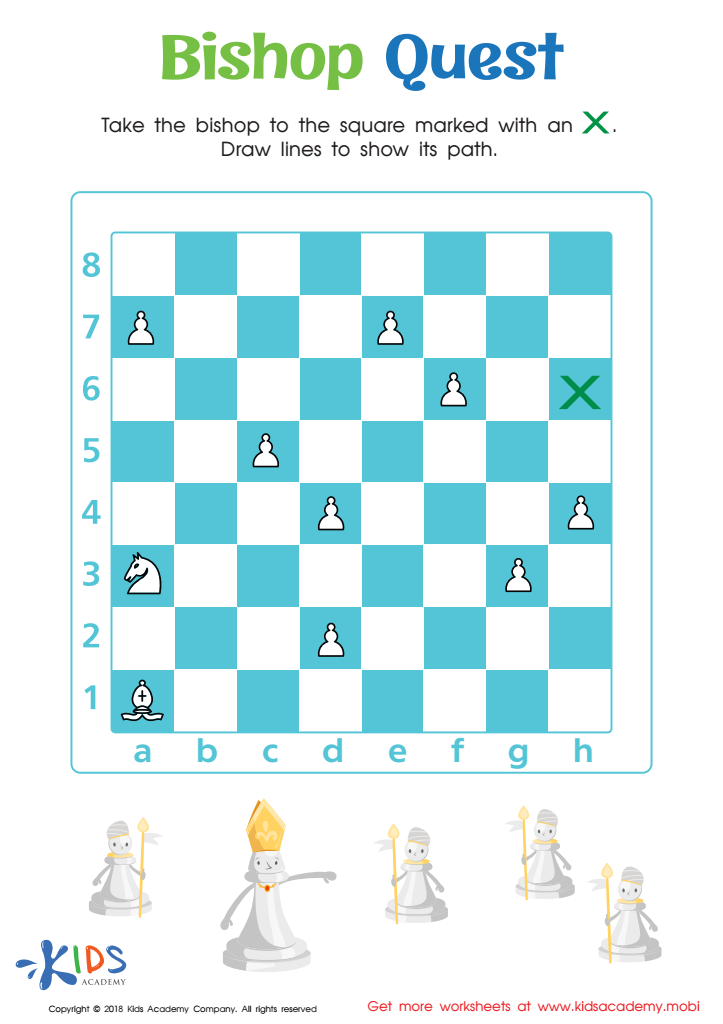

Bishop Quest Worksheet
Problem-solving skills in chess for children aged 3-7 encapsulate cognitive and developmental benefits that parents and teachers should passionately consider. At its core, chess introduces young minds to the fundamental aspects of logic, strategy, and critical thinking. In guiding children to anticipate their opponent’s moves, chess teaches patience, foresight, and planning. Key cognitive skills, such as pattern recognition, spatial awareness, and memory, are honed through the systematic analysis demanded by each move on the board.
Furthermore, early engagement with chess instills a sense of discipline and perseverance. A game that calls for focus and careful decision-making can naturally extend into other areas of life, inclining children towards thoughtful and deliberate actions. Importantly, chess promotes a healthy attitude towards challenge and failure; children see losing not as an end but as an opportunity to reflect and improve, fostering resilience and a growth mindset.
From a social-emotional standpoint, chess provides a constructive platform for interactivity and communication. When played in a school setting or family environment, it becomes a medium for enhancing interpersonal skills and bonding, reinforcing lessons on fairness, respect, and sportsmanship. By integrating chess into early education, parents and teachers can foster all-rounded, adaptable, and intellectually curious individuals, well-equipped to navigate various spheres of life.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students