Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
83 filtered results
-
From - To


Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet
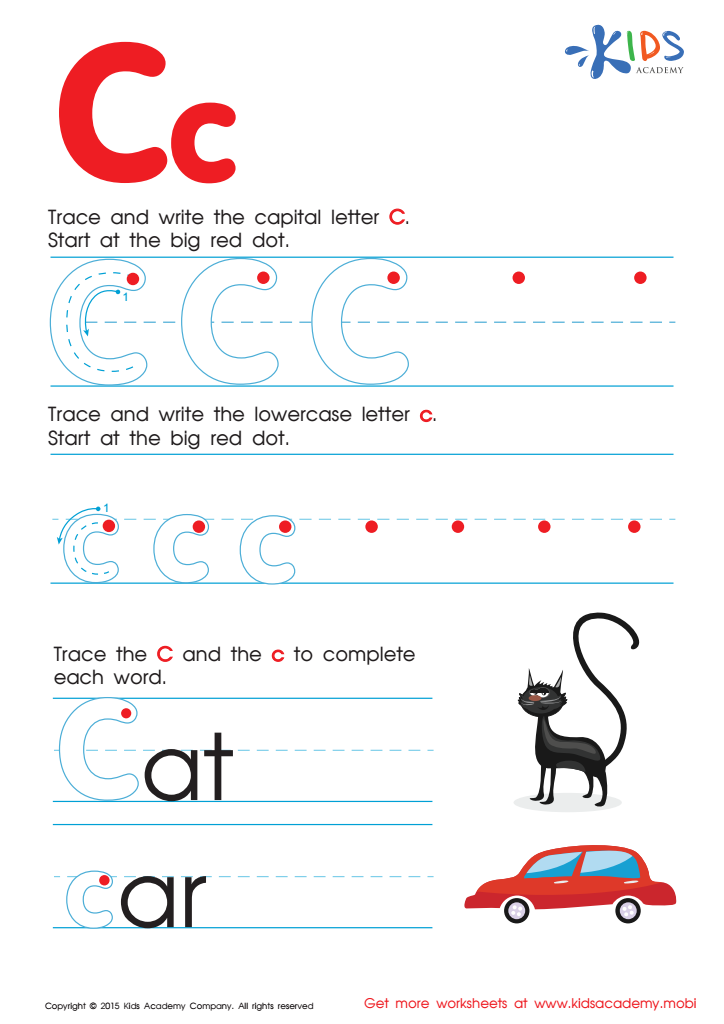

Letter C Tracing Page
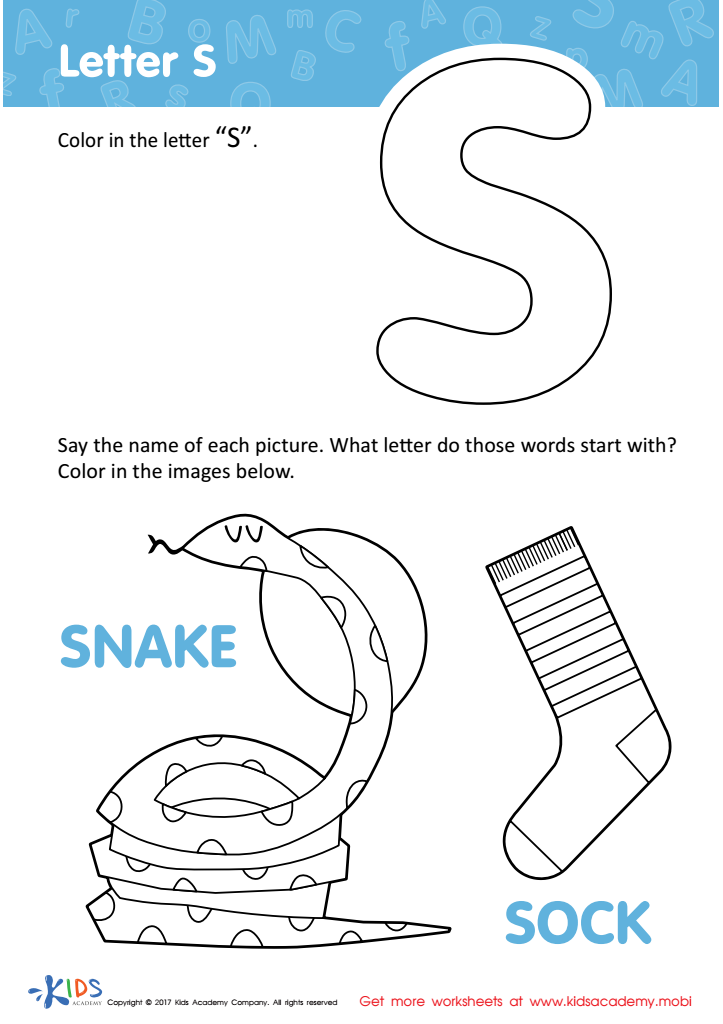

Letter S Coloring Sheet


Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


Letter G Tracing Page


Pink Tracing Color Words Worksheet
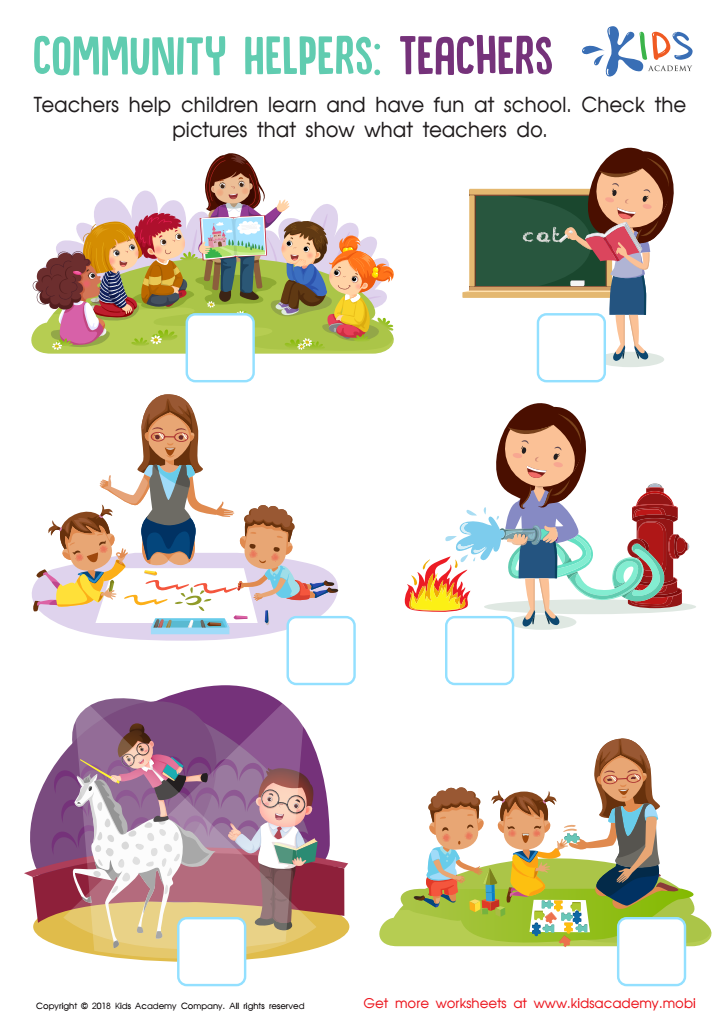


Teachers Community Helpers Worksheet
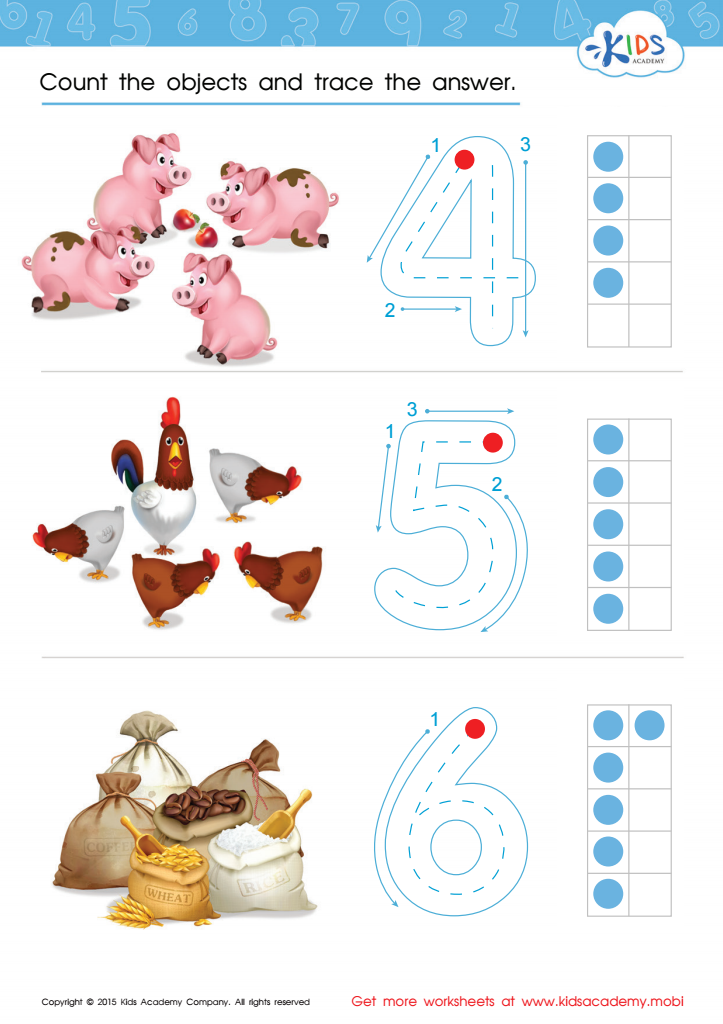

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable
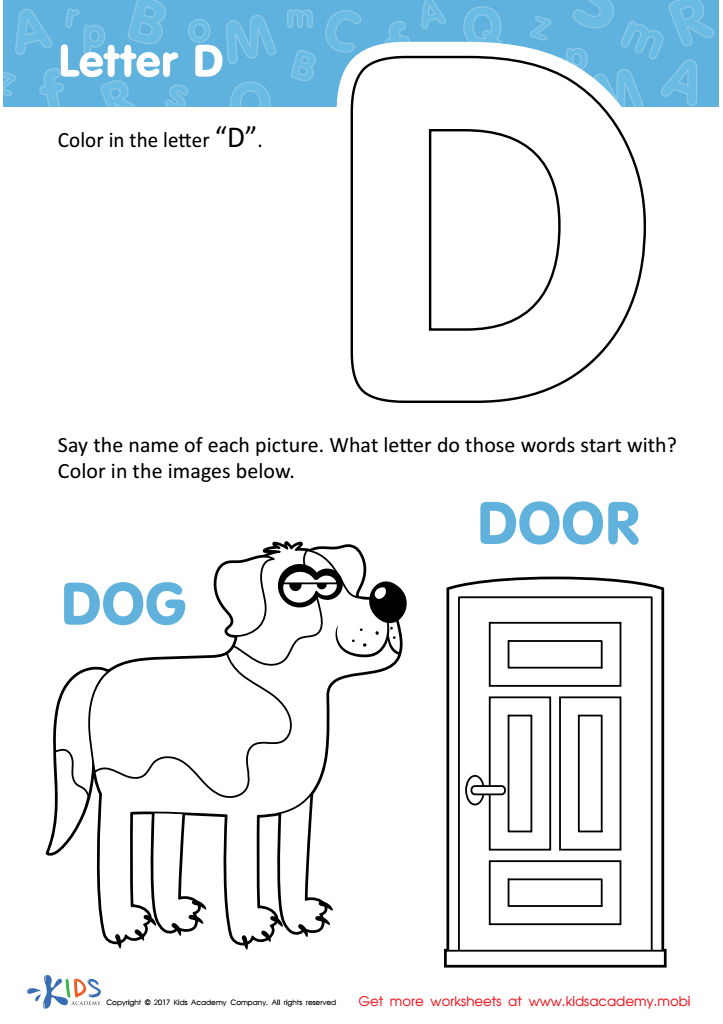

Letter D Coloring Sheet


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet


Bat Rhyming Words Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Spanish Word Tracing: Hola Worksheet


Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet

Letter N Tracing Page


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Orange Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Lowercase Letters d e f Worksheet

Count the Carrots and Trace the Number 7 Printable
Handwriting practice for children aged 3-4 is crucial for several reasons. First, it lays the foundation for fine motor skills. At this developmental stage, children are refining their hand-eye coordination and dexterity, essential for tasks like writing, drawing, and later, typing. Engaging in handwriting practice helps strengthen these skills, allowing for smoother motions when forming letters.
Secondly, early handwriting experience fosters cognitive development. As children learn to trace and write letters, they connect sounds to symbols, enhancing both literacy skills and phonemic awareness. This prescriptive practice primes them for reading success, as they begin to recognize letters and their respective sounds.
Additionally, handwriting promotes self-expression. Creating shapes and letters allows children to convey their thoughts and feelings visually, boosting their confidence and sense of accomplishment.
Lastly, practicing handwriting can enhance focus and concentration. The repetitive nature of writing requires children to concentrate, which can enhance their overall attention span.
Overall, investing time in handwriting practice for ages 3-4 is not merely about teaching a skill; it's about nurturing a child’s emotional, cognitive, and physical development, setting the groundwork for academic success and lifelong learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















