Fine Motor Skills ABC Letters Worksheets for Ages 3-5 - Page 2
38 filtered results
-
From - To
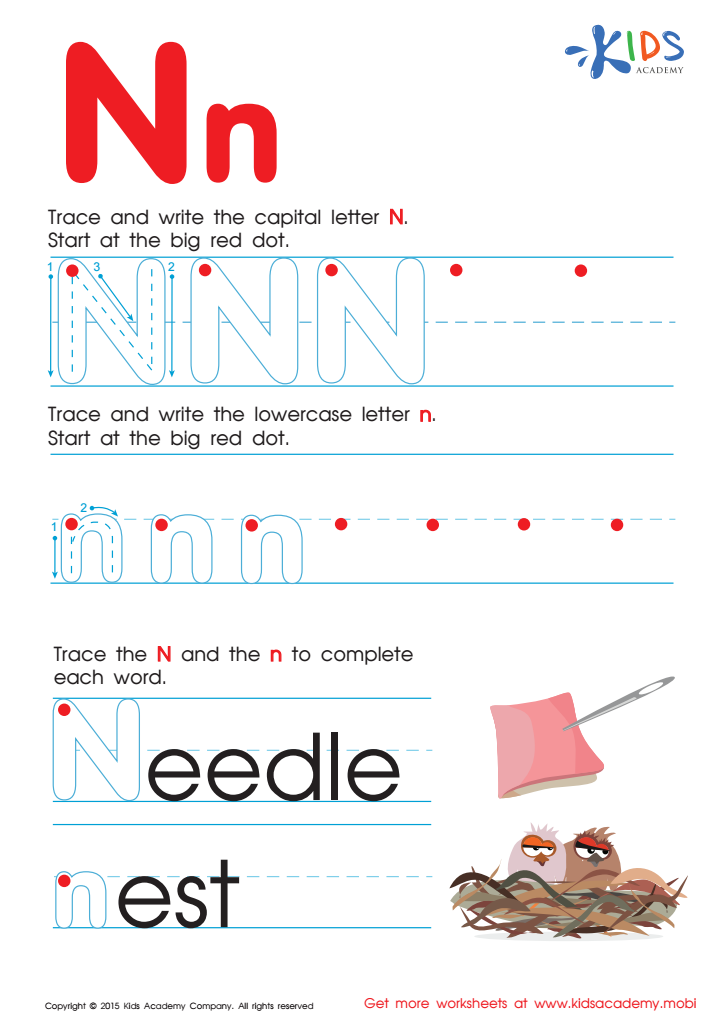

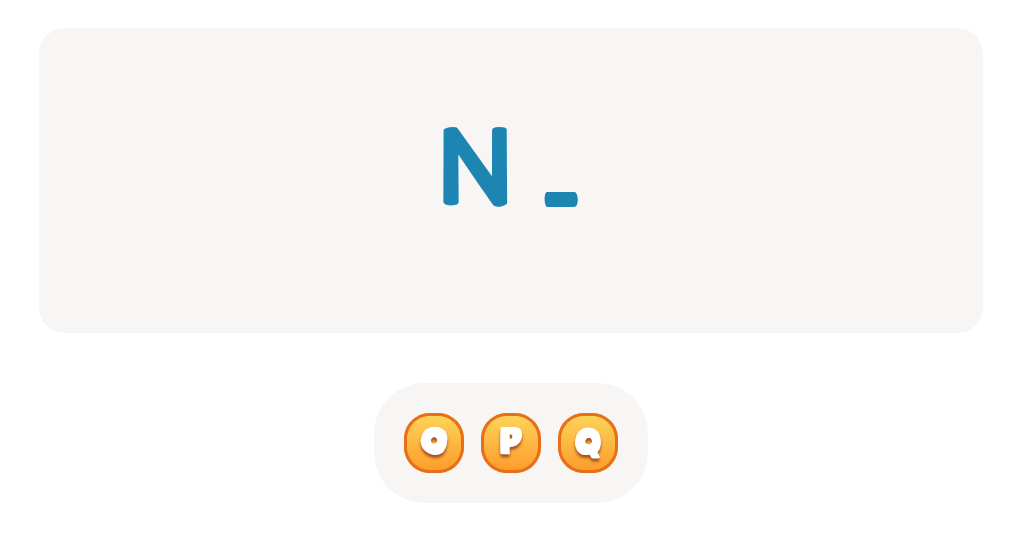
Letter N Tracing Page


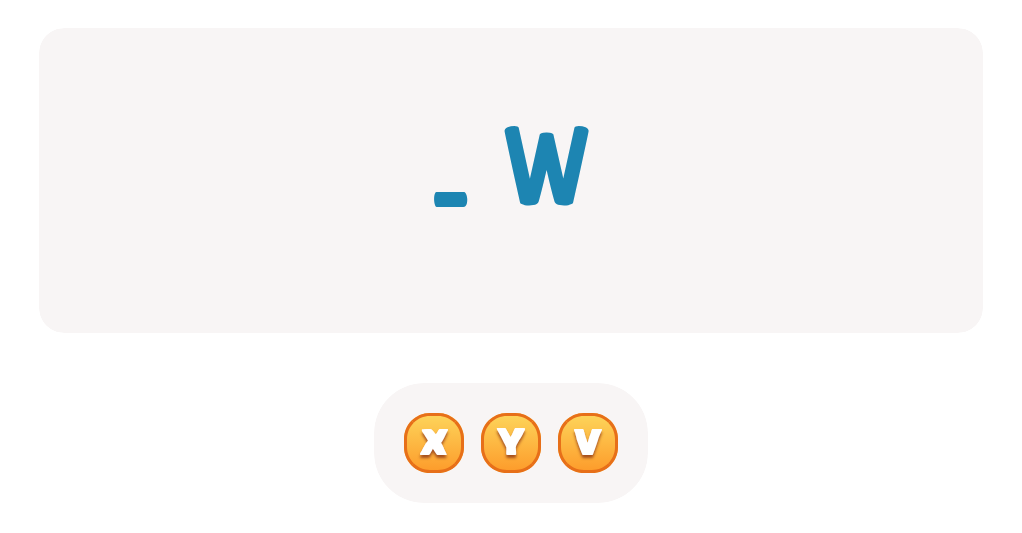
Letter V Tracing Page

Letter P Coloring Sheet

Letter E Tracing Page


Letter G Coloring Sheet


Letter Z Coloring Sheet


Letter J Coloring Sheet

Letter Y Coloring Sheet


Letter F Tracing Page


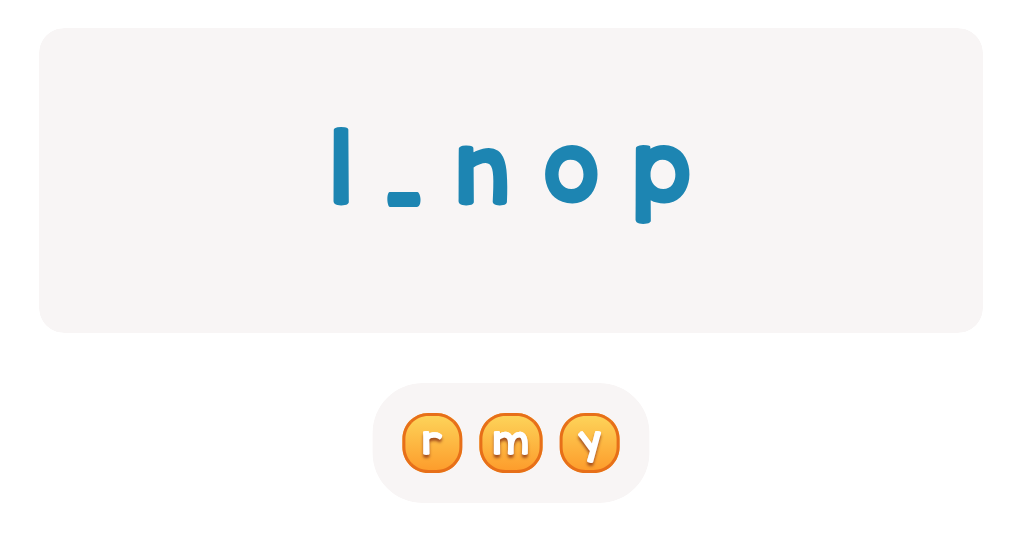
Uppercase Letters Y Z Worksheet

Letter F Coloring Sheet

Letter T Tracing Page


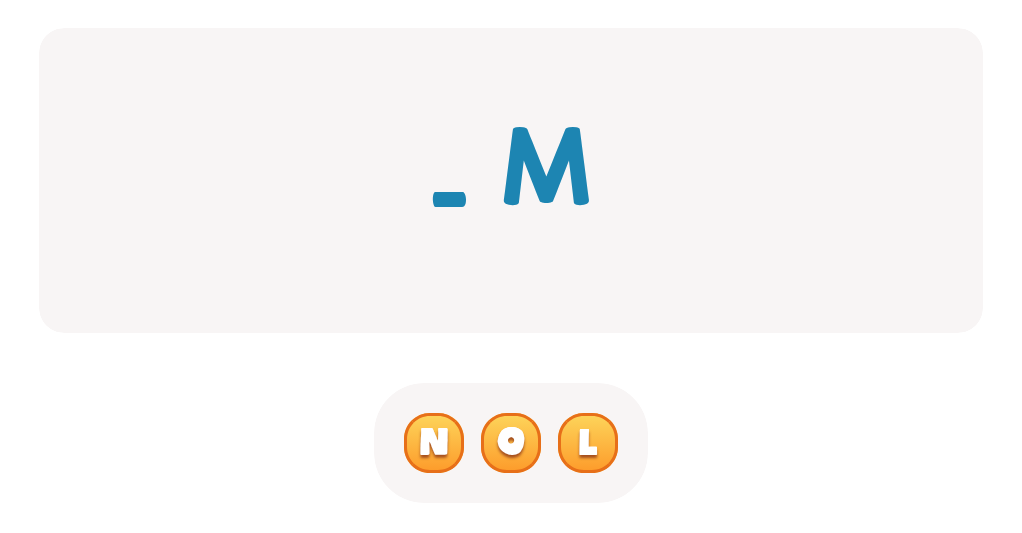
Letter N Coloring Sheet


Letter D Tracing Page
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children's overall development, particularly in the formative ages of 3 to 5. These skills refer to the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are essential for tasks like writing, drawing, and manipulating small objects.
Focusing on fine motor skills, especially in the context of learning the ABC letters, equips children with the foundation for literacy. As they practice gripping crayons or markers to form letters, they're not only enhancing hand strength and dexterity but also developing the essential ability to hold writing instruments properly. This early exposure plays a significant role in their future academic success.
Moreover, fine motor development is linked to cognitive processing, problem-solving, and creativity. Engaging in activities that promote these skills—such as tracing, coloring, and using playdough—can ignite a child's interest and motivation in learning.
Additionally, strong fine motor skills boost a child's confidence when progressing to more complex tasks in school. By nurturing these abilities, parents and teachers play a pivotal role in laying a solid educational groundwork that can positively impact children's lifelong learning and independence. Thus, emphasizing fine motor skills as learners engage with letters fosters a holistic approach to early childhood education.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students