Shape Recognition 2D Shapes Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
37 filtered results
-
From - To

Trace and Draw More Shapes Worksheet

Missing Shapes: Trains Worksheet

Robot Shapes Worksheet

Matching Shapes Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet
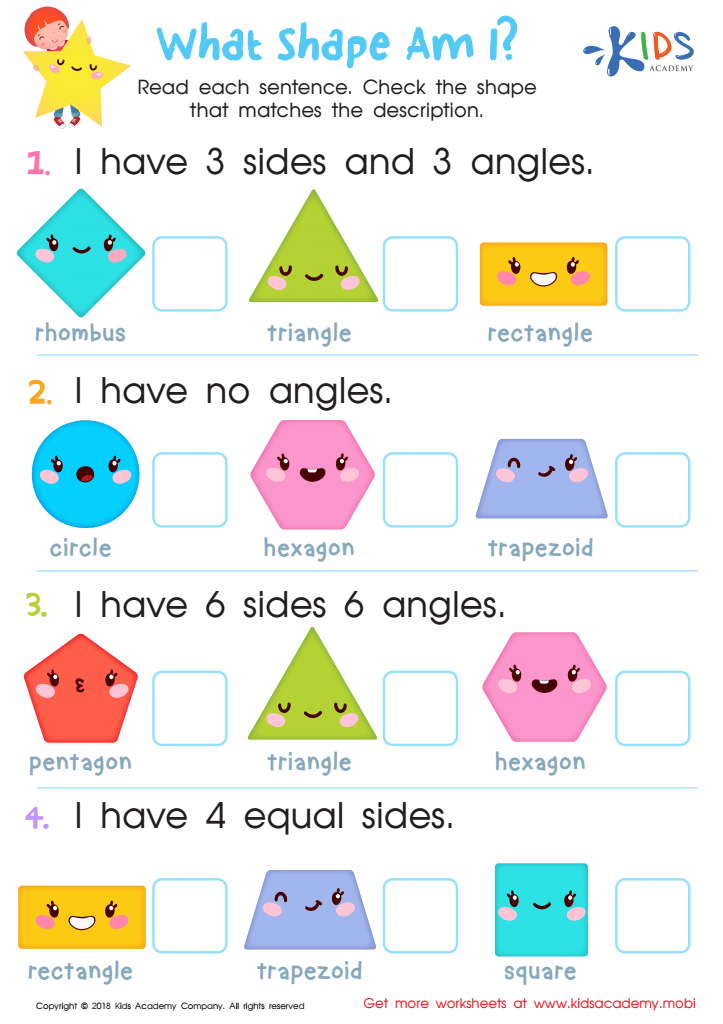

What Shape Am I? Worksheet
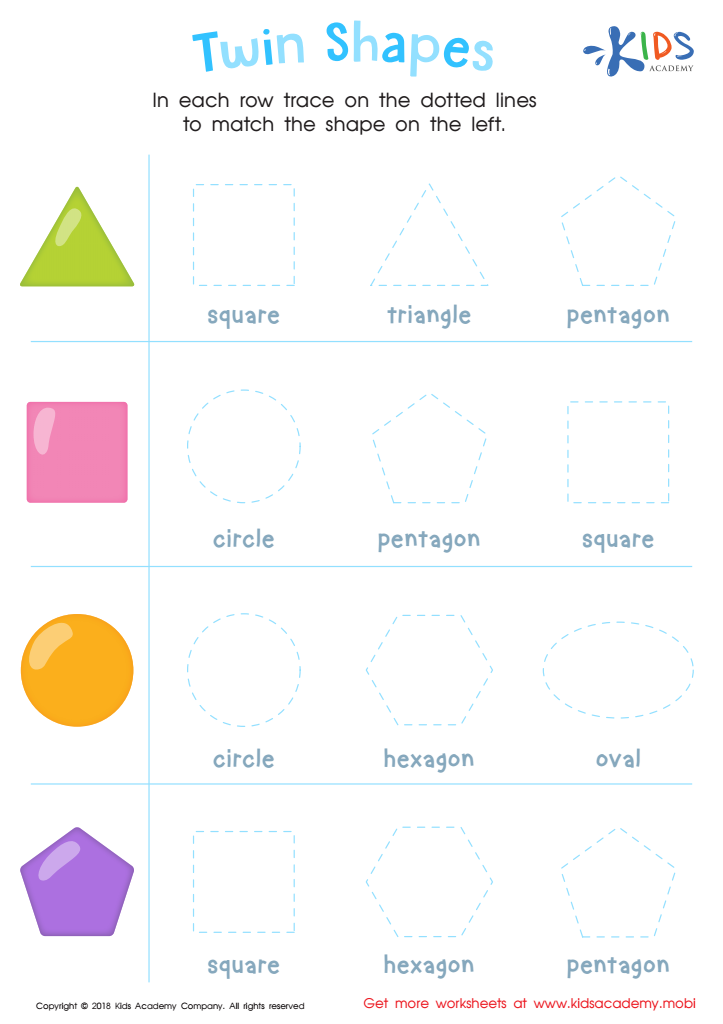

Twin Shapes Dot-to-Dot Worksheet
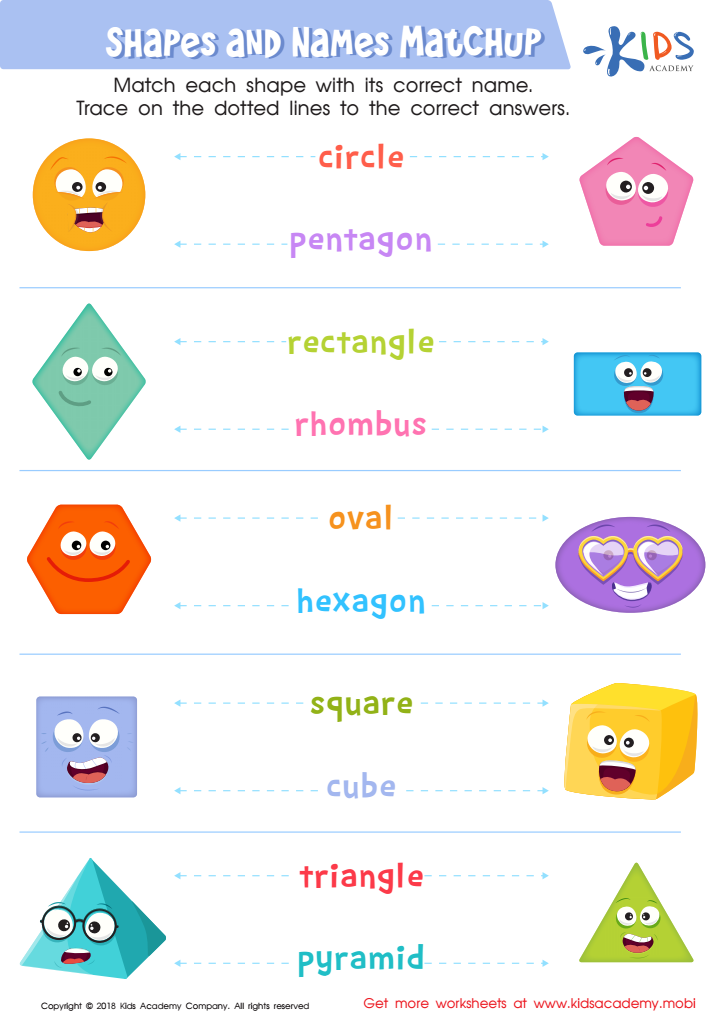

Shapes and Names Matchup Worksheet
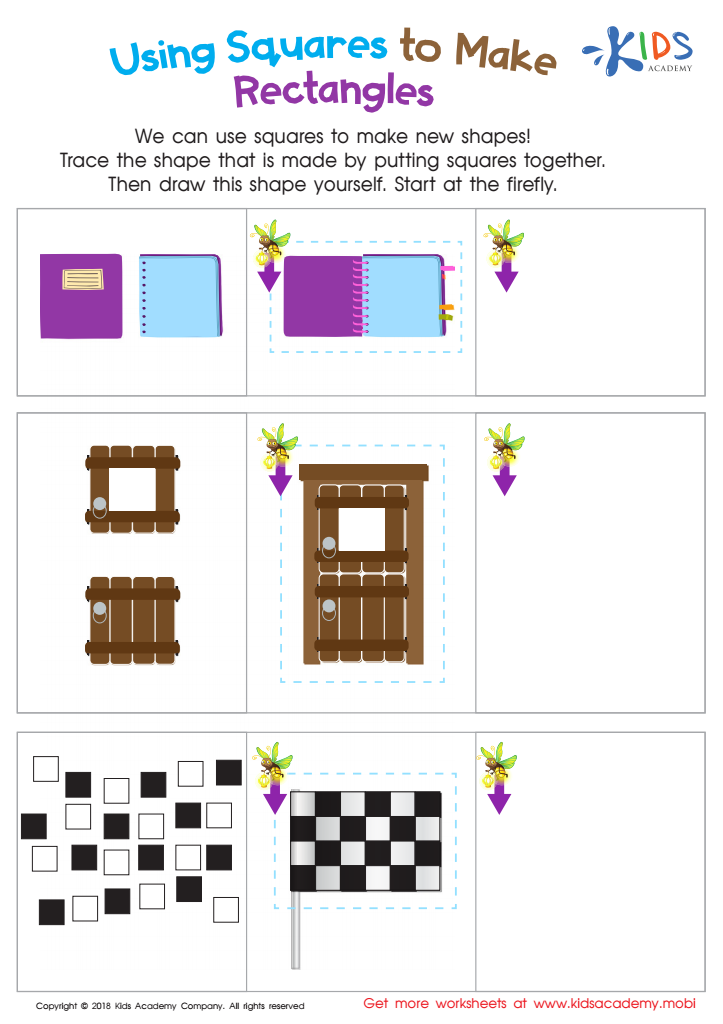

Using Squares to Make Rectangles Worksheet

Drawing Ovals And Triangles with Fun Printable

Shapes Matchup Worksheet

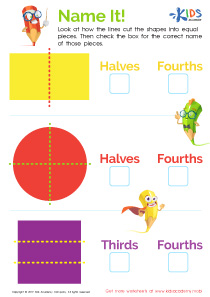
Sorting Shapes - Part 2 Worksheet

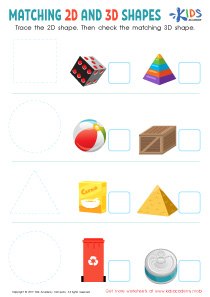
Build and Match Worksheet
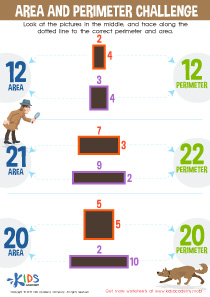
Shape recognition is foundational for young children aged 4 to 8, as it plays a crucial role in their cognitive development and prepares them for comprehensive mathematics learning. First, shape recognition aids in developing spatial awareness, helping children understand how objects relate to each other in space. This skill is essential for later mathematical concepts, such as geometry and measurement.
Moreover, identifying 2D shapes fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. When children learn to differentiate between squares, circles, triangles, and more, they practice categorization and classification, skills applicable across various domains in life.
Parents and teachers should also remember that early exposure to shapes helps build vocabulary and communication skills. As children describe shapes, they practice using language confidently, boosting literacy development.
Additionally, engaging activities related to shape recognition promote fine motor skills, as children often manipulate shapes through drawing or crafting. Early familiarity with shapes leads to a stronger grasp of patterns and relationships in mathematics, enriching future learning experiences.
In sum, shape recognition is not merely an introductory math skill; it encompasses essential cognitive, linguistic, and motor skills that parents and teachers play a vital role in nurturing during these formative years.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students