Fine Motor Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 2
82 filtered results
-
From - To
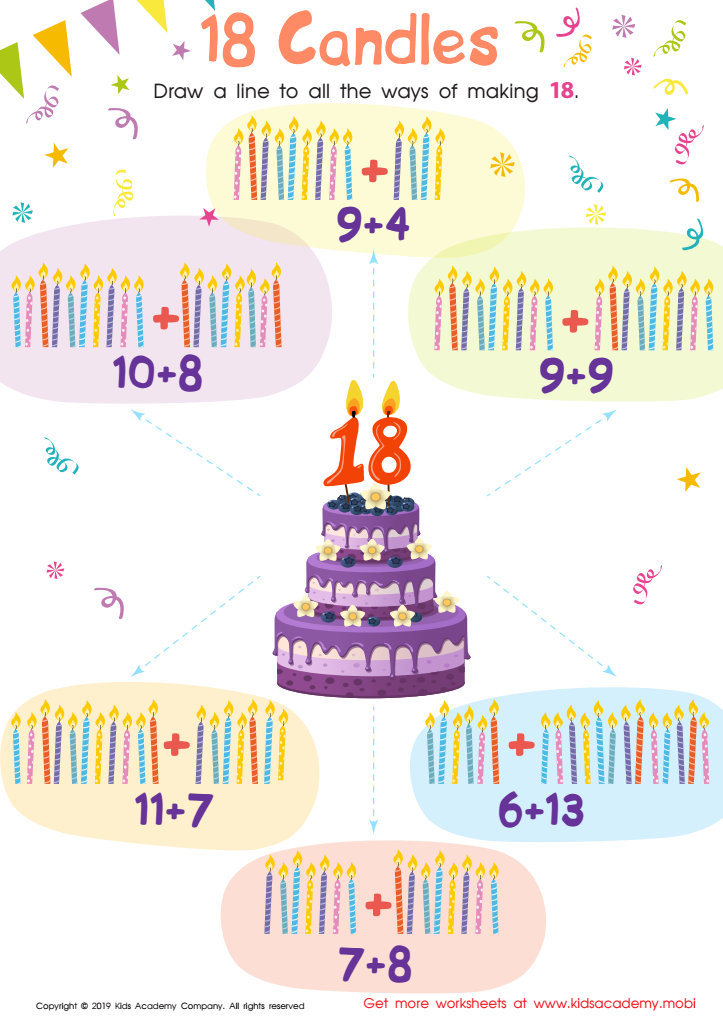

18 Candles Worksheet
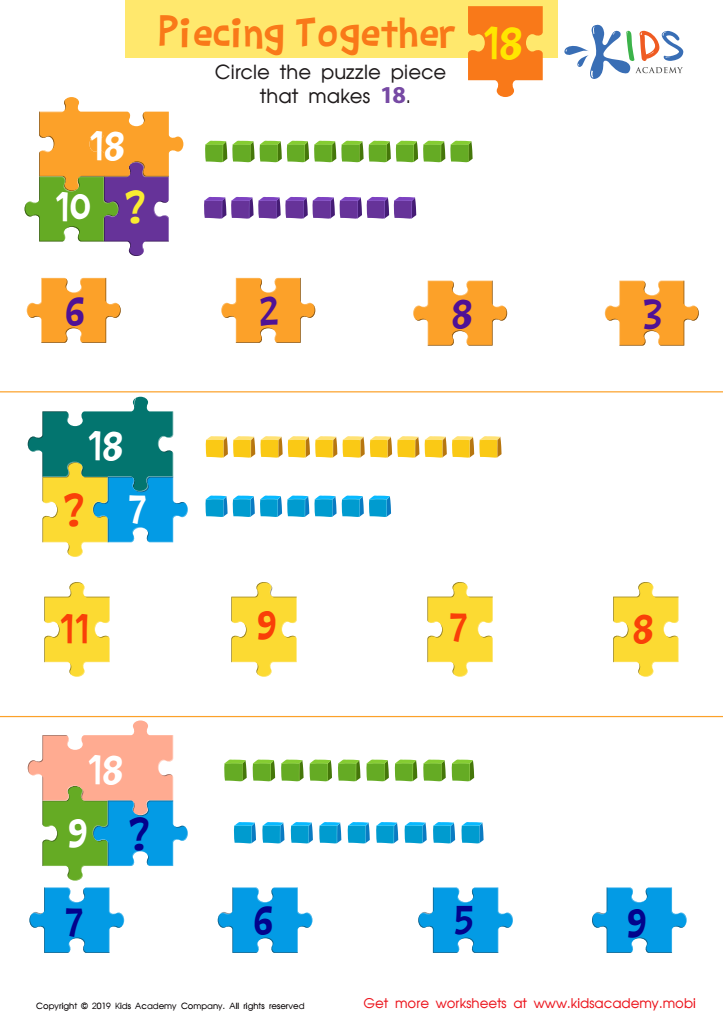

Piecing Together 18 Worksheet
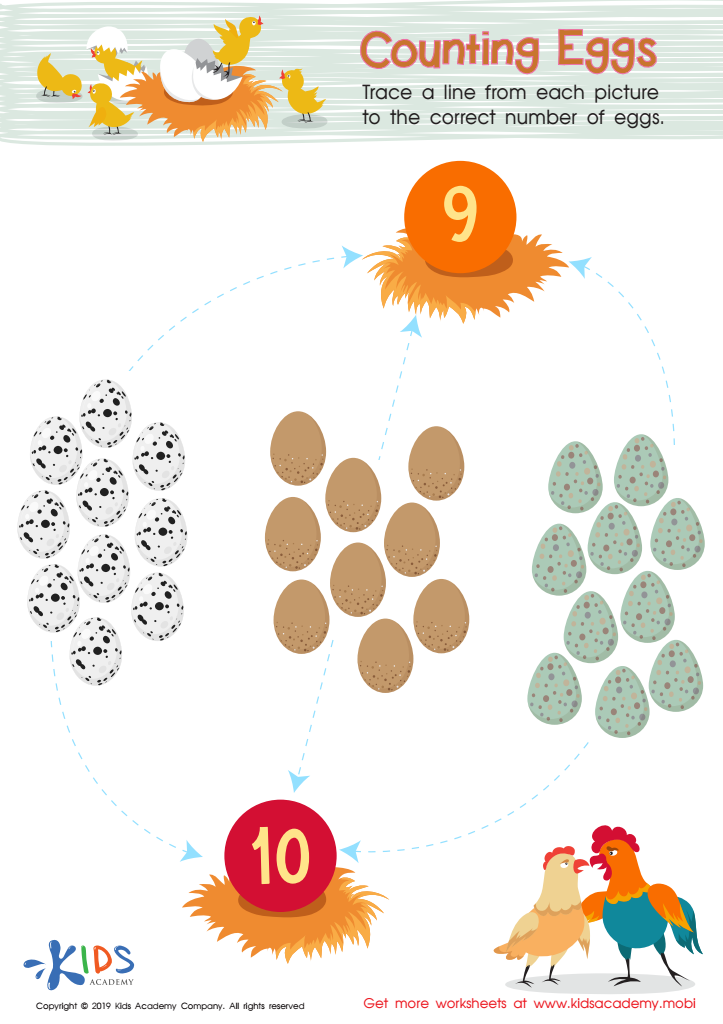

Counting Eggs Worksheet
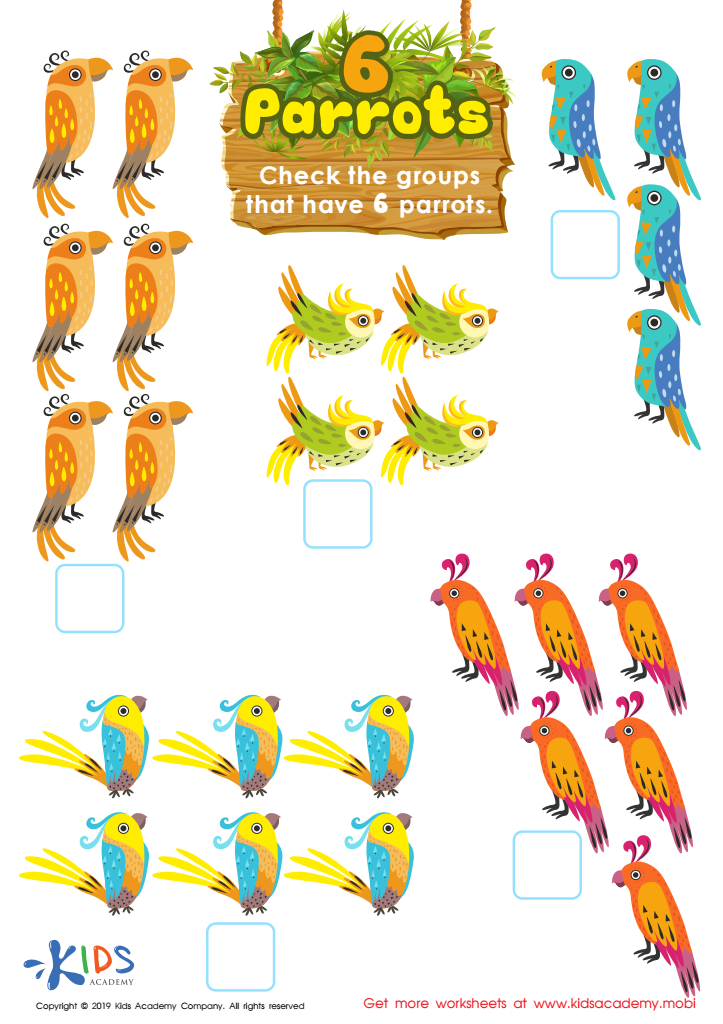

6 Parrots Worksheet
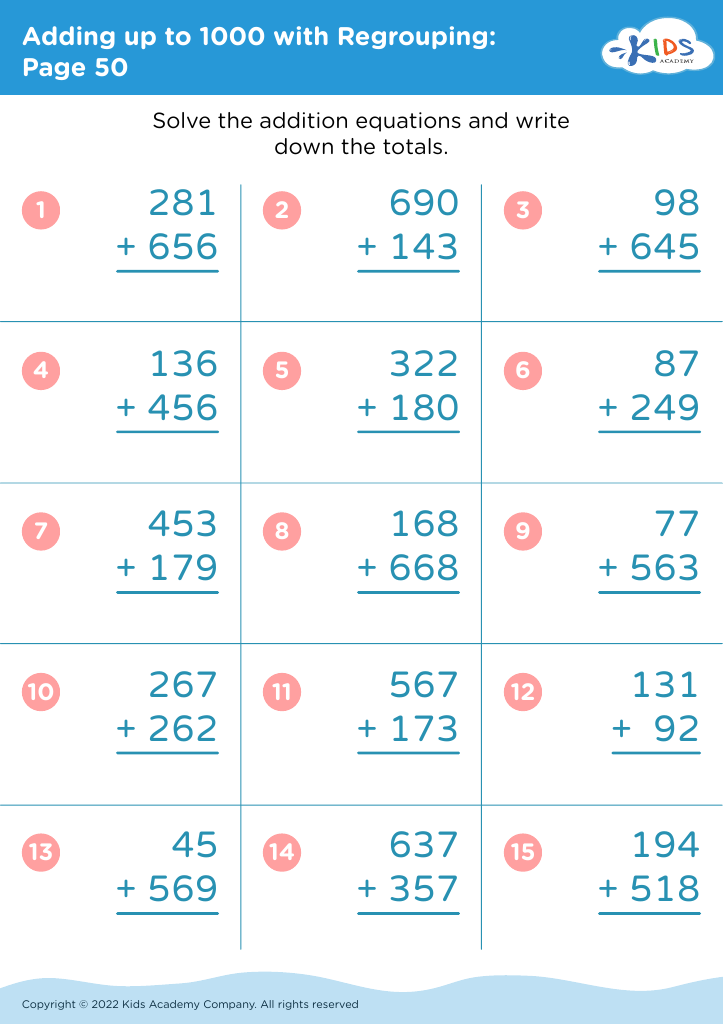
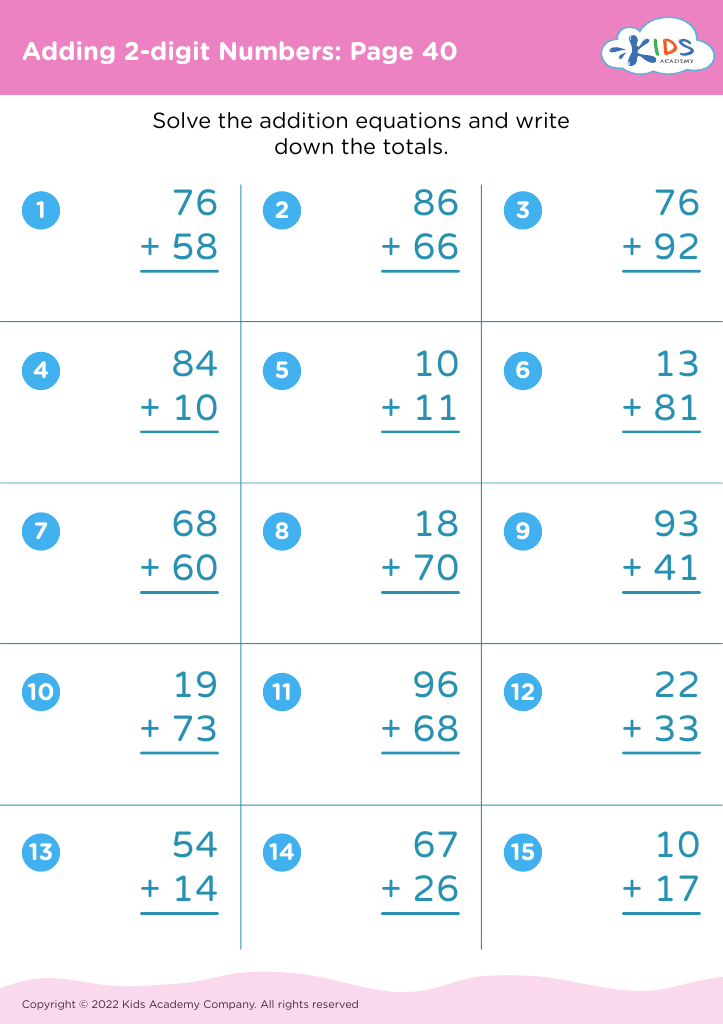
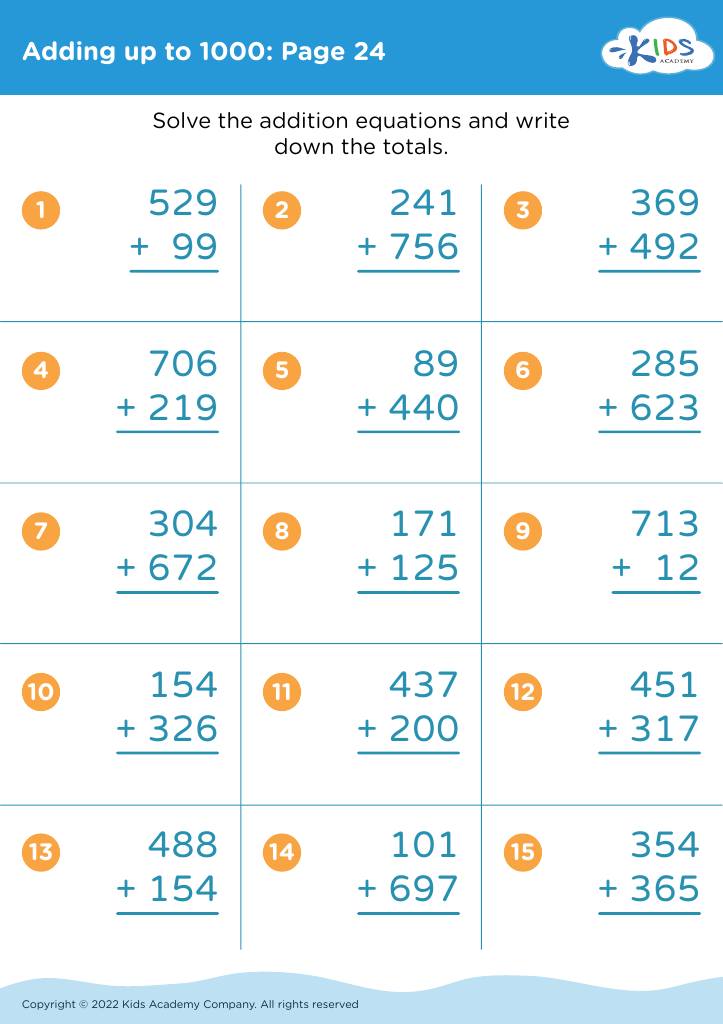
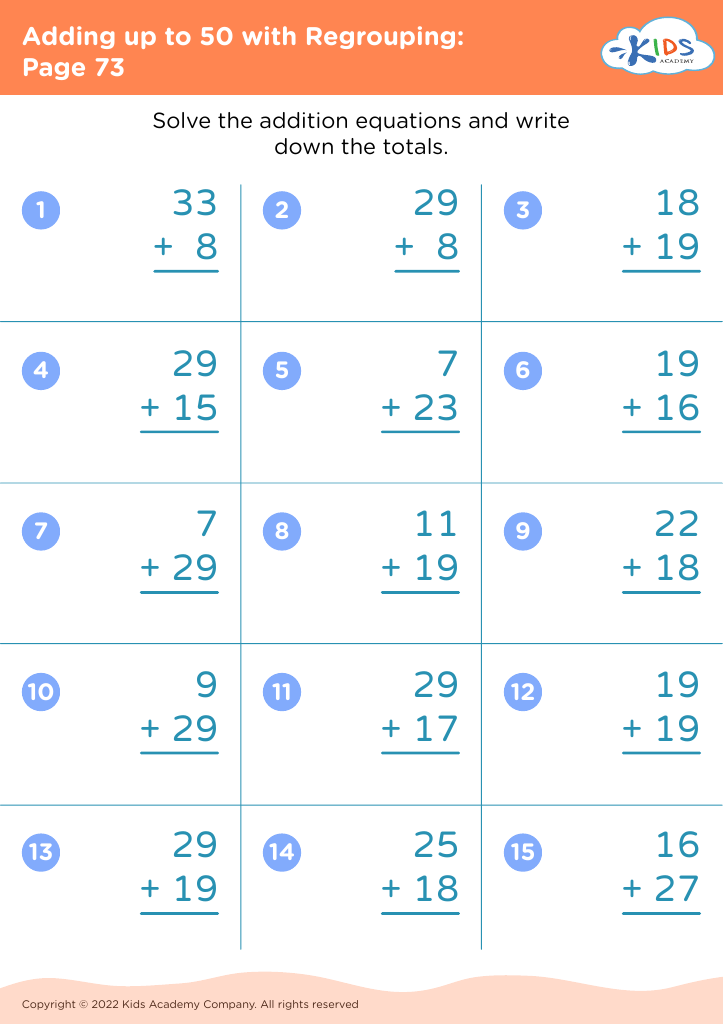
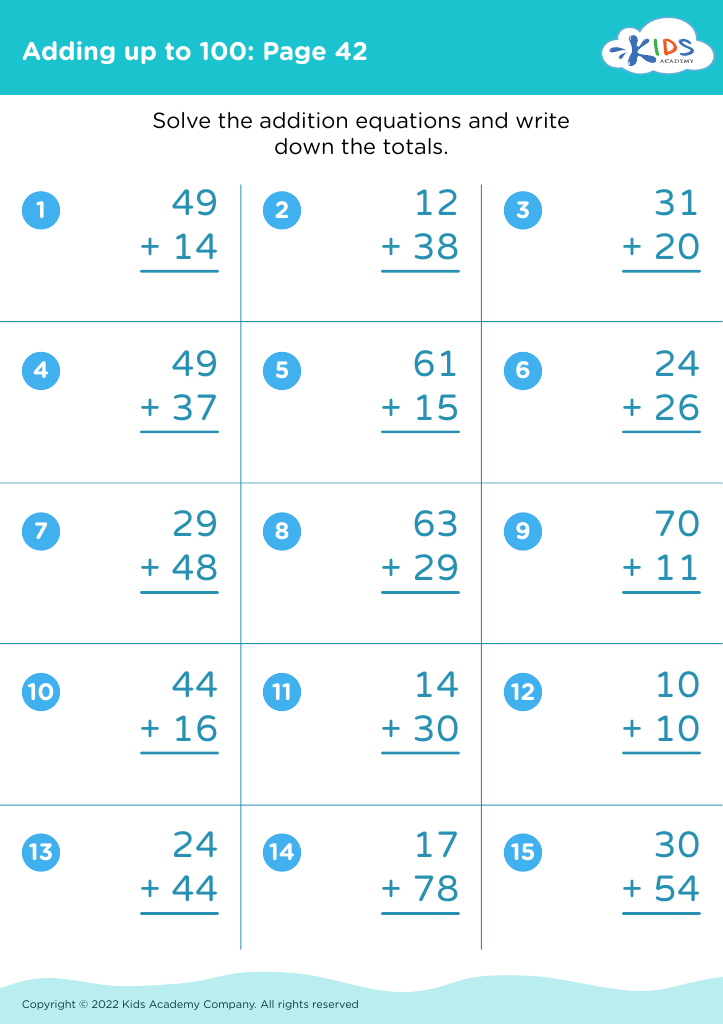
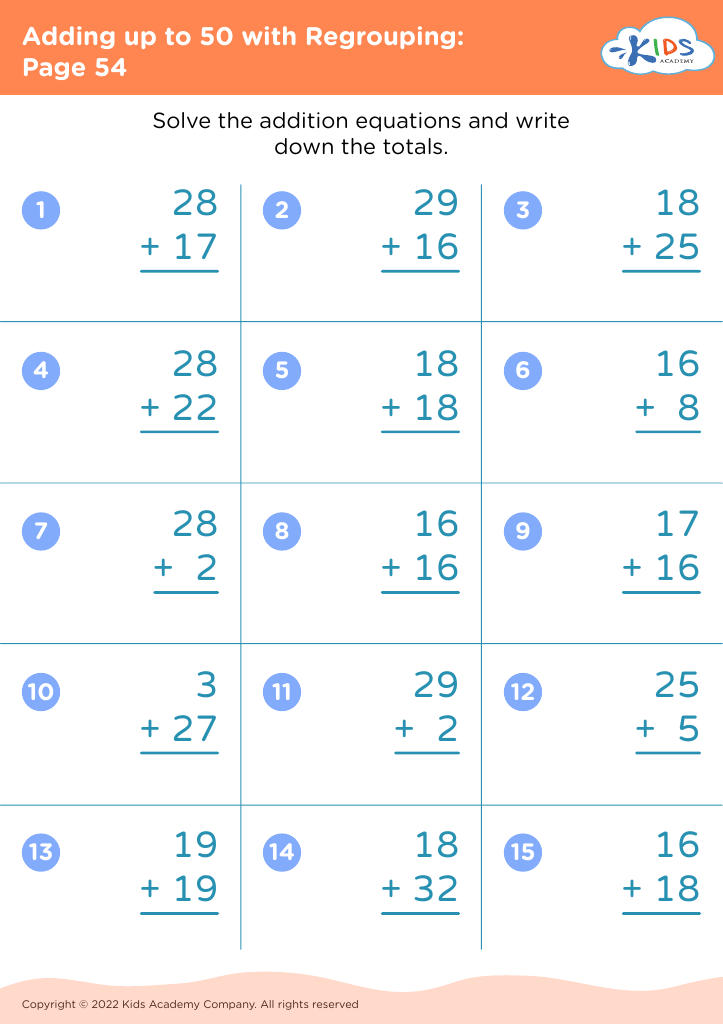
Parents and teachers should care deeply about fine motor skills for addition and subtraction for ages 4-8, because the development of these skills lays a crucial foundation for children's overall education and daily functioning. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in movements—usually the synchronization of hands and fingers with the eyes. Mastering these skills is essential for children as they learn to write numbers, manipulate small objects like counters or beads, and use educational tools such as pencils and scissors.
When children practice addition and subtraction activities, they often draw small objects, write numbers, and sort items—tasks that build fine motor dexterity. For example, using objects like buttons or blocks to solve math problems requires grasping, moving, and properly placing items, which enhances muscle strength and coordination in their hands and fingers.
Developing fine motor skills also improves hand-eye coordination, which is essential not only for mathematics but for other subjects and activities like art and physical education. When children perform tasks smoothly and confidently, they are more likely to develop a positive attitude toward learning. Moreover, these skills are linked to self-care activities such as buttoning shirts, tying shoelaces, and even feeding themselves. By supporting fine motor skill development, parents and teachers are essentially setting children up for greater academic success and daily independence, providing them with tools that they will use for the rest of their lives.



 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students