Fine Motor Skills Geometry Worksheets for Ages 5-8 - Page 2
29 filtered results
-
From - To


Patchwork Math Worksheet
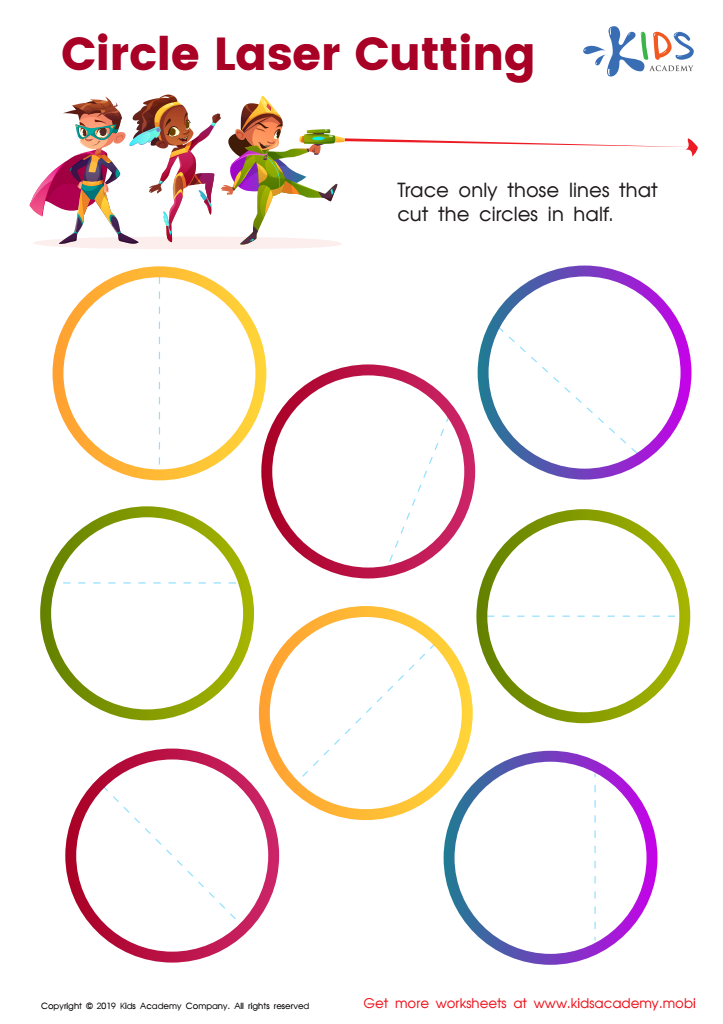

Circle Laser Cutting Worksheet
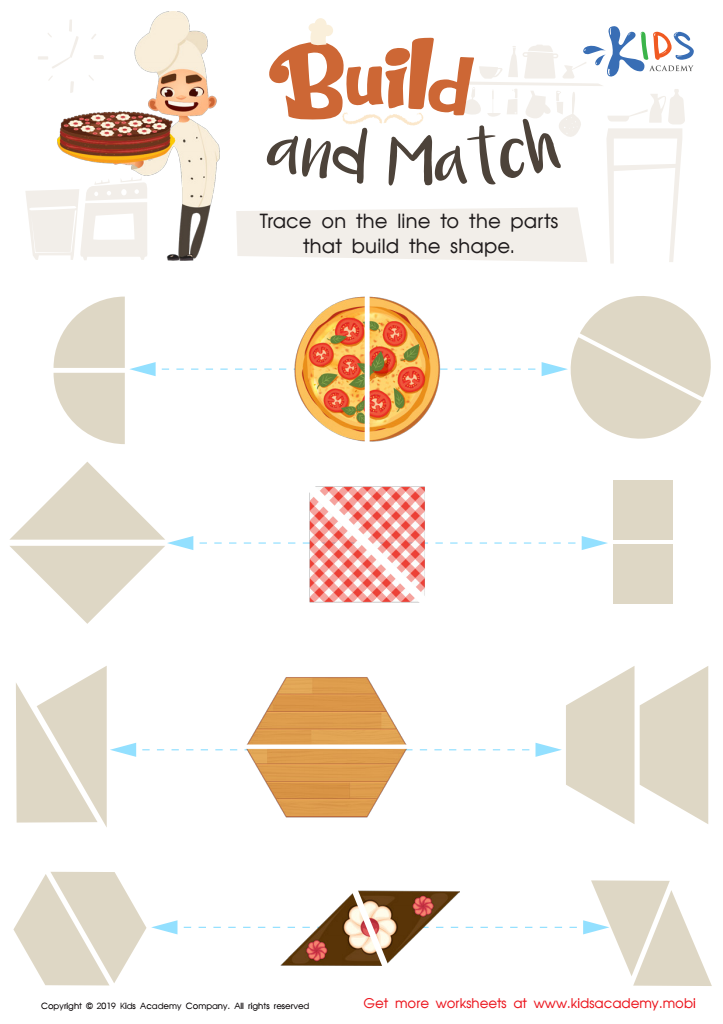

Build and Match Worksheet
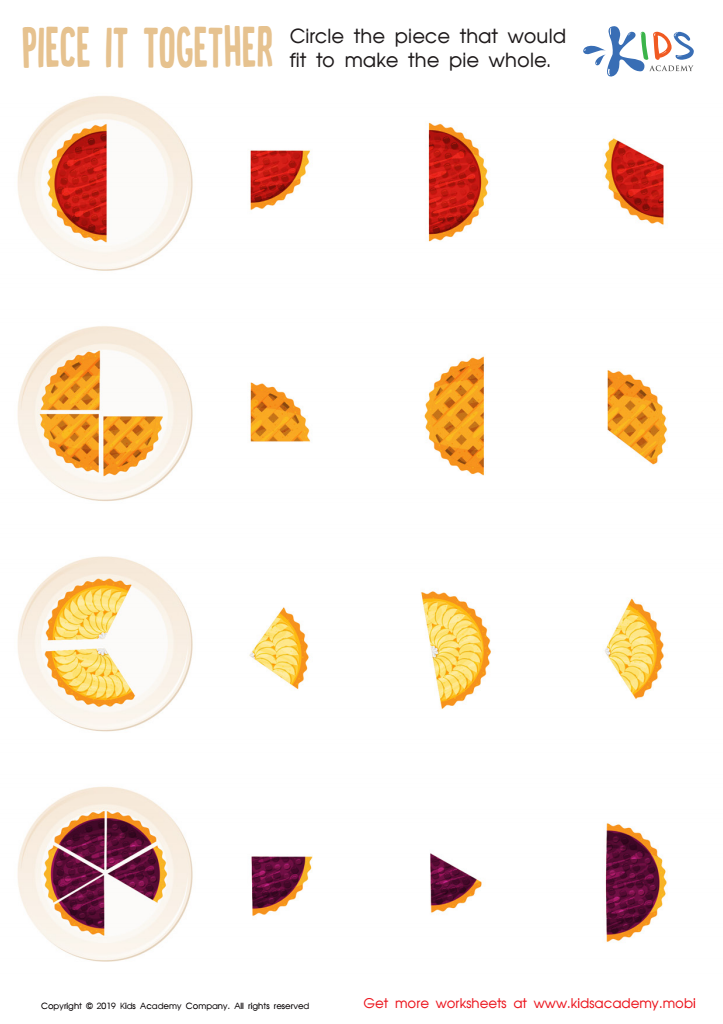


Piece it together Worksheet

Construction Shapes Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for young children, particularly in the context of learning geometry. Between ages 5-8, children develop the necessary skills to manipulate objects, which enhances their understanding of geometric concepts. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, enabling activities such as drawing, cutting, and building with blocks.
For parents and teachers, fostering these skills is essential as they provide the foundation for spatial awareness and problem-solving abilities. Children learn to recognize shapes, understand symmetry, and develop an appreciation for measurements through hands-on activities. Engaging in geometry using fine motor exercises not only promotes cognitive development but also boosts confidence, as children gain mastery over their abilities.
Moreover, mastery of fine motor tasks directly correlates with a child's performance in academic settings, including writing and mathematics. When parents and teachers actively participate in activities that reinforce fine motor skills within a geometric context—like crafting, puzzles, or tracing shapes—they make learning enjoyable and impactful. This integration paves the way for future success in STEM fields, fostering enthusiasm for math and science early on, ultimately contributing to a child's overall development and lifelong learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students