Fine Motor Skills Easy Worksheets for Ages 4-7
81 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our specially designed easy worksheets for ages 4-7. Perfect for young learners, these engaging activities help develop crucial hand-eye coordination and dexterity through fun and interactive exercises. From tracing and cutting to drawing and assembling, each worksheet is crafted to make learning enjoyable and effective. Our collection not only boosts fine motor abilities but also lays a strong foundation for future academic success. Ideal for both parents and teachers, these resources provide an excellent way to support your child’s early development in a playful and educational setting.


Christmas Tree Tracing Winter Words Worksheet


Snowflake Tracing Winter Words Worksheet
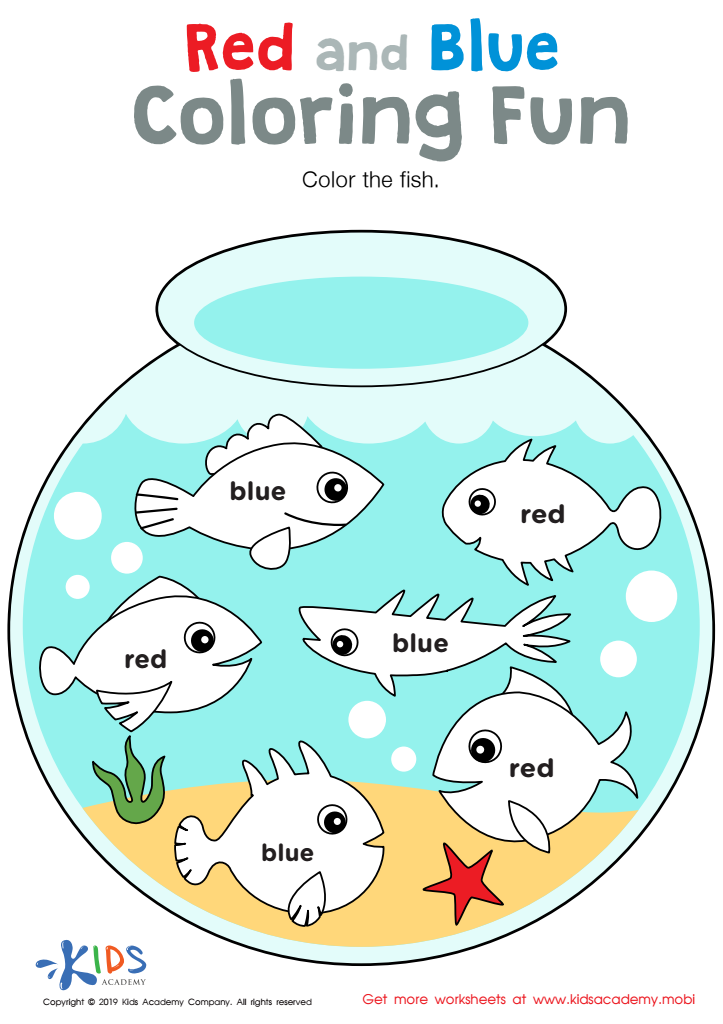


Red and Blue Coloring Fun Worksheet


Number 10 Printable


Happy Diwali Printable

Yellow and Green Coloring Fun Worksheet


Pegasus Printable


Number 5 Printable

Composing a Robot's Face of Crescents And Stars Worksheet

Matching Halves Worksheet

Sea Adventure Coloring Page


Find 7 Worksheet


Letter T Coloring Sheet


Little Blue Belle Worksheet
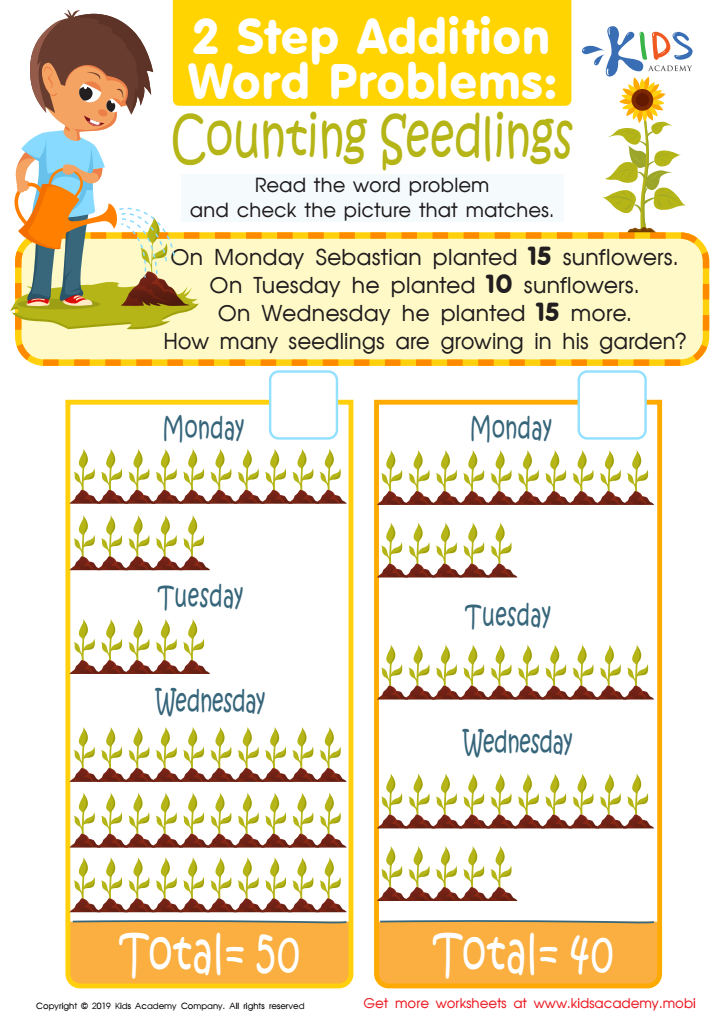

Counting Seedlings Worksheet


Humming Bird Worksheet


Ten in the Bed: Vocabulary Worksheet


Number 4 Printable
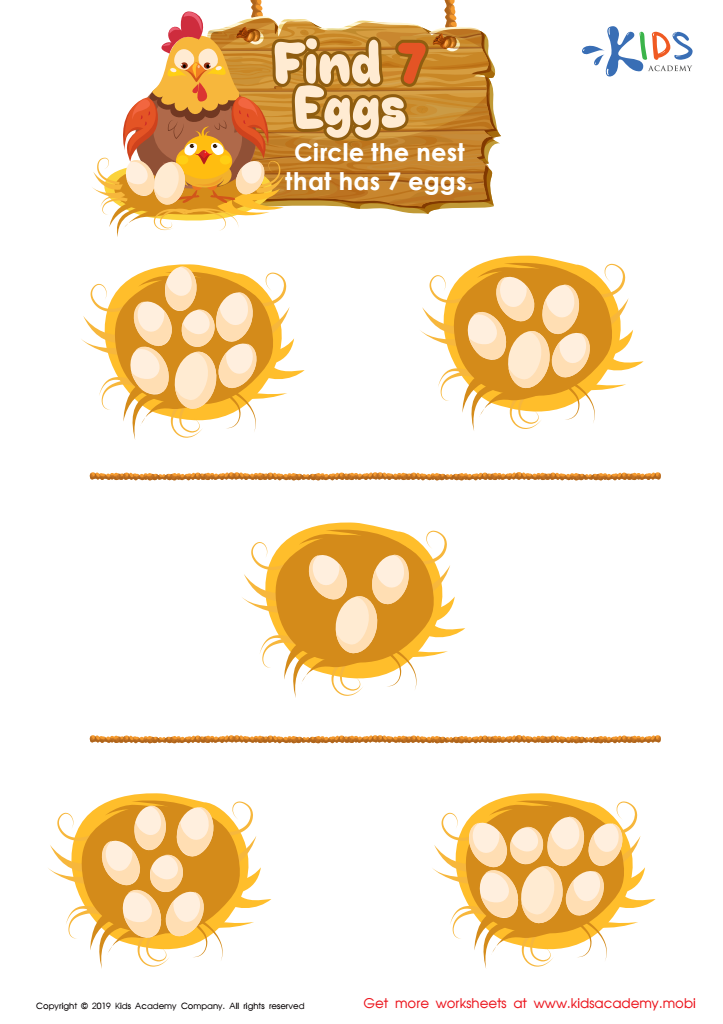

Find 7 Eggs Worksheet


More Octopus Facts Worksheet
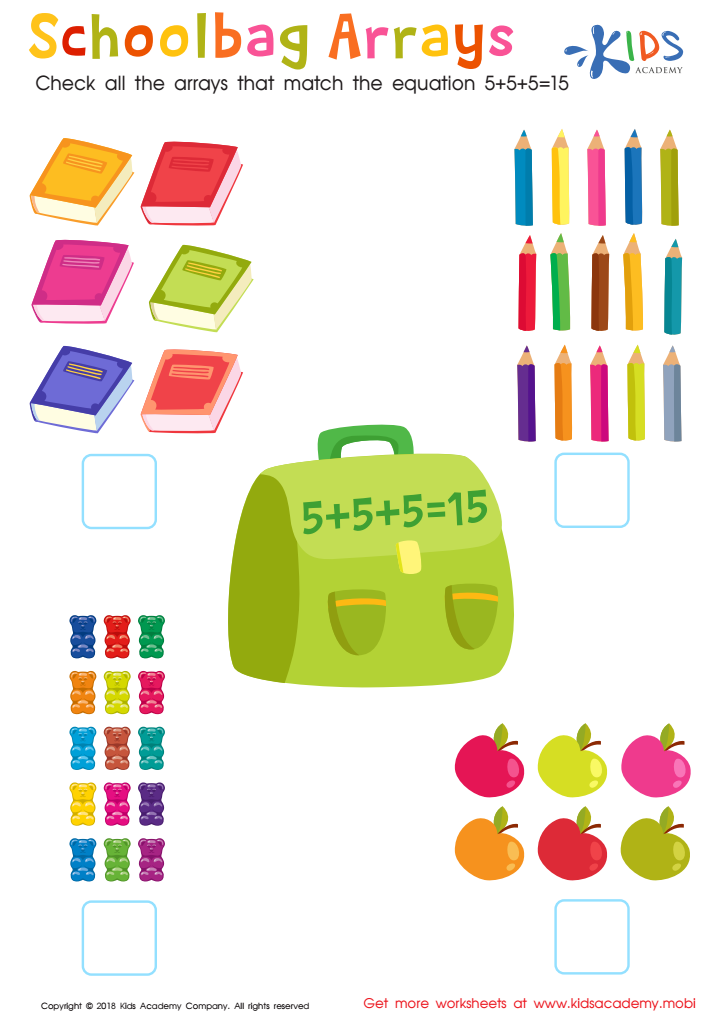

Schoolbag Arrays Worksheet
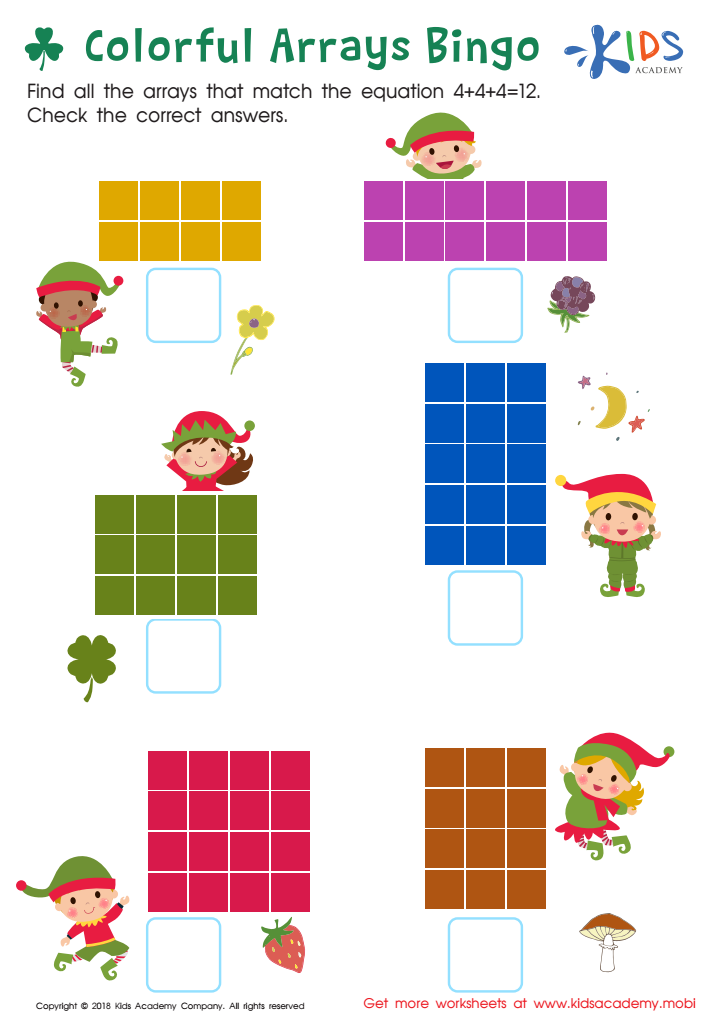

Colorful Arrays Bingo Worksheet


Baby Pandas Worksheet

Letter R Coloring Sheet
Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills for children aged 4-7 as these skills are essential for everyday activities and future academic success. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are crucial for tasks such as writing, buttoning clothes, and using utensils. When children can perform these activities effectively, they develop a sense of independence and confidence.
At this age, fine motor skills also lay the foundation for more complex tasks, such as drawing, which enhances creativity, and holding a pencil correctly, which is vital for learning how to write. Strong fine motor skills can improve hand-eye coordination, which is important not just for writing but for other school-related activities, including using a computer mouse and participating in art and craft projects.
Moreover, the development of fine motor skills can impact cognitive development. Engaging in tasks that require precise hand movements can improve attention to detail and problem-solving abilities. Consequently, supporting fine motor skill development can lead to better academic performance and a smoother transition to more demanding school tasks.
In summary, fostering fine motor skills in children aged 4-7 provides them with the necessary tools to excel both academically and in everyday life, promoting overall development and self-sufficiency.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















