Fine Motor Skills Worksheets for Ages 4-8 - Page 4
401 filtered results
-
From - To


Little Blue Belle Worksheet


Counting Spider Eyes Worksheet


Letter D and G Tracing Worksheet
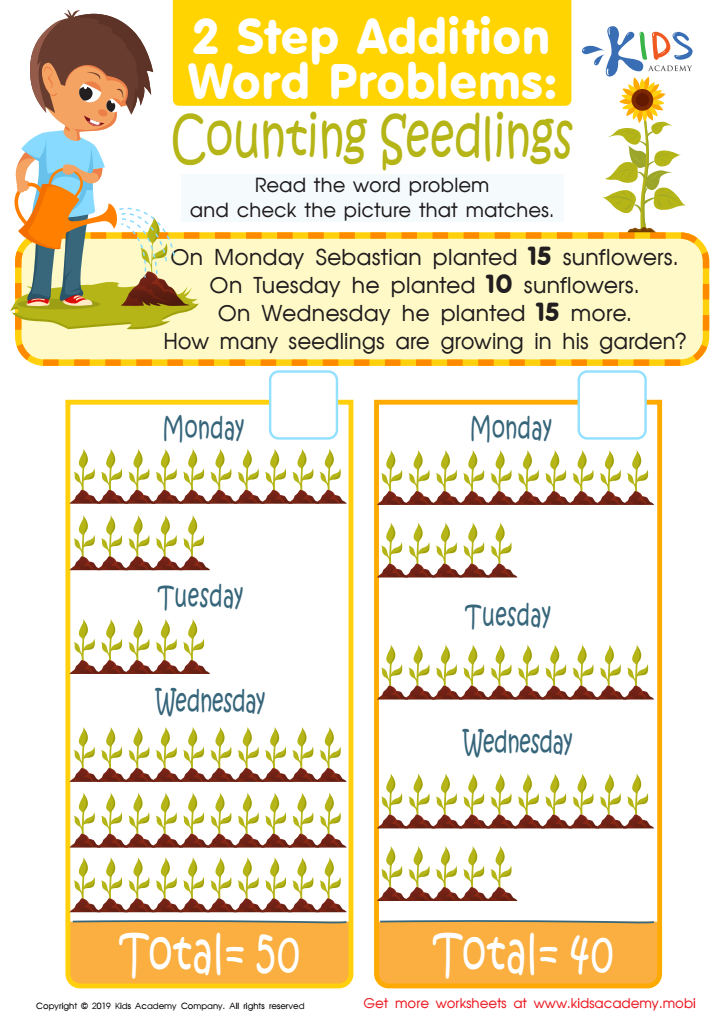

Counting Seedlings Worksheet


Cursive Numbers: 0 Worksheet
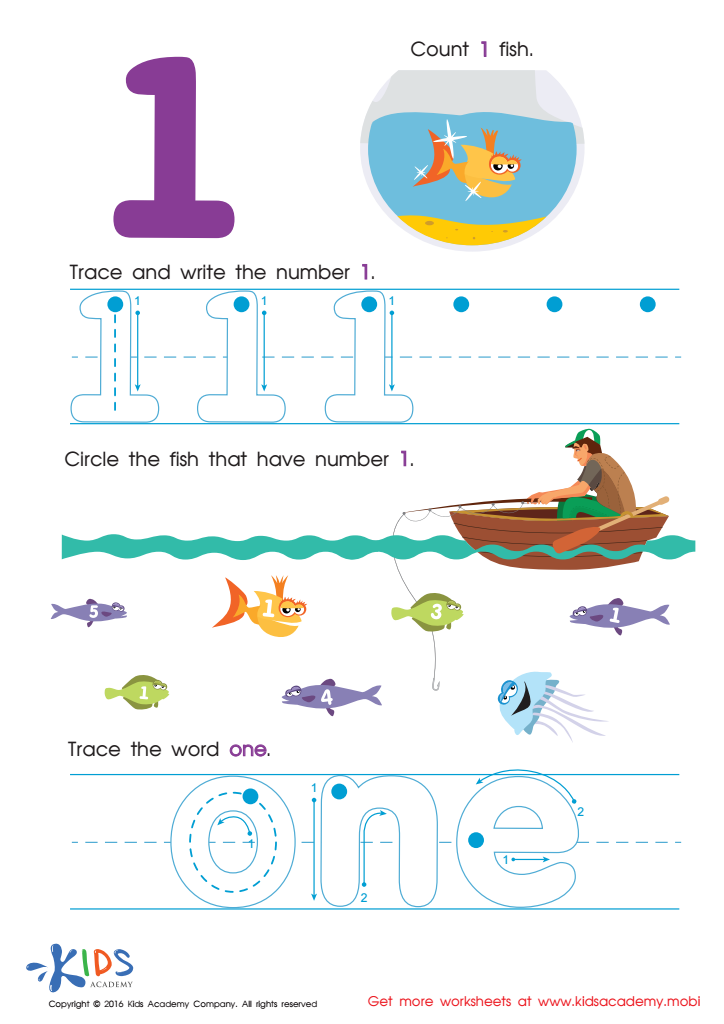

Learning to Write 1 Worksheet


Twinkle Little Star Coloring Worksheet


Humming Bird Worksheet


Ten in the Bed: Vocabulary Worksheet


Number 4 Printable


Presidential Maze Through the 5’s Worksheet


Fish Worksheet
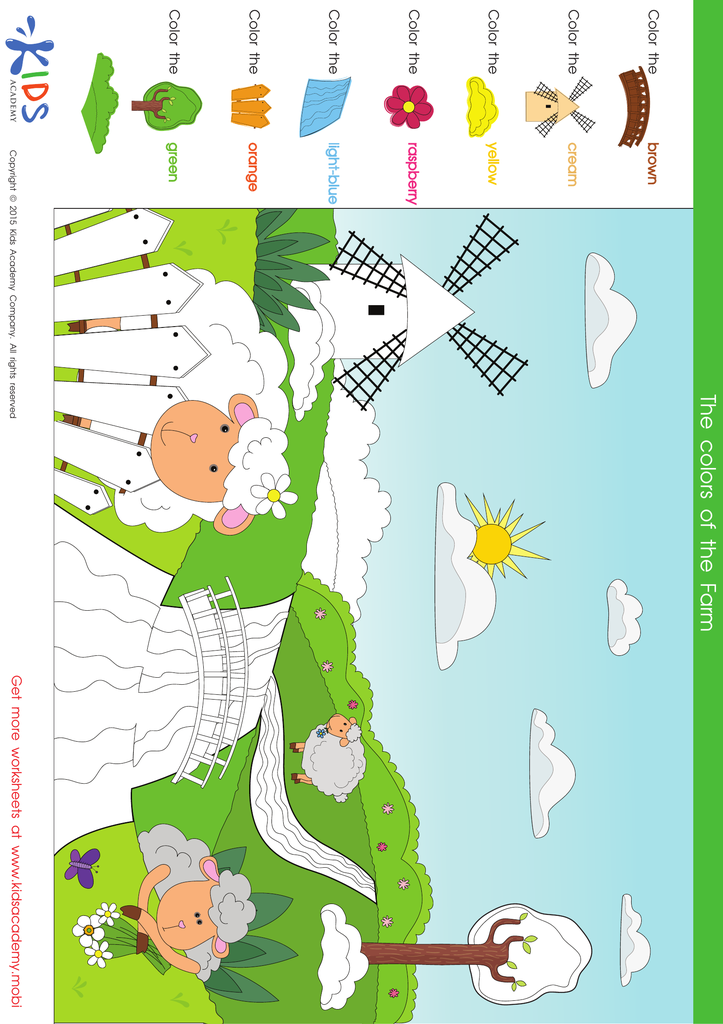

Color the Sheep in the Field Coloring Pages
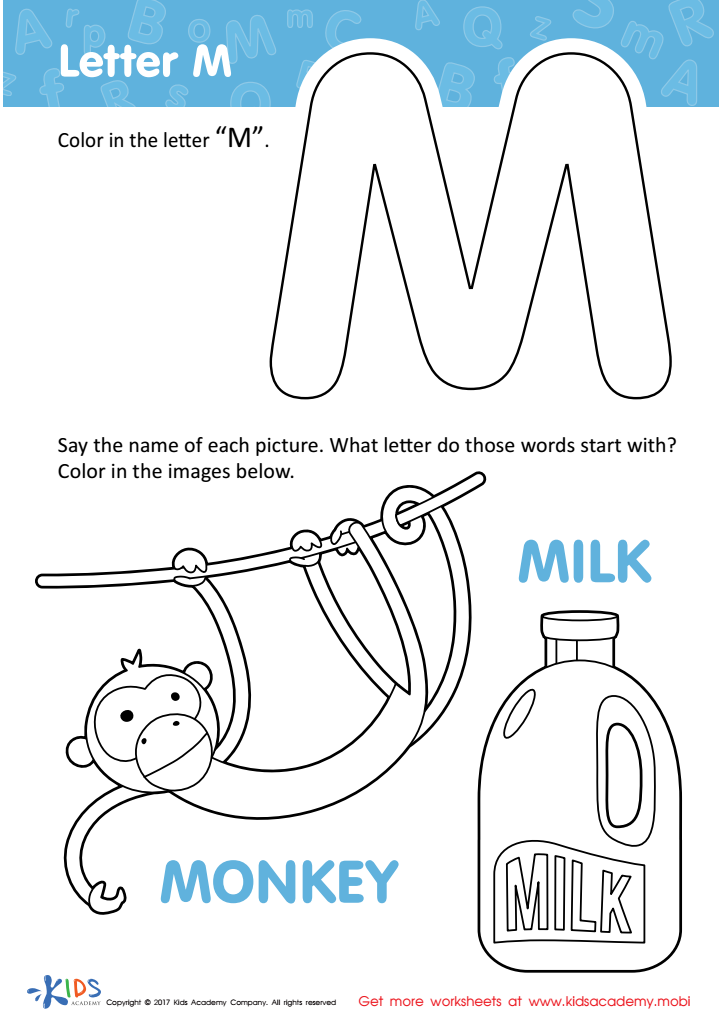

Letter M Coloring Sheet
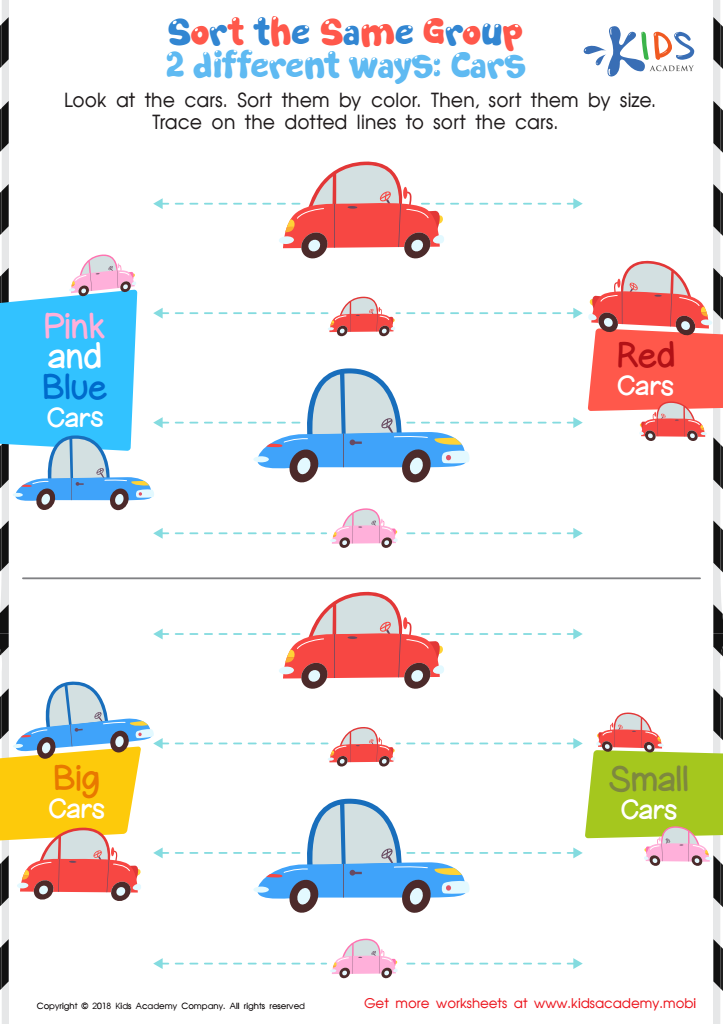


Sort the Same Group 2 Different Ways: Cars Worksheet
Developing fine motor skills in children ages 4-8 is crucial for several reasons and should be of great concern to parents and teachers. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscle movements in the hands and fingers, which are essential for everyday activities such as writing, drawing, and tying shoelaces. At this age, children are beginning to engage in more complex tasks that require precision and control.
For one, proficiency in fine motor skills directly impacts a child's ability to perform academic tasks. Writing legibly, cutting with scissors, pasting, and manipulating objects all require fine motor control, and difficulty with these tasks can lead to frustration and hinder academic progress. Improved fine motor skills also enhance hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness, which are foundational for learning math and science concepts.
Additionally, cultivating fine motor skills during early childhood supports overall cognitive development. Handling small objects or using tools like pencils and paintbrushes fosters problem-solving, planning, and critical thinking skills. Furthermore, children who master these skills typically exhibit higher confidence and independence, positively impacting their self-esteem and willingness to take on new challenges.
Therefore, ensuring that children ages 4-8 engage in activities that strengthen their fine motor skills is an investment in their comprehensive development, ensuring they are well-prepared for academic success and everyday life tasks.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students







.jpg)











