Observational skills development Science Worksheets for Ages 4-9
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's curiosity and analytical thinking with our Observational Skills Development Science Worksheets for Ages 4-9. Specially designed to foster early scientific inquiry, these engaging activities guide young learners through the wonders of observation. Children will practice noticing details, identifying patterns, and drawing conclusions, laying a crucial foundation for scientific exploration. Each worksheet is crafted to captivate and educate, making learning both fun and effective. Suitable for classroom or home use, these resources support hands-on learning and critical thinking. Unlock your child's potential and spark a lifelong love of discovery today!
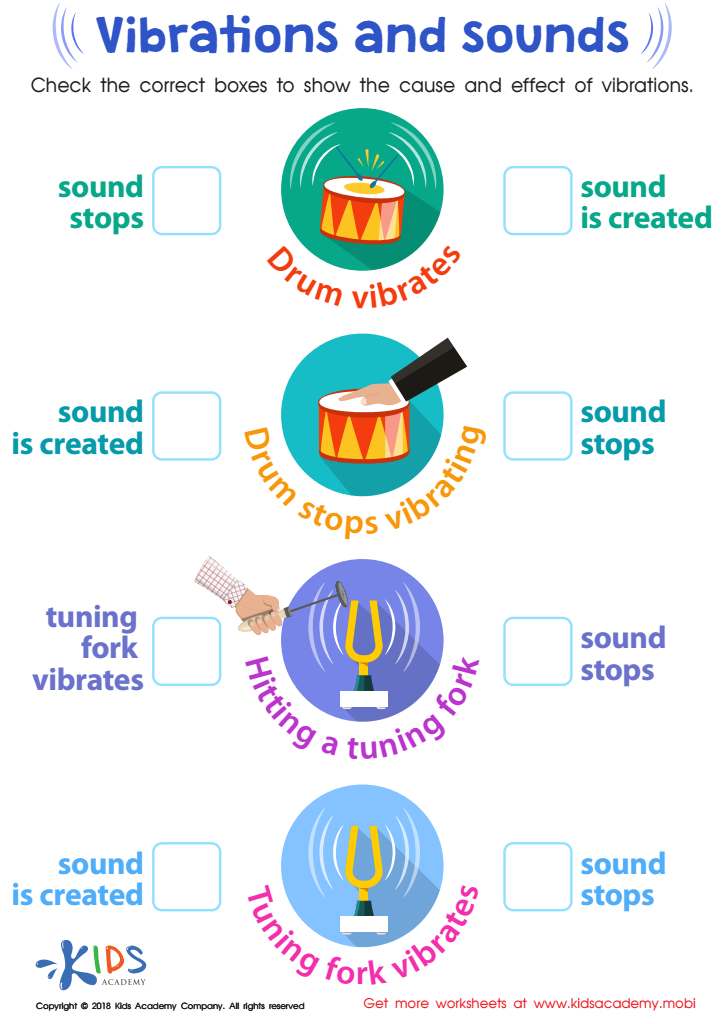

Vibrations and Sounds Worksheet
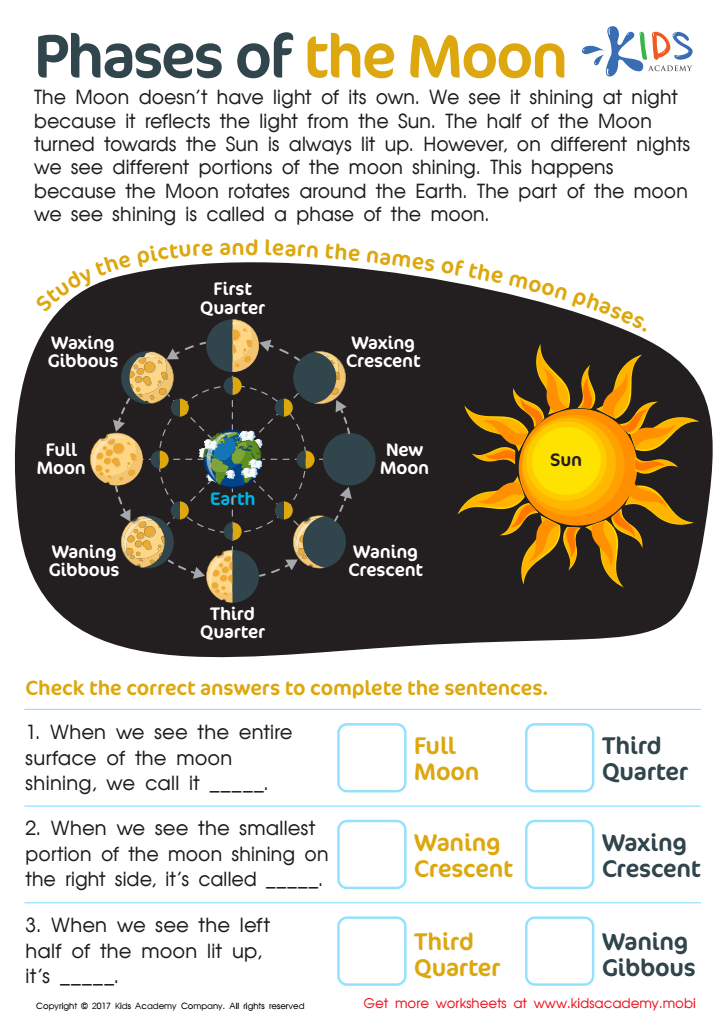

Phases of The Moon Worksheet
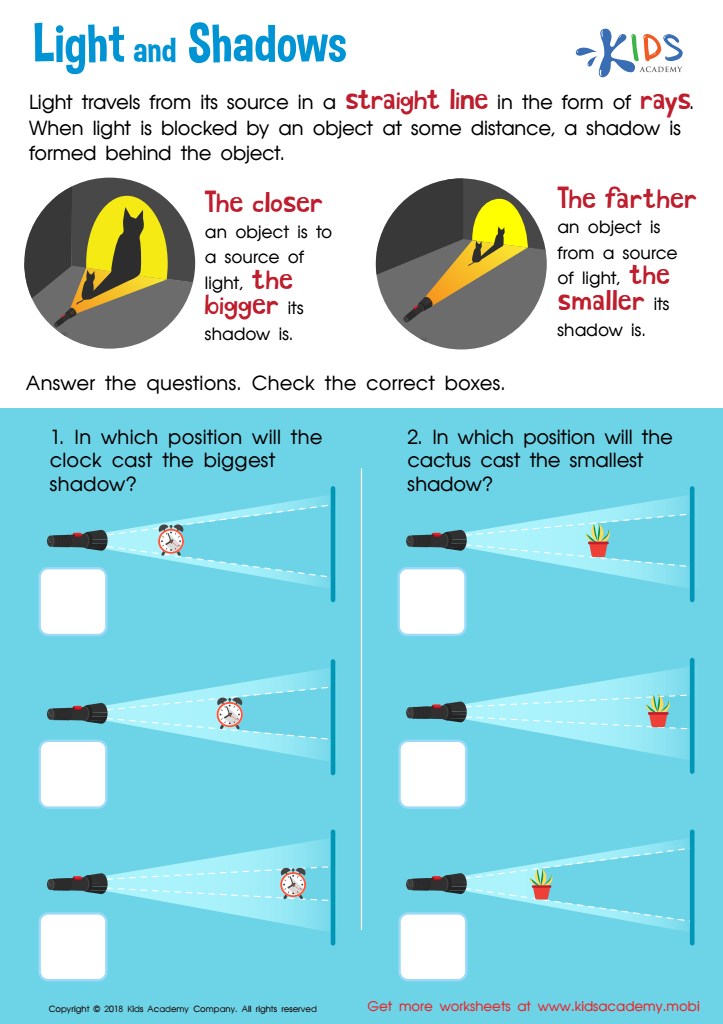

Light and Shadow Worksheet for Grade 3
Observational skills are fundamental for the cognitive and perceptual development of children, especially between the ages of 4 and 9. During this critical phase, fostering these skills in the context of science education can yield long-lasting benefits.
Firstly, observational skills enhance vigilance and attention to detail, which are foundational for academic success. By carefully observing, children become more mindful and attentive, improving their ability to grasp and retain new information across various subjects.
Secondly, developing observational skills in a science curriculum encourages critical thinking and curiosity. Children learn to ask questions, seek evidence, and make connections between observations and conclusions, thereby cultivating a scientific mindset. These habits foster an inquiry-based approach to learning that can extend beyond science to everyday life decisions.
Moreover, these skills promote language development and communication. Describing what they observe in precise terms helps children build a rich vocabulary and improves their ability to articulate thoughts clearly, both verbally and in writing.
Parents and teachers play an integral role by providing a stimulating environment with diverse and engaging observational activities. Nature walks, simple experiments, and guided curiosity sessions can transform everyday experiences into powerful learning opportunities.
In essence, prioritizing observational skills in young children lays a robust foundation for intellectual growth, problem-solving abilities, and lifelong learning.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students















