Fine Motor Skills Reading Worksheets for Ages 5-7 - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To


Monster's Face Coloring Worksheet


The Bingo Song: Coloring The Farmer Worksheet


How to Draw a Smiley Face Worksheet
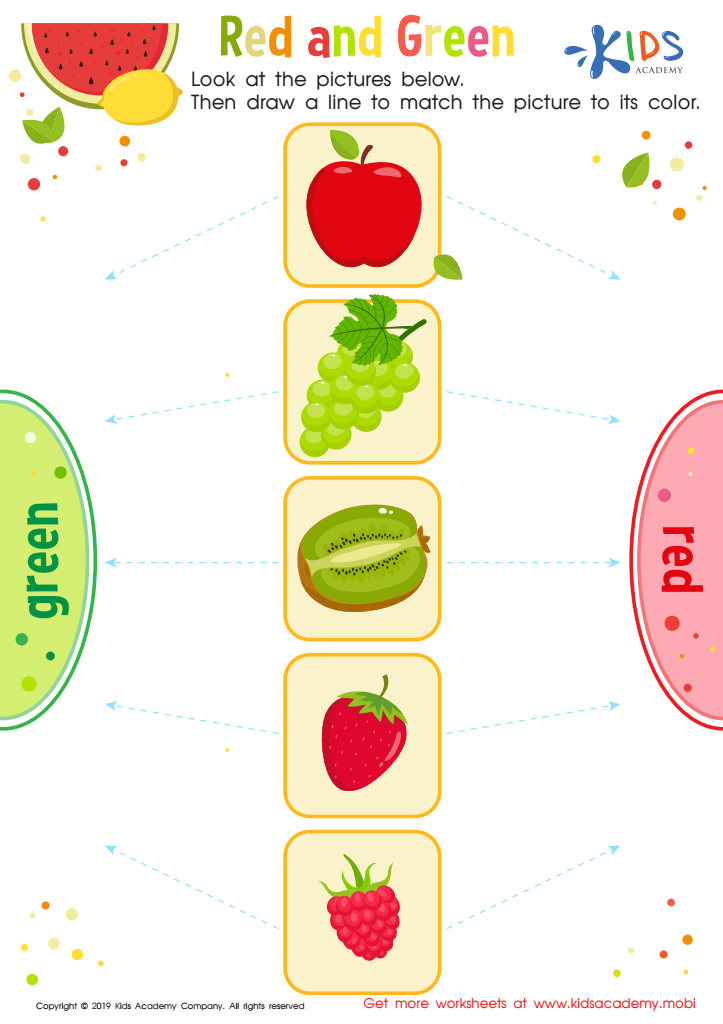

Red and Green Worksheet


Happy Family Coloring Worksheet


Bee Rhyming Words Worksheet


Baby, Boat, Bird Worksheet Sight Words Worksheet


How to Draw House Worksheet


White and Pink Coloring Fun Worksheet
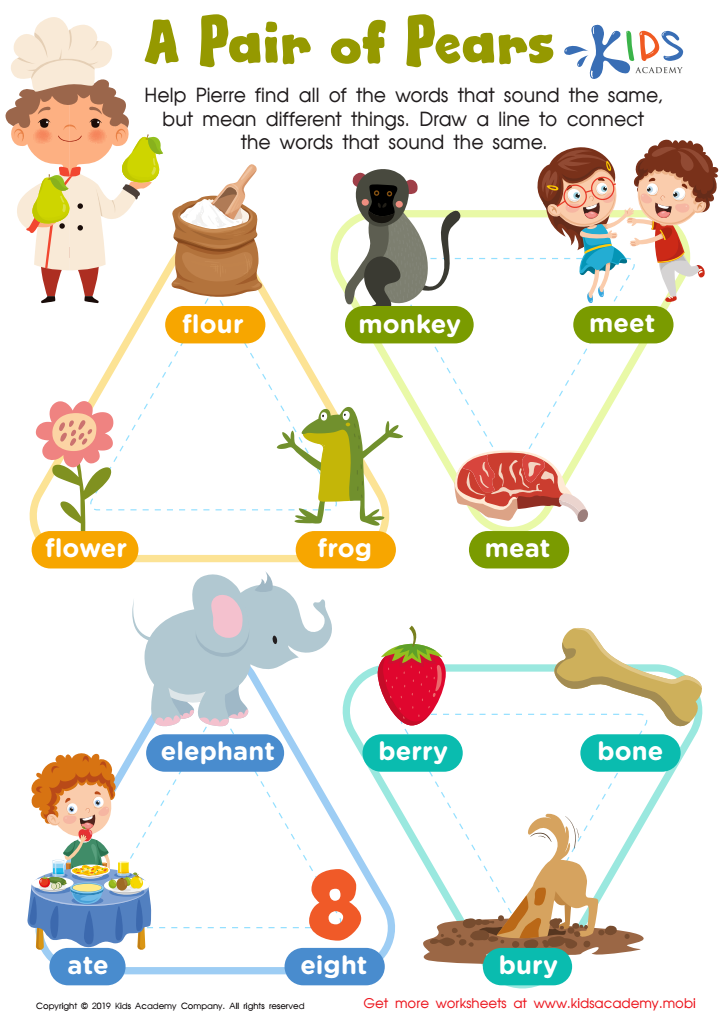

Pair Pears Worksheet
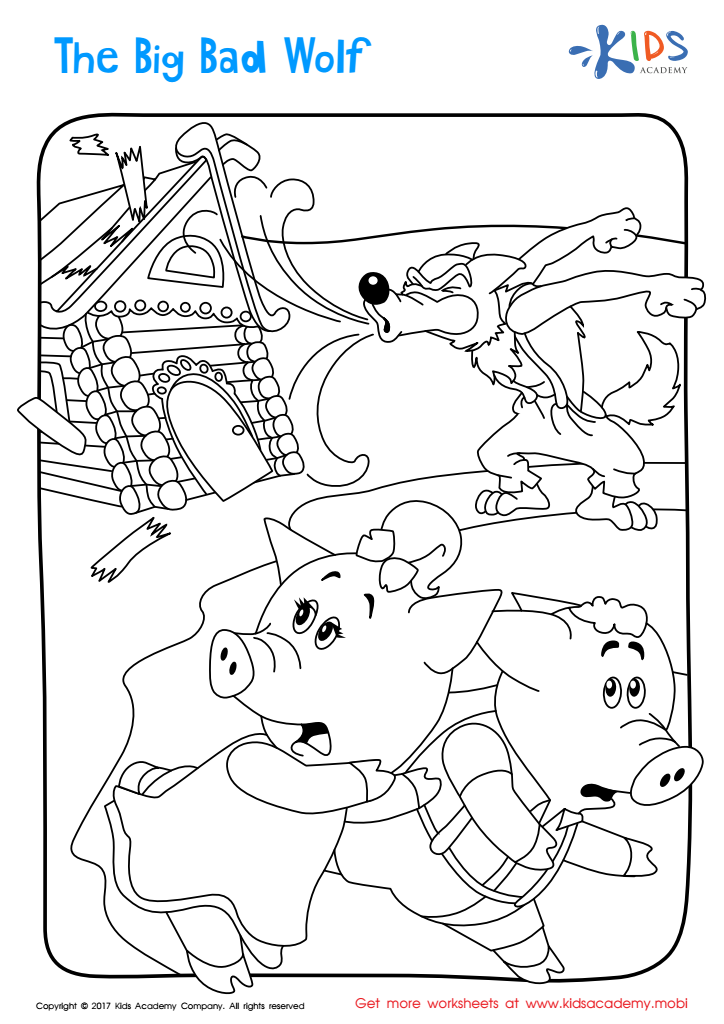

Big Bad Wolf Printable Coloring Page


The Bingo Song: Coloring The Dog Worksheet


Pen Rhyming Words Worksheet


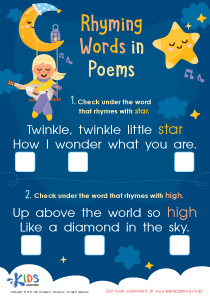
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star – Coloring by Numbers


Wheels on the Bus – Coloring by Numbers


Hickory Dickory Dock – Coloring by Numbers
Fine motor skills refer to the coordination of small muscles in movements—usually involving the synchronisation of hands and fingers—with the eyes. For children aged 5-7, developing these skills is foundational not only for their academic success but also for everyday functioning. Strong fine motor skills assist children in performing tasks such as writing, cutting with scissors, and assembling small objects, all of which are essential in a classroom setting.
Reading fine motor skills prepares students for writing, as they require hand-eye coordination, finger control, and dexterity – all needed for gripping a pencil and forming letters precisely. Equally important is the ability to turn pages, point to text, and follow along in reading activities. By practising these skills, children become more independent and gain confidence in their abilities, fostering a positive attitude toward learning.
Furthermore, engaging children in fine motor activities like tracing shapes, squeezing clay, or using tweezers can also improve concentration and cognitive development. These activities often require focus and problem-solving, thereby nurturing other aspects of their intellectual growth. Consequently, as caregivers and educators, paying attention to the development of fine motor skills is integral to supporting children's comprehensive educational journey and day-to-day self-management skills.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students