Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 2
96 filtered results
-
From - To


Letter U Coloring Sheet


Italian Word Tracing: Ciao Worksheet


Yellow Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet

Letter C Tracing Page

Letter S Coloring Sheet


English Word Tracing: Hello Worksheet


Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


Letter G Tracing Page


The Presidential Symbol Worksheet


Pink Tracing Color Words Worksheet
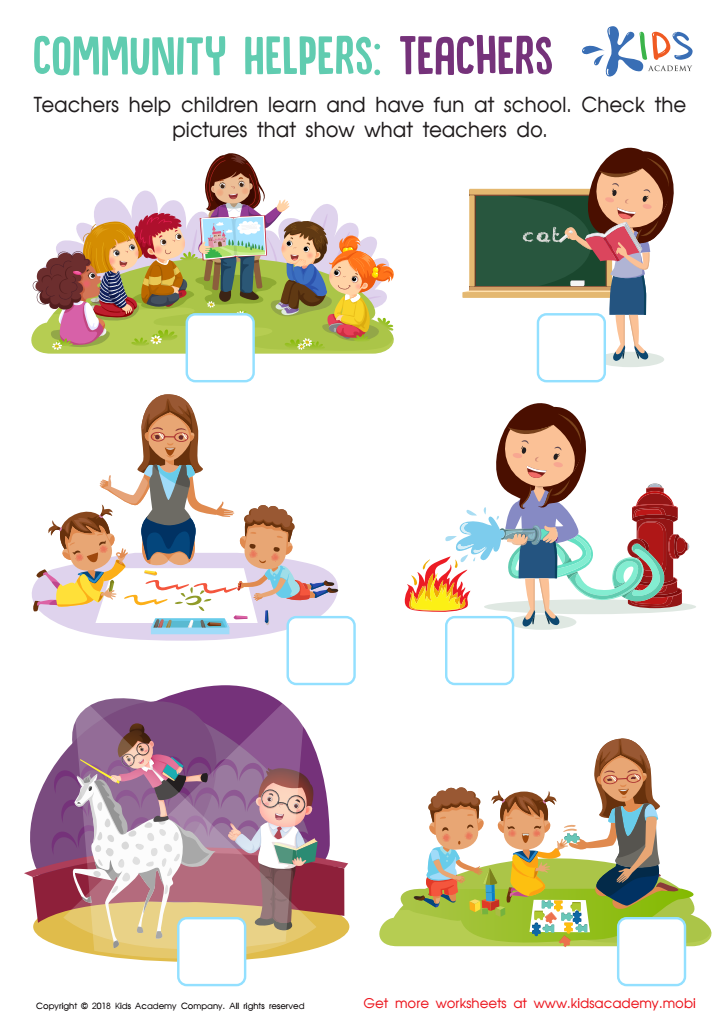


Teachers Community Helpers Worksheet

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable

Letter D Coloring Sheet


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet


Bat Rhyming Words Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Spanish Word Tracing: Hola Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet
Handwriting practice for children aged 3-7 is crucial for several developmental reasons. At this young age, children are developing their fine motor skills, which are essential for tasks such as gripping a pencil, tying shoelaces, and buttoning clothes. Engaging in handwriting activities strengthens these skills and promotes hand-eye coordination.
Furthermore, handwriting practice supports cognitive development. When children learn to form letters and words, they’re also learning to recognize patterns and understand the basics of language, which are foundational for reading and academic success. It has also been linked to better retention of information and the development of organizational skills.
Emotionally and socially, handwriting practice can boost a child's confidence. Successfully writing their name or small words provides a sense of accomplishment. This confidence can carry over into other areas of learning and social interaction. Moreover, it encourages attention to detail and patience, fostering a growth mindset.
By integrating handwriting practice into daily routines, both parents and teachers can give children a significant head start in both their academic journey and personal skill development, ensuring a solid foundation for future learning. Activities like tracing, drawing shapes, and writing letters can make the process engaging and enjoyable.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students