Handwriting practice Worksheets for Ages 4-5 - Page 2
83 filtered results
-
From - To


Lowercase Letters y z Worksheet

Letter C Tracing Page

Letter S Coloring Sheet


Uppercase Letters G, H, and I Worksheet


Letter G Tracing Page


Pink Tracing Color Words Worksheet
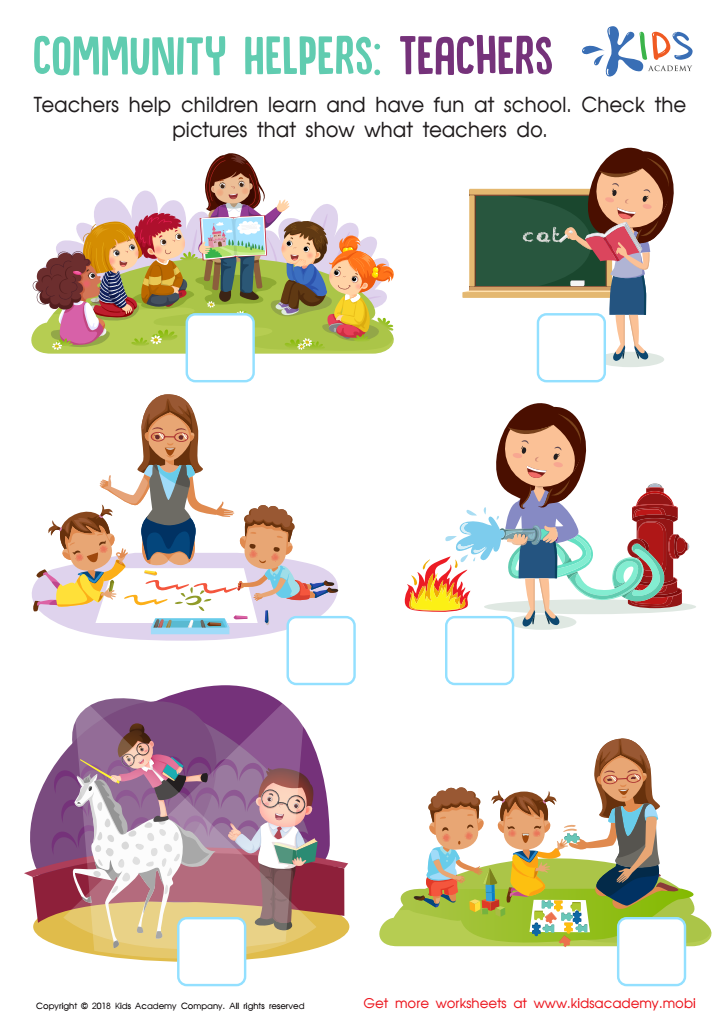


Teachers Community Helpers Worksheet

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable

Letter D Coloring Sheet


Letter Y Tracing Page


Letter E Tracing Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet


Letters X and Q Tracing Worksheet


Bat Rhyming Words Worksheet


Letter W Coloring Sheet


Spanish Word Tracing: Hola Worksheet


Lowercase Letters m n o Worksheet


Letter O Coloring Sheet

Letter N Tracing Page


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Orange Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Lowercase Letters d e f Worksheet

Count the Carrots and Trace the Number 7 Printable
Handwriting practice for children aged 4-5 is crucial for several reasons. First, it fosters fine motor skills development, helping children gain better control over their hand movements. This is essential not just for writing, but also for everyday tasks like tying shoelaces and using utensils.
Secondly, handwriting is directly linked to literacy skills. When children engage in writing activities, they reinforce spelling and grammar, enhancing their understanding of words. The physical act of writing helps solidify letter recognition and vocabulary, laying a strong foundation for reading.
Additionally, handwriting practice promotes cognitive development. As young children form letters and shapes, they engage their brains in processing information, improving memory and concentration. This cognitive engagement can lead to better problem-solving skills and creativity.
Finally, beauty in handwriting can instill a sense of pride and self-esteem in children. Celebrating their writing accomplishments can motivate them to express themselves, fostering a love for communication that will benefit them throughout their education.
In summary, encouraging handwriting practice at an early stage helps in developing essential motor skills, literacy, cognition, and self-esteem, making it a foundational component of a child's early learning experiences.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















