Counting Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
48 filtered results
-
From - To


Count by 2's: Trains Worksheet


Skip Counting by 10 through Different Communities Worksheet
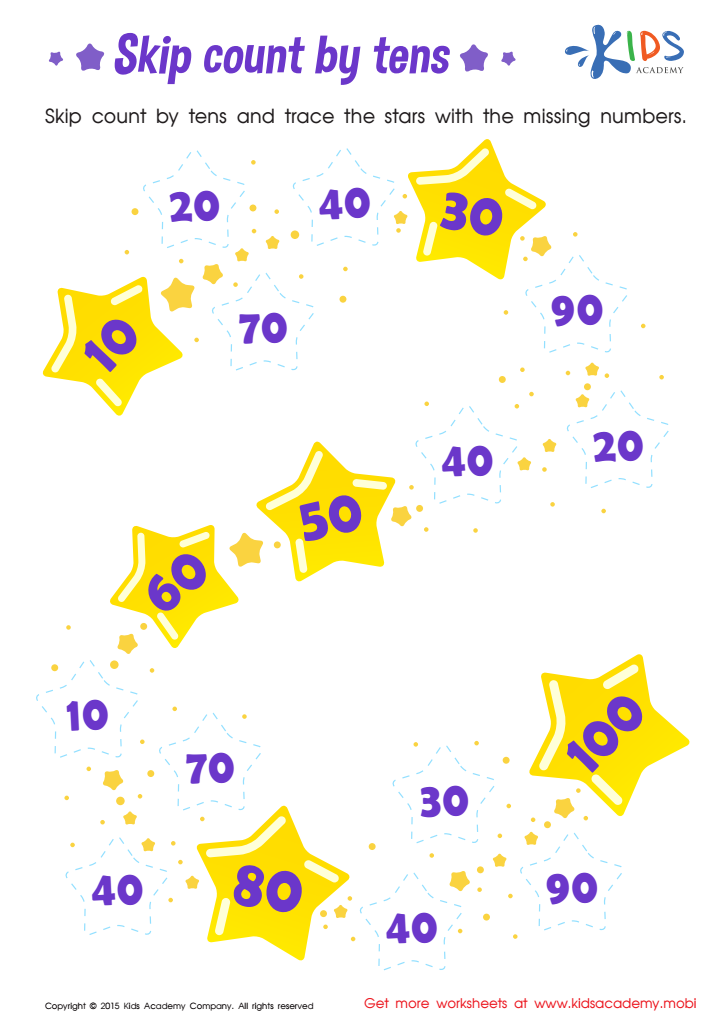


Learn dozens: Skip Count by Tens Printable
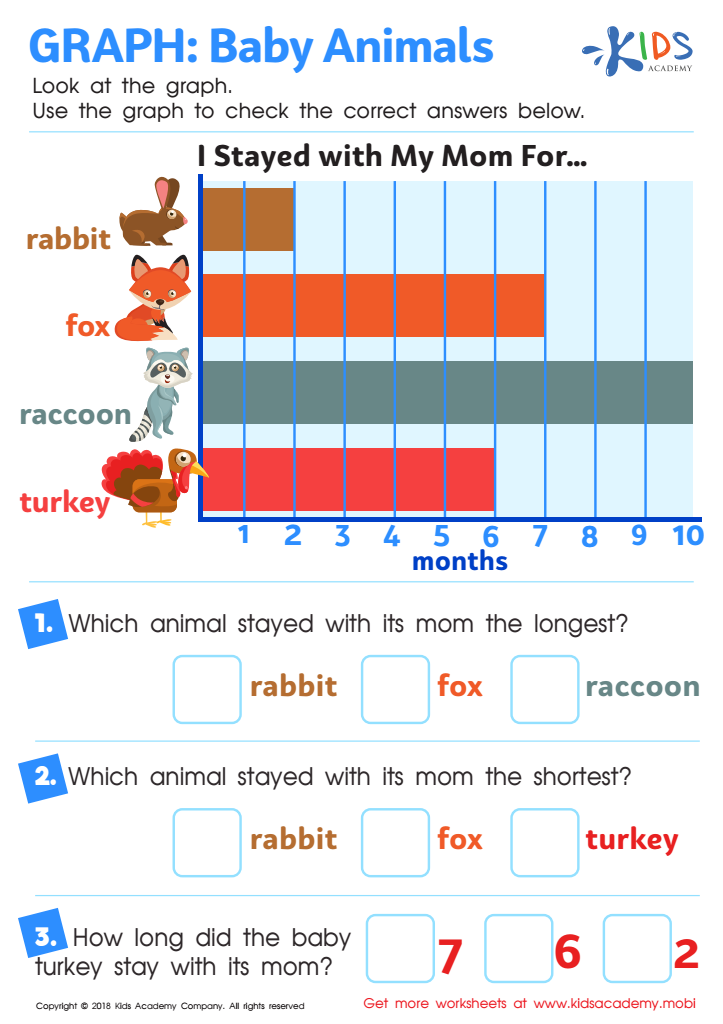

Graph: Baby Animals Worksheet
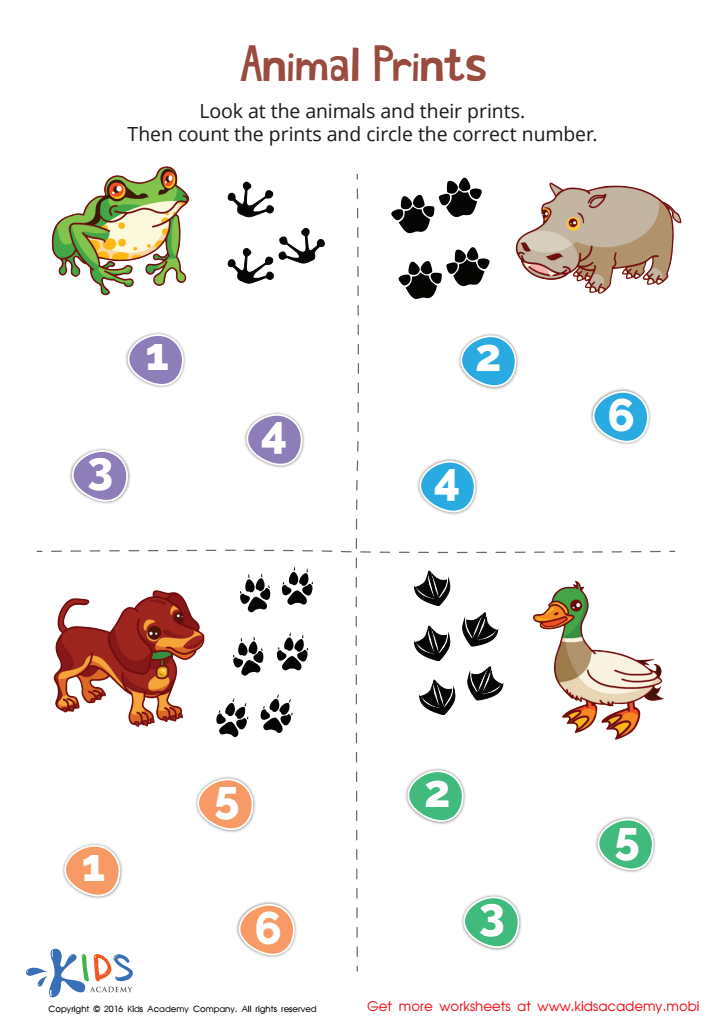


Animal Prints Match-Up Worksheet


Dot to Dot Worksheet for 3rd Grade


Counting Sea Animals Worksheet


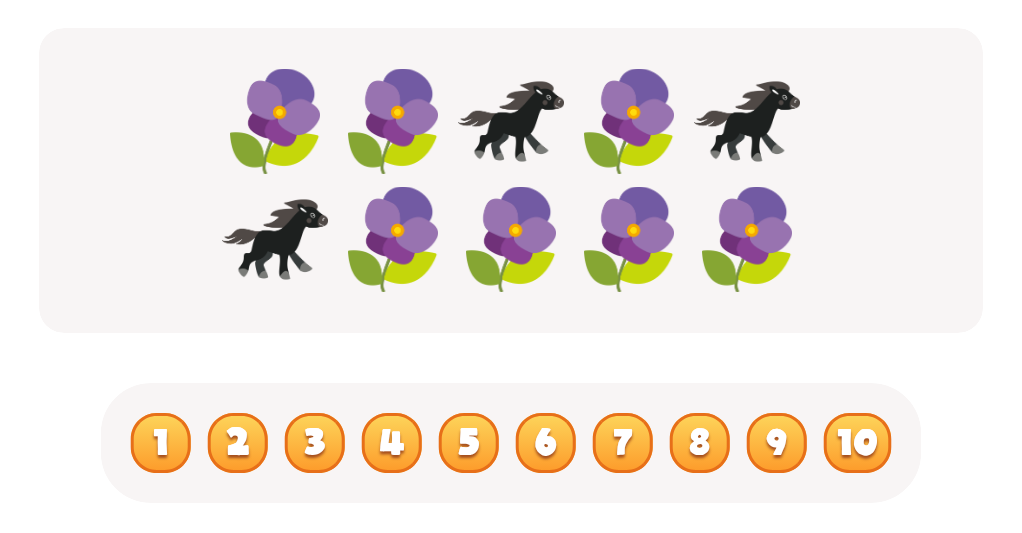
Counting Flowers Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet
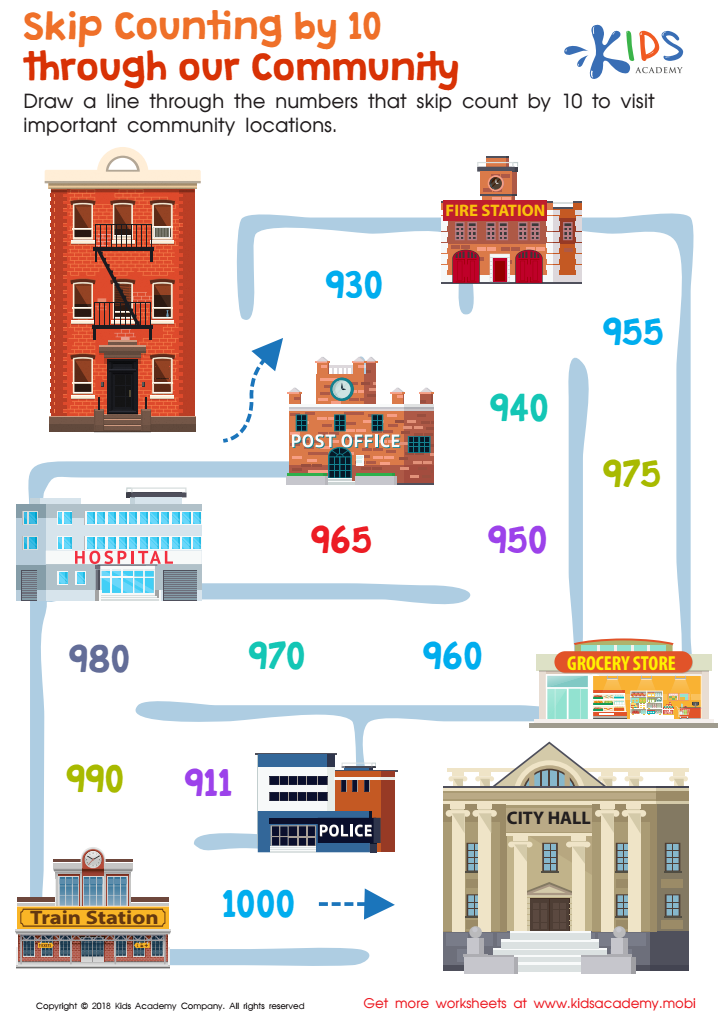

Skip Counting by 10 Through Our Community Worksheet


Magic Numbers Worksheet
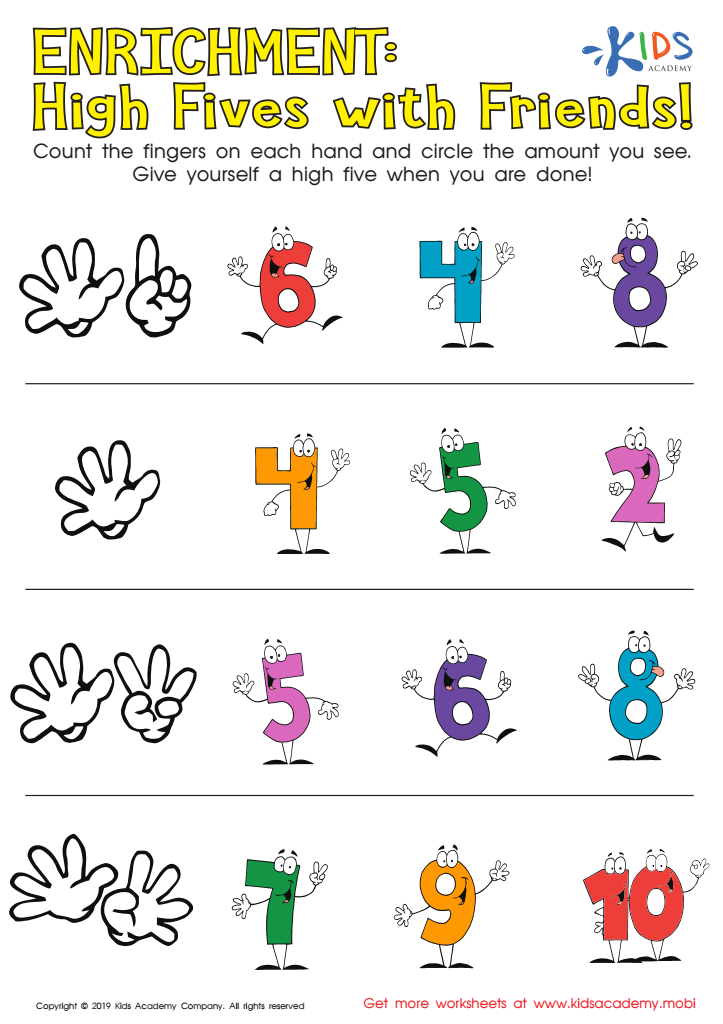

Enrichment: High Fives with Friends! Worksheet
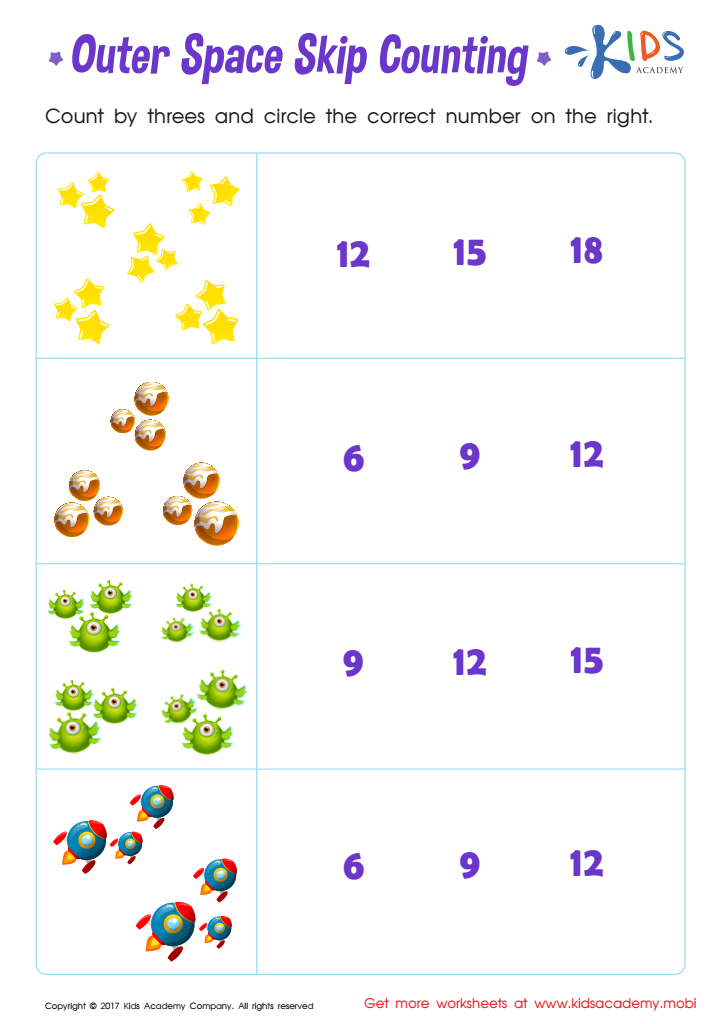

Skip Counting by 3s: Outer Space Skip Counting Printable
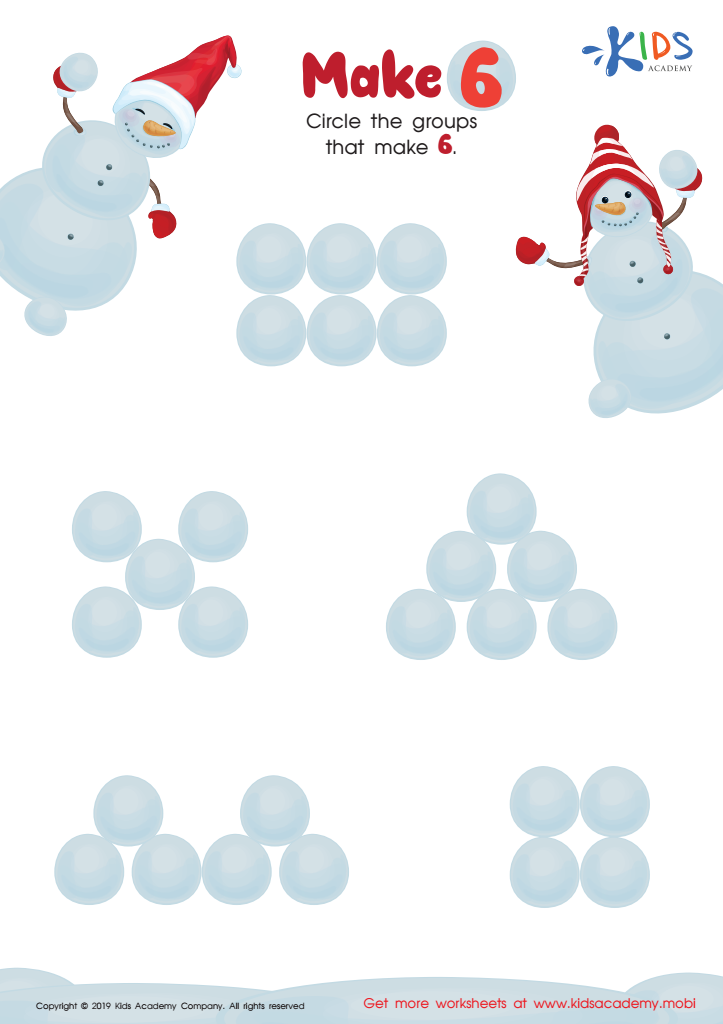

Make 6 Worksheet
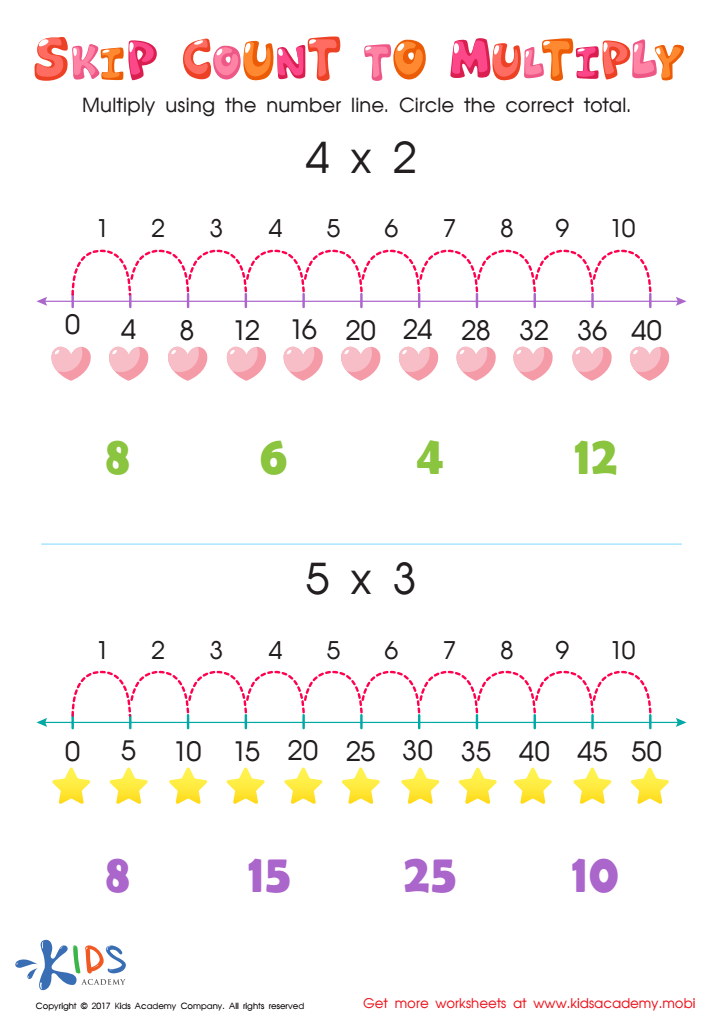

Skip Count Multiplication Worksheet

Falling Leaves Worksheet


Counting: Assessment 3 Worksheet
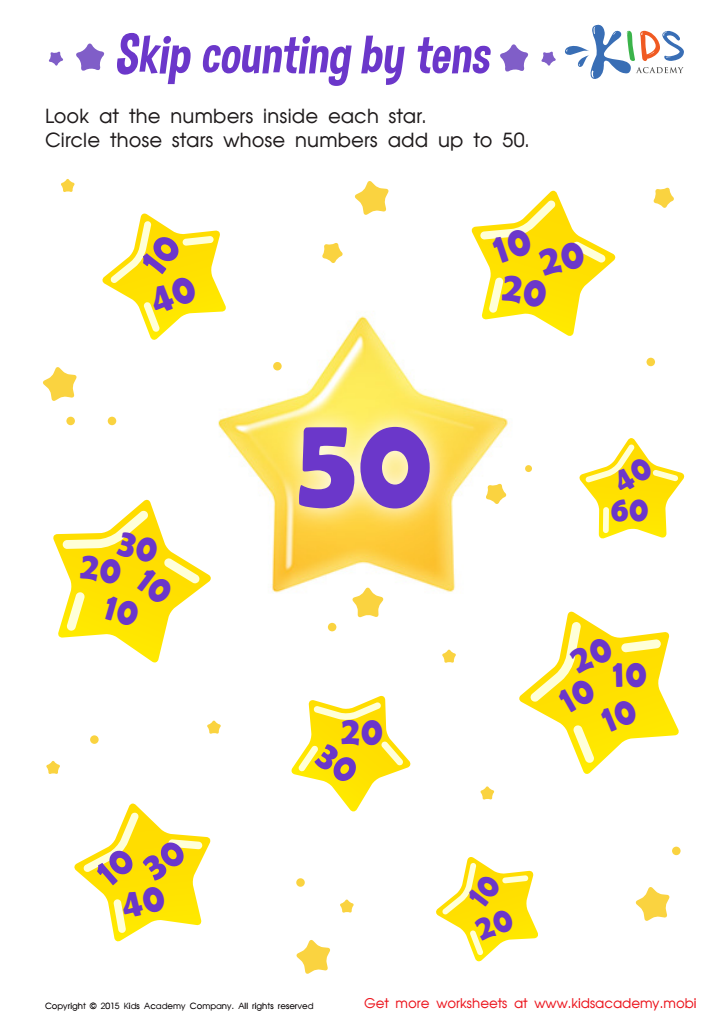


Learn Dozens: Skip Counting by Tens Printable

Learn Dozens: Counting by Tens Printable


Reptile and Amphibians Division Worksheet


Race Car Ramp Worksheet


Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet


Triceratops Counting to 9 Worksheet


One Less: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Counting is one of the foundational skills in early childhood education and is critical for children ages 3-8 for a variety of reasons. At its core, counting is the basis for developing number sense—a crucial aspect of mathematics that involves understanding numbers, knowing their relationships, and grasping their operations. For young learners, the ability to count introduces them to patterns, order, and quantification, serving as the building blocks for more complex mathematical concepts like addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
Moreover, counting fosters cognitive development by enhancing memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. When children practice counting, they also engage in logical thinking and develop an understanding of cause-and-effect relationships. This is not just limited to math; these cognitive skills are transferable to other areas of learning and daily life activities.
Socially, counting in groups or with a teacher encourages cooperative learning and verbal communication, helping children articulate their thought processes and understand others. This can boost confidence and social skills, preparing them better for school and societal interactions.
Emotionally, success in counting and other early math skills can provide positive reinforcement, fostering a sense of achievement and curiosity for learning.
Therefore, both parents and teachers should prioritize teaching counting in these formative years, as it lays the groundwork for future academic success and life skills.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students