Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-8
211 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's mathematical journey with our Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 4-8. Specially designed to bridge cognitive learning and physical coordination, these engaging worksheets not only boost math skills like counting, addition, and subtraction but also refine small muscle movements in hands and fingers. Perfect for young learners, each activity encourages precision and confidence, laying a robust foundation for future academic success. Explore a variety of fun and interactive tasks, including tracing, cutting, and drawing, tailored to develop both fine motor skills and essential math concepts in a delightful, educational manner.


Number 10 Printable
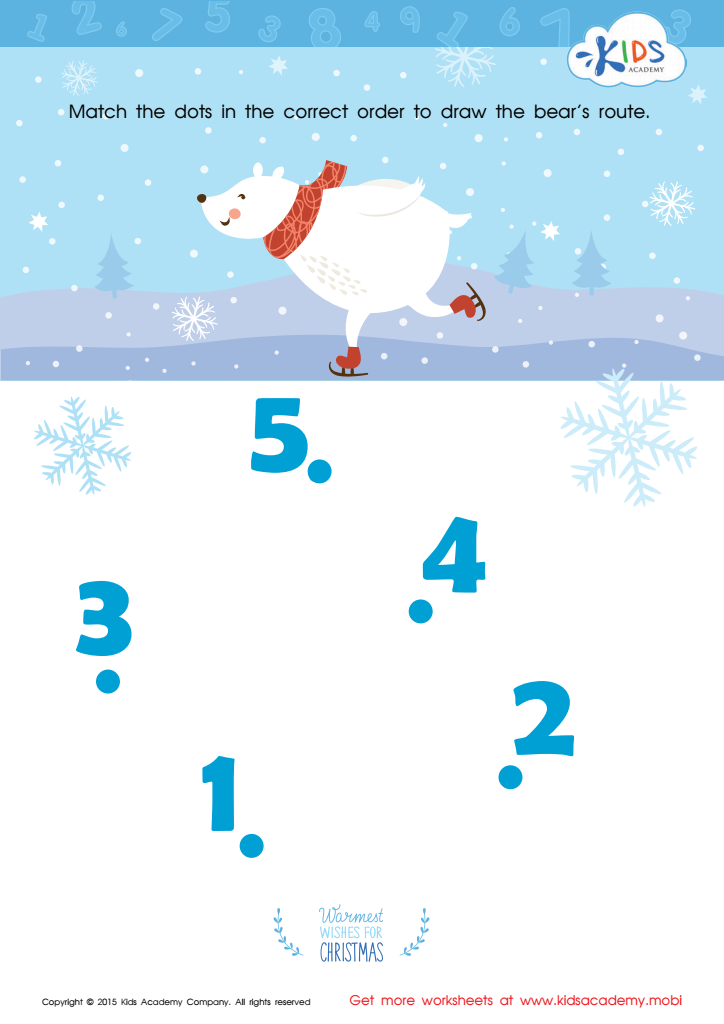


Drawing the Bear's Route by Number Worksheet

Skip Counting by 3s: Funny Aliens Printable
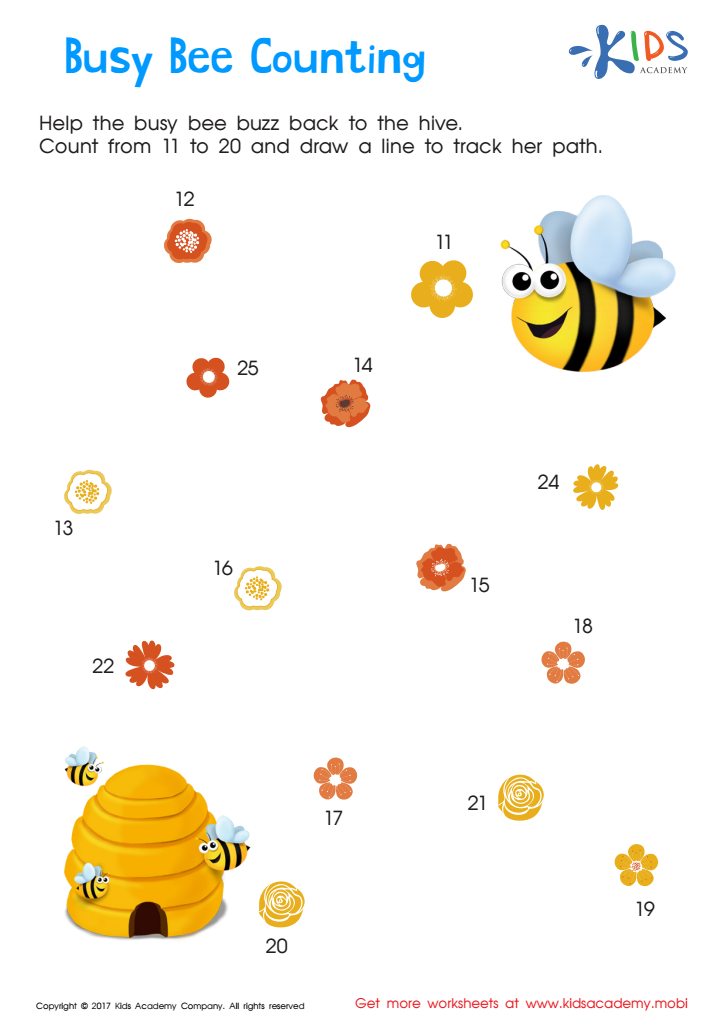


Ordering 11–20: Busy Bee Counting Worksheet
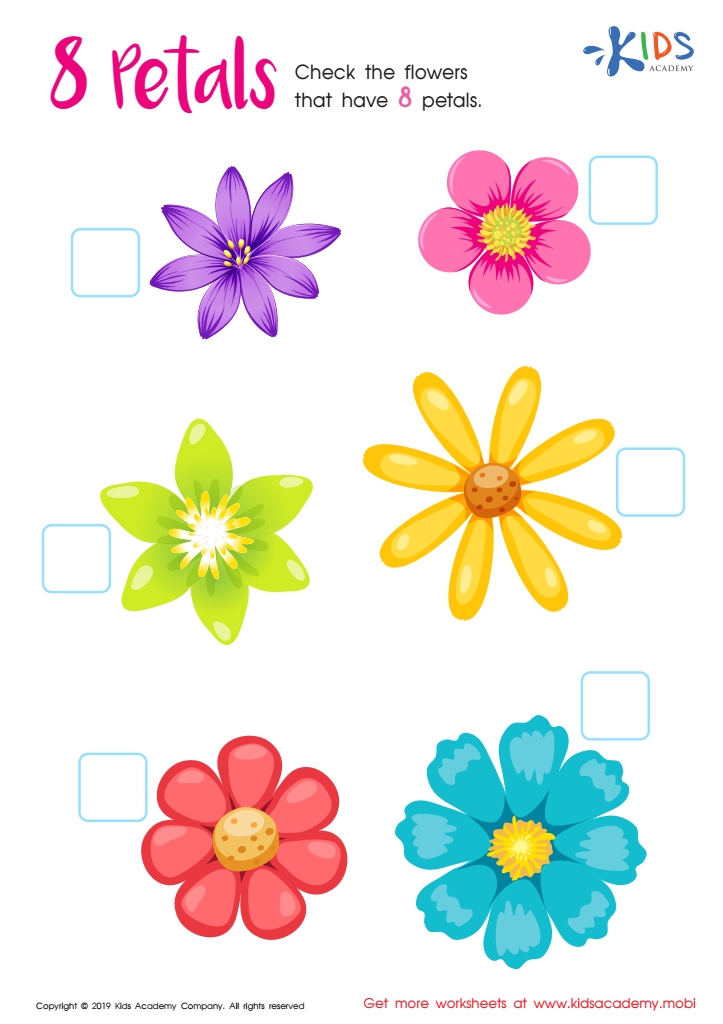


8 Petals Worksheet
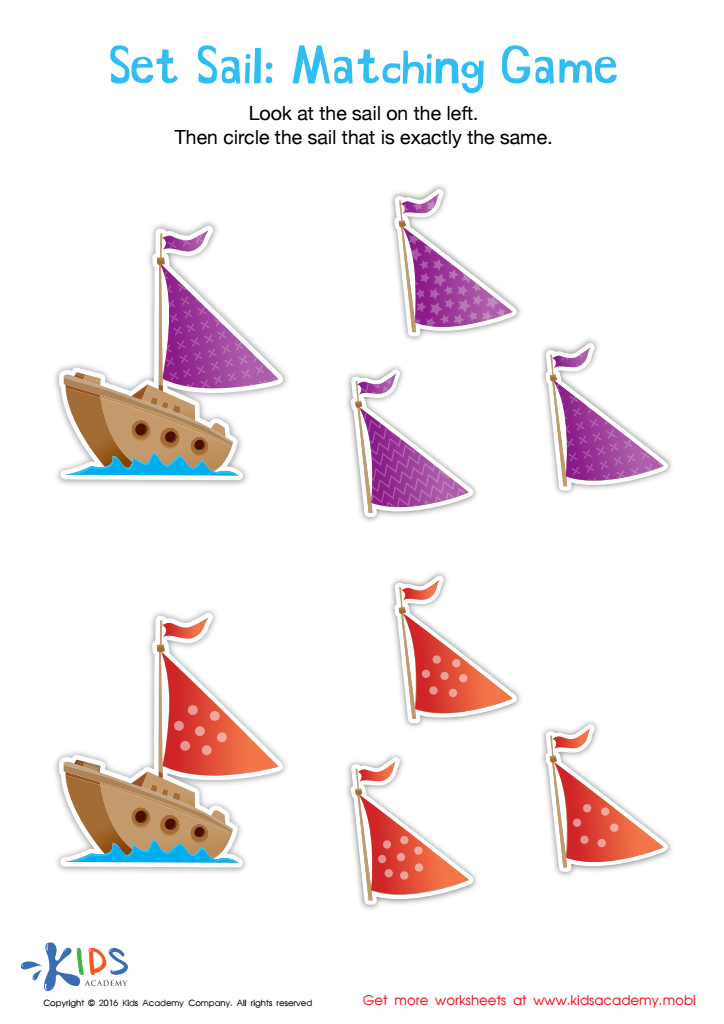


Set Sail Worksheet


Number 5 Printable

Count and Trace 7 – 10 Worksheet

Valentines Day 2 Printable


Holiday Counting Worksheet

Composing a Robot's Face of Crescents And Stars Worksheet

Matching 4 – 3 Worksheet

Matching Halves Worksheet

Practice Drawing Hexahedrons And a Rhombus Worksheet
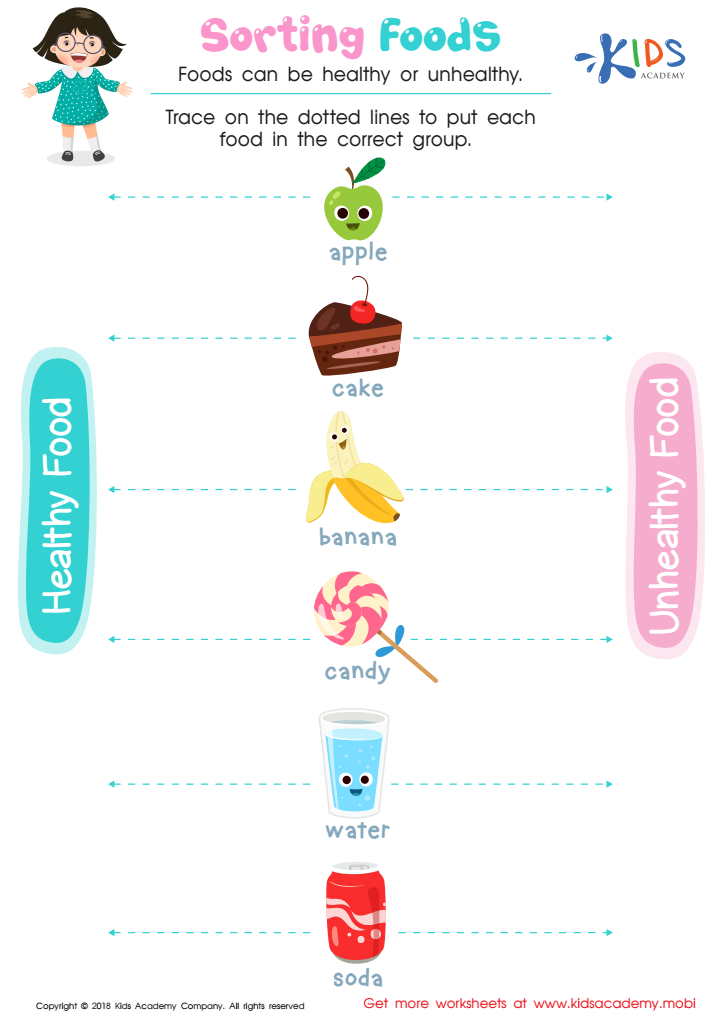

Sorting Food Worksheet


Cursive Numbers: 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 4-8 because they form the foundation for many important developmental milestones, including math skills. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, allowing children to perform precise tasks like writing, cutting, and manipulating objects. For young children, math lessons that incorporate fine motor skill activities can enhance learning outcomes in multiple ways.
First, fine motor skills enable children to effectively use tools such as pencils, scissors, and manipulatives like counting beads. These tools are often integral in teaching foundational math concepts, such as number recognition, counting, and basic arithmetic. For example, using tweezers to pick up beads and place them in a counting frame improves both number knowledge and hand-eye coordination.
Second, engaging in fine motor skill activities can boost cognitive development and problem-solving abilities. Tasks requiring precision help children develop their concentration, attention to detail, and sequential planning, all of which are important for solving math problems.
Lastly, early proficiency in fine motor skills can increase a child's confidence and independence in school. Mastery of these skills reduces frustration and encourages a positive attitude toward challenging subjects like math. Thus, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills development alongside traditional math instruction to give children a well-rounded educational foundation.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
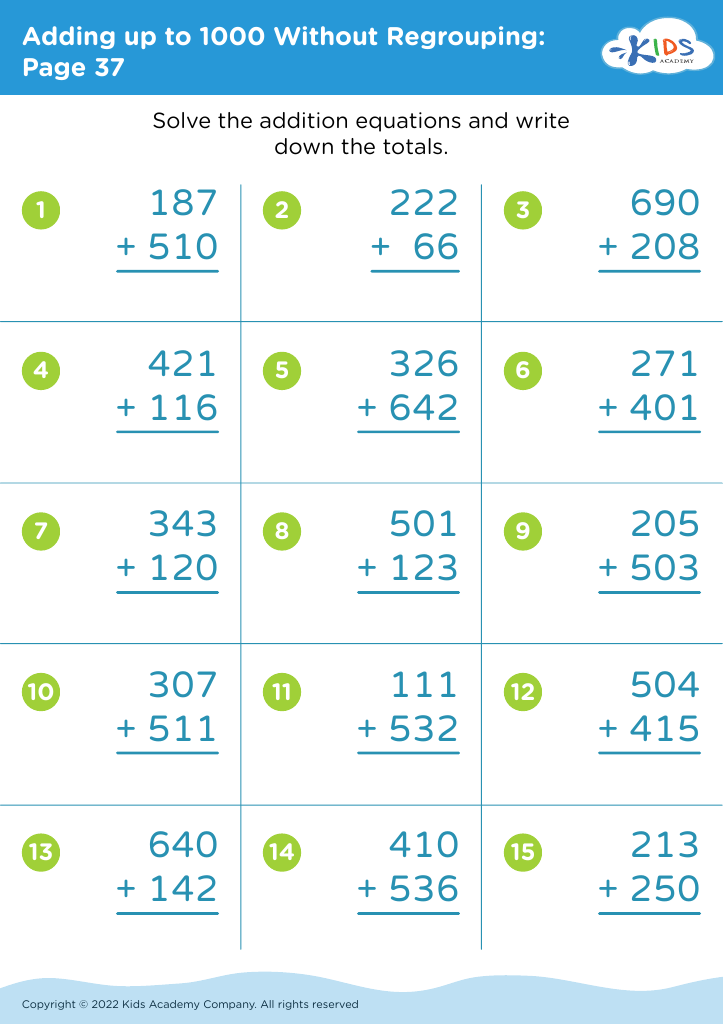
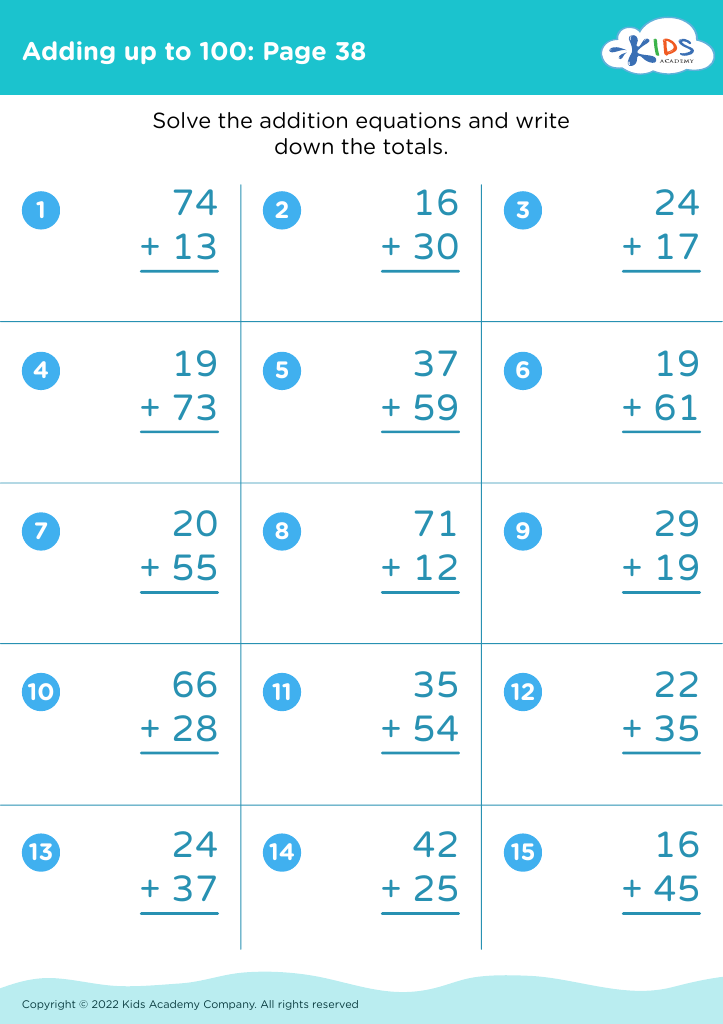

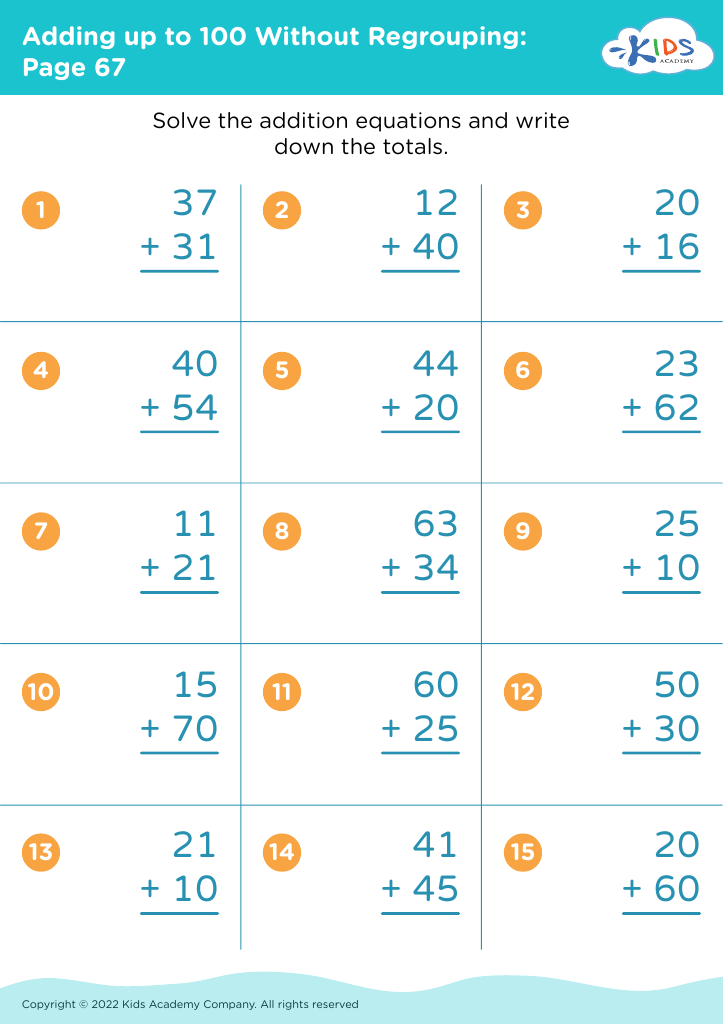





.jpg)