Problem-Solving Skills Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for 9-Year-Olds - Page 2
58 filtered results
-
From - To


Tricky Problems Worksheet: Part 2

Two-Step Hiking Problems Worksheet


Match the Word Problems Worksheet

Little Witch Problem Solving Worksheet

Two-Step Problems Worksheet


Halloween Word Problems Printable


Farm Stand Mass Worksheet


Step Subtraction Word Problems Worksheet
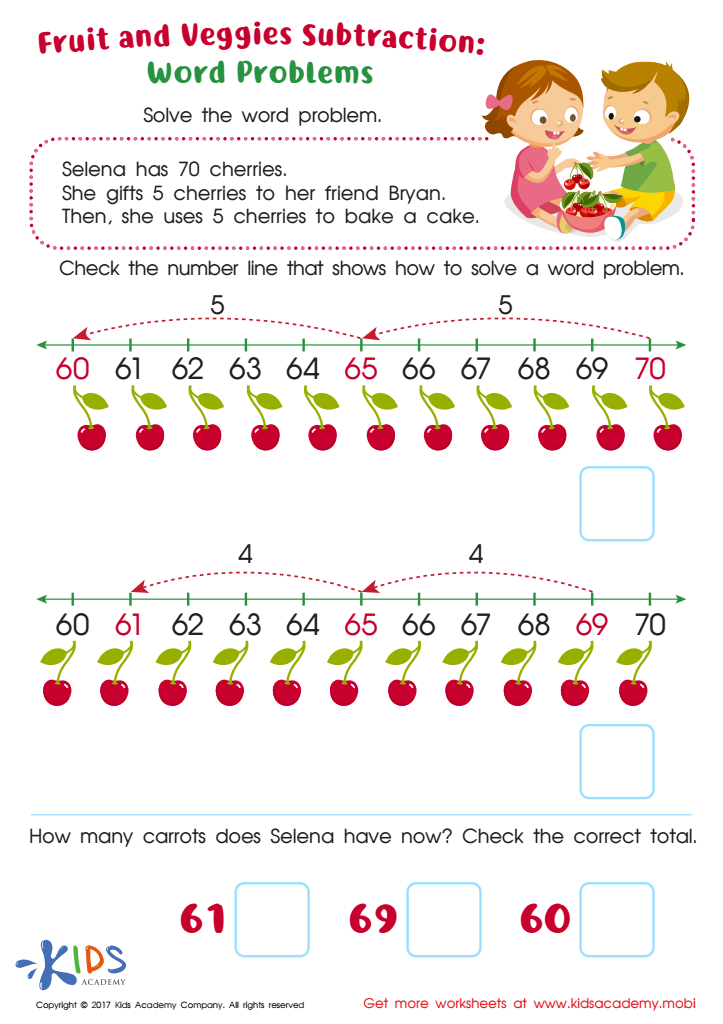

Subtraction Word Problems Free Printable


Fairytale Addition Worksheet
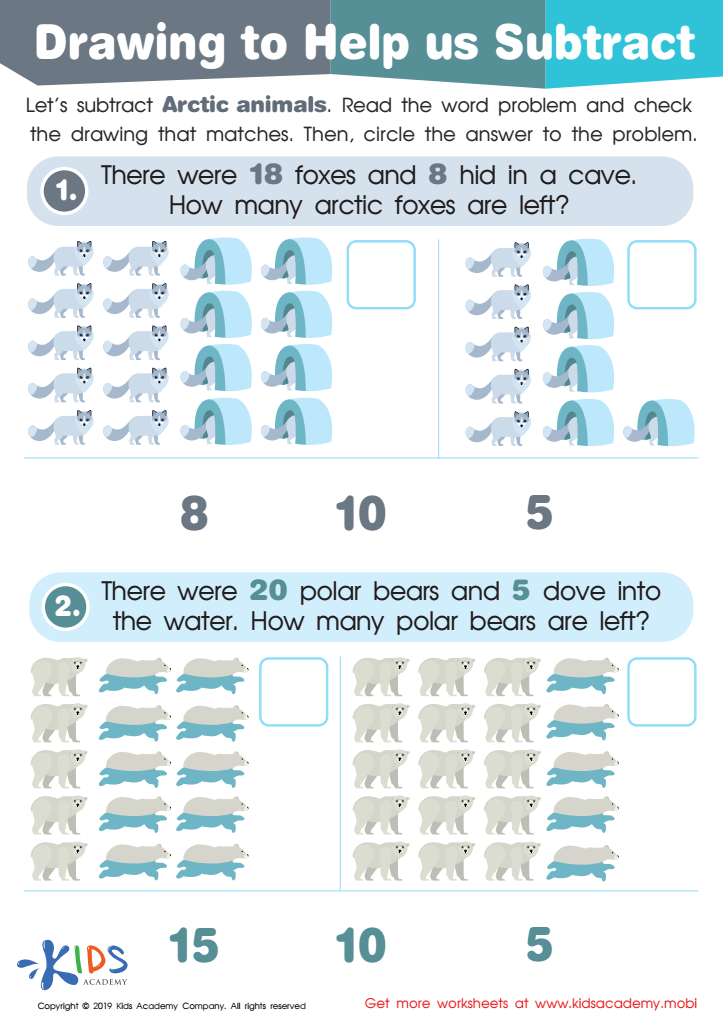

Drawing to Help Us Subtract Worksheet


Match and Solve: Cupcakes Problem Worksheet


Word Problems: Assessment 2 Worksheet


Addition and Subtraction: Word Problems Worksheet
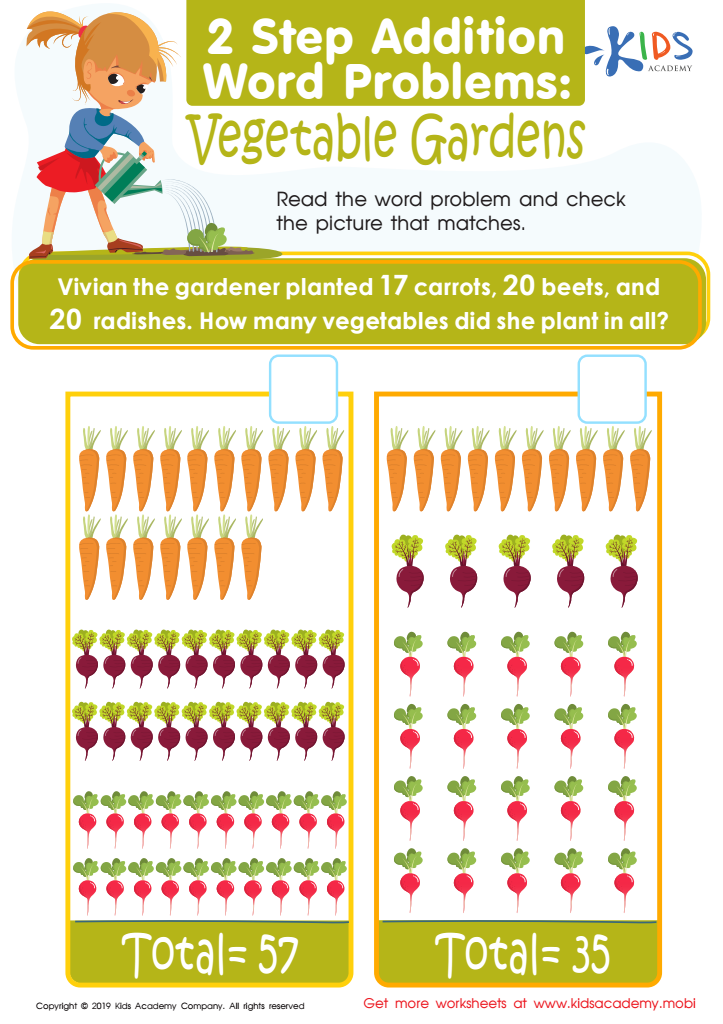

Vegetable Gardens Worksheet
At around nine years old, children are at a critical stage for developing foundational academic skills, including problem-solving abilities in addition and subtraction. Cultivating these skills is essential because they form the bedrock of future mathematical understanding and competencies. For one, strong addition and subtraction skills enable more advanced arithmetic operations, like multiplication and division, vital for higher-level math concepts encountered in later grades.
Moreover, problem-solving skills in mathematics extend beyond mere number manipulation—they foster logical thinking, pattern recognition, and systematic approaches to tackling challenges. These abilities are crucial not just in academics but also in everyday life situations, such as budgeting pocket money, understanding time management, or planning simple activities.
Parents and teachers play pivotal roles in encouraging and nurturing these skills. When educators integrate problem-solving exercises into their curricula, and when parents support these efforts at home through engaging activities and positive reinforcement, children are more likely to develop confidence in their abilities. This confidence translates to a positive attitude towards learning, reducing math anxiety and making educational experiences more enjoyable and beneficial.
Ultimately, enhancing problem-solving skills in addition and subtraction at this age crafts an essential framework that supports lifelong learning and practical life aptitude, making it a responsibility shared by both parents and educators.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students