Fine Motor Skills Normal Math Worksheets for Ages 5-8 - Page 2
43 filtered results
-
From - To


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Mary's Bag Worksheet


Three–Dimensional Shapes: Cylinder Worksheet


Counting Busy Bees Worksheet
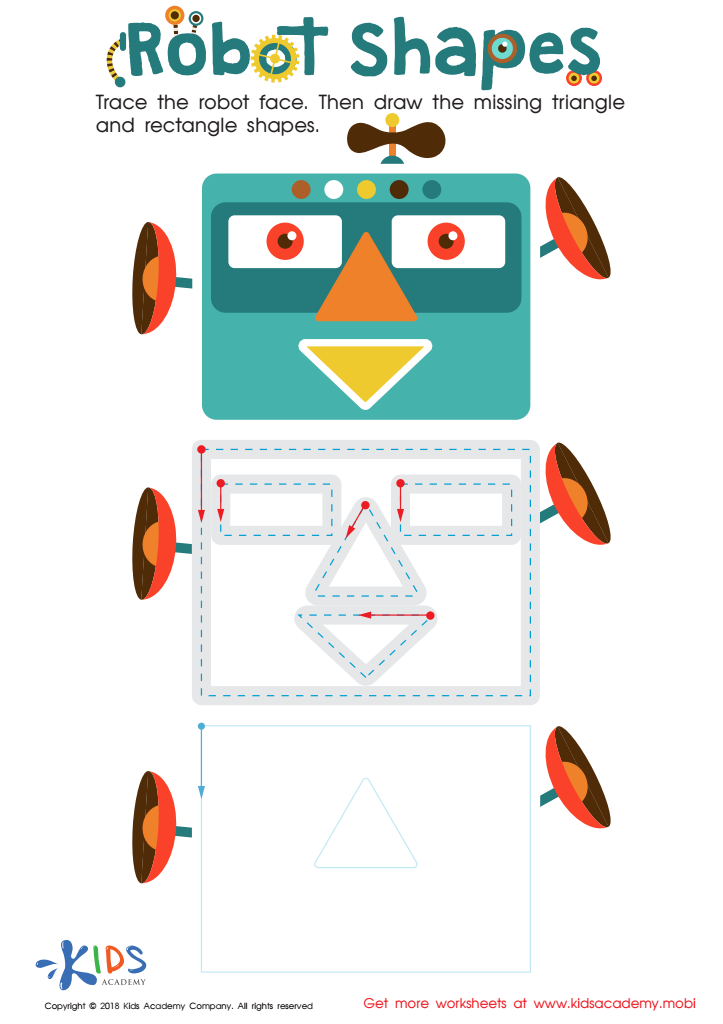

Robot Shapes Worksheet
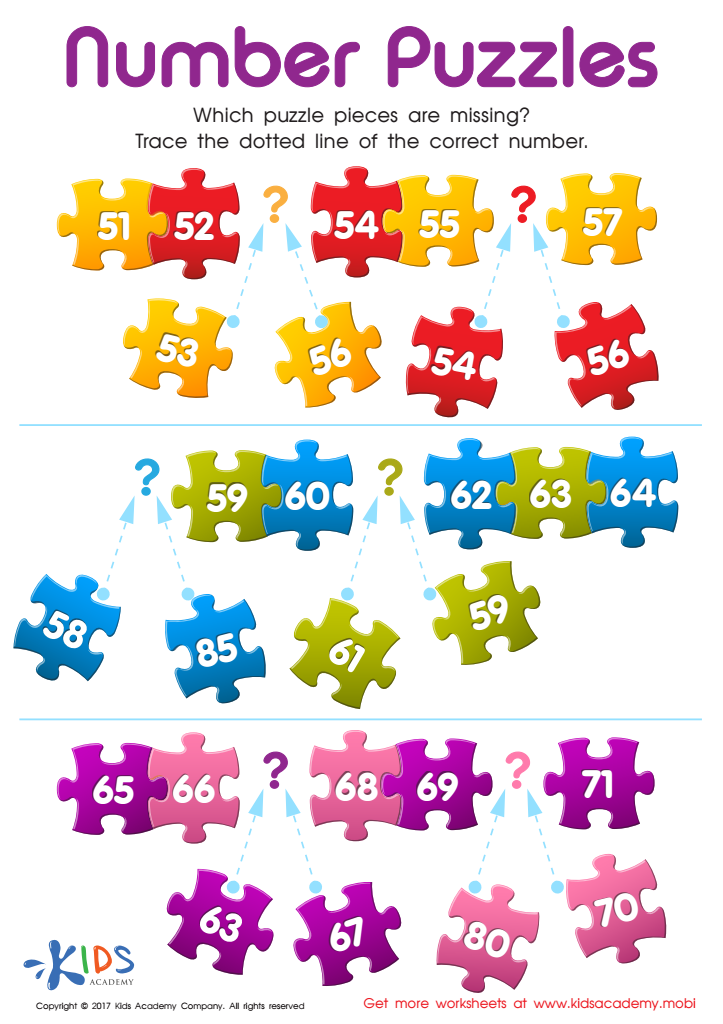

Number Puzzles Worksheet
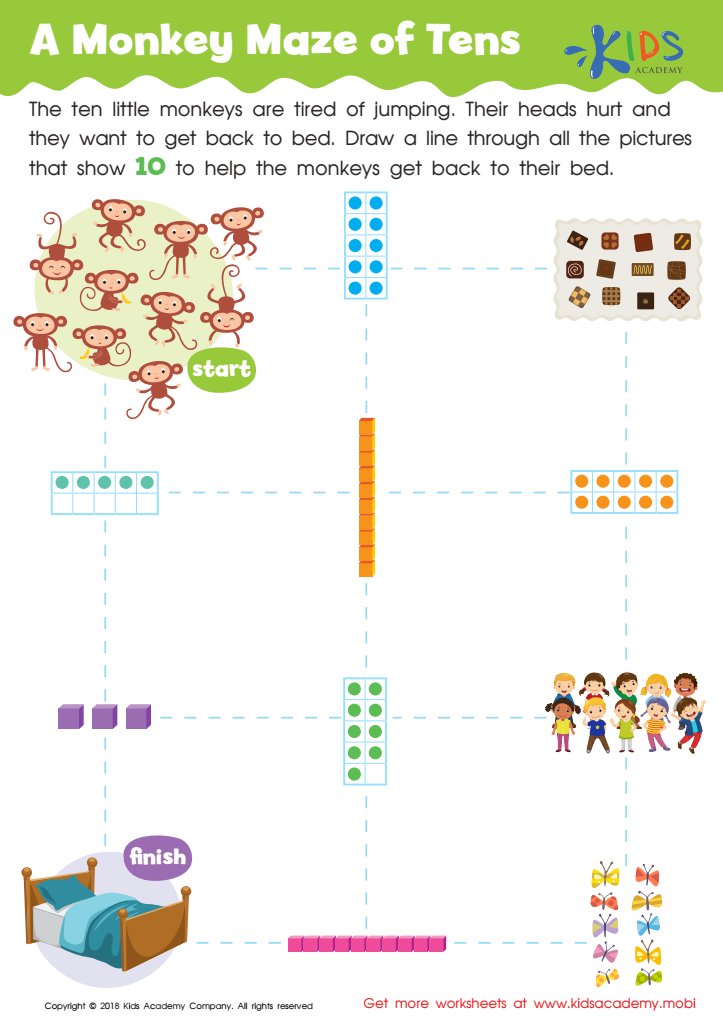

A Monkey Maze of Tens Worksheet
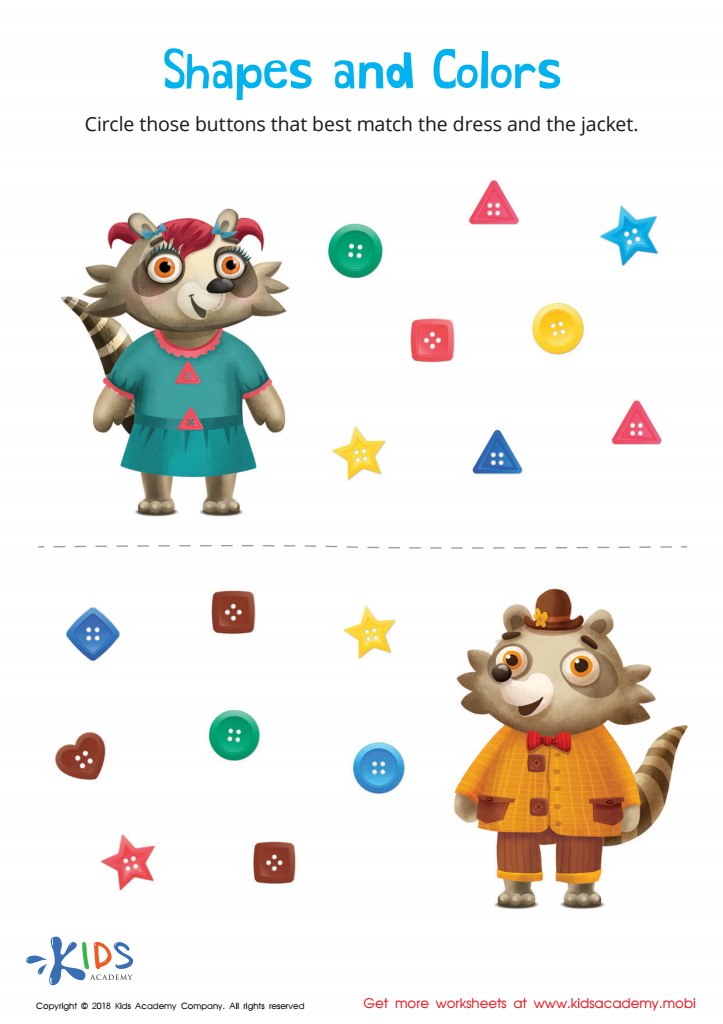


Shapes and Colors Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet


Reading Liquid Measurement Worksheet
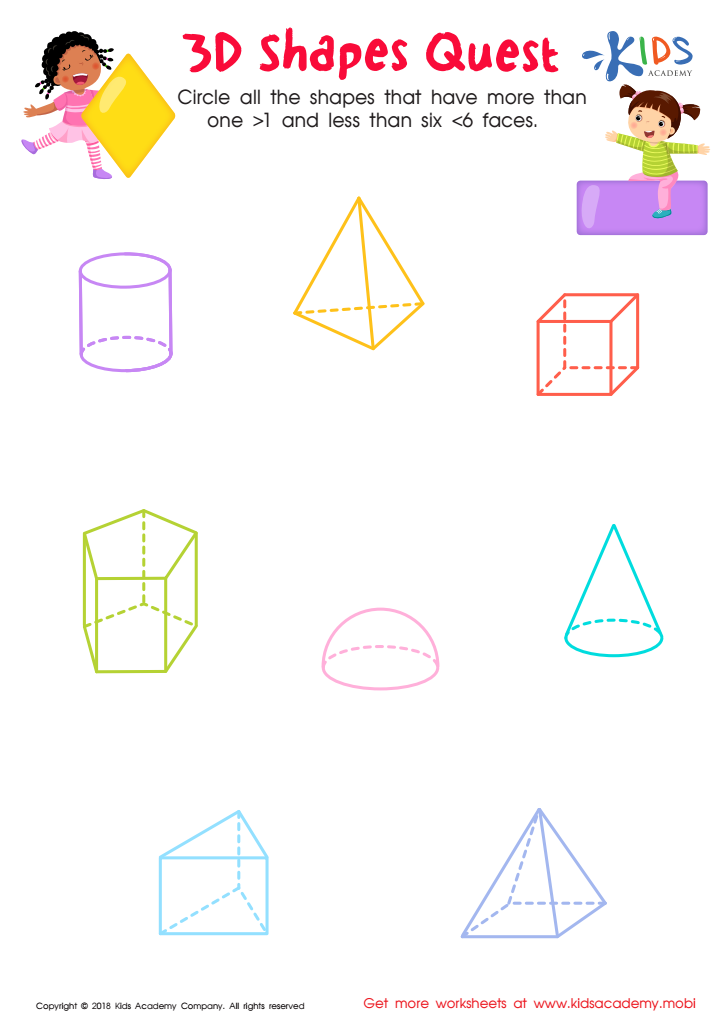

3D Shapes Quest Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet


Bubble Matching Fun Worksheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet
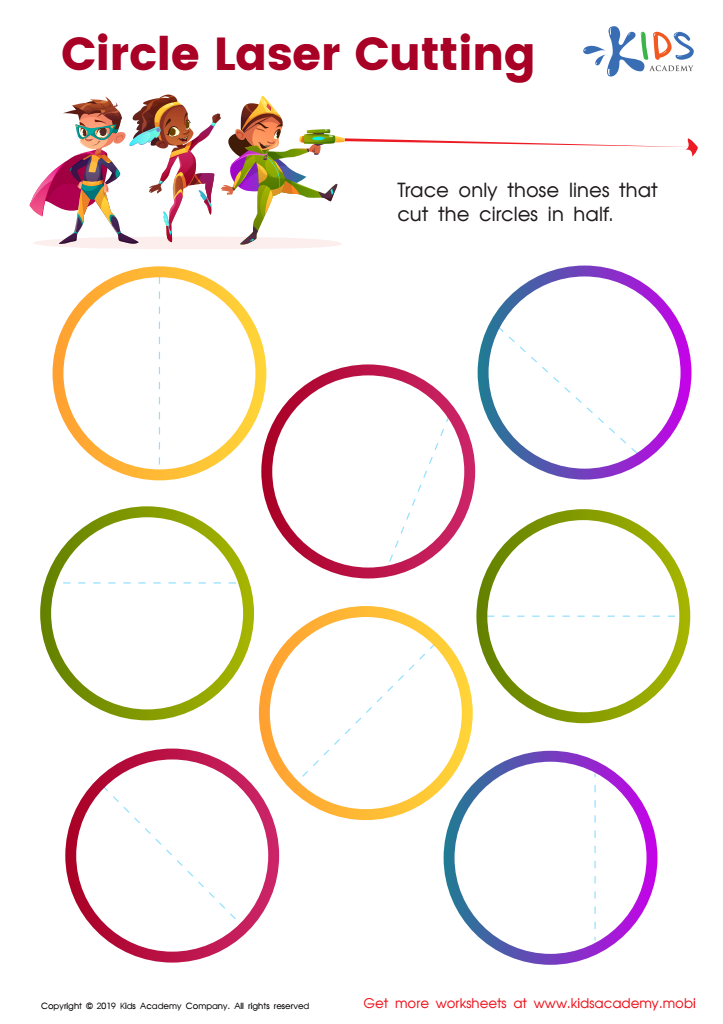

Circle Laser Cutting Worksheet


Octopus 8’s Worksheet


Ben Franklin’s Inventions – Count to 120 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 5-8 because they form the foundation for more advanced tasks and overall development. These skills involve the coordination of small muscles, particularly in the hands and fingers, vital for performing daily activities such as writing, buttoning clothes, and tying shoelaces. When children develop fine motor skills, they gain greater independence and self-confidence.
In an academic setting, fine motor skills are essential for good handwriting, drawing, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. These abilities facilitate a smoother transition into tasks that become more complex as they grow older. For example, children who struggle with fine motor skills may find it difficult to keep up with classroom activities that involve writing, leading to frustration and potentially decreased academic performance.
Furthermore, the development of fine motor skills is intertwined with cognitive development, including problem-solving and spatial awareness, which are foundational for subjects like math. Engaging in activities that enhance fine motor skills, such as playing with building blocks, crafting, or practicing letter formation, not only supports academic readiness but also opens pathways to creativity and critical thinking.
In sum, parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skill development because it profoundly affects a child's independence, academic competence, and overall confidence, setting the stage for future success.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students



.jpg)