Fine Motor Skills Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-4 - Page 2
70 filtered results
-
From - To

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable


Count the Stegosaurus's Spikes Worksheet


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Chicken & Egg Dot–to–dot Worksheet


Number 9 Printable


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Number 7 Worksheet


Count and Trace 1 – 3 Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Mary's Bag Worksheet


Counting Butterflies Worksheet


Counting Busy Bees Worksheet

Number Puzzles Worksheet

Sidewalk Counting Worksheet
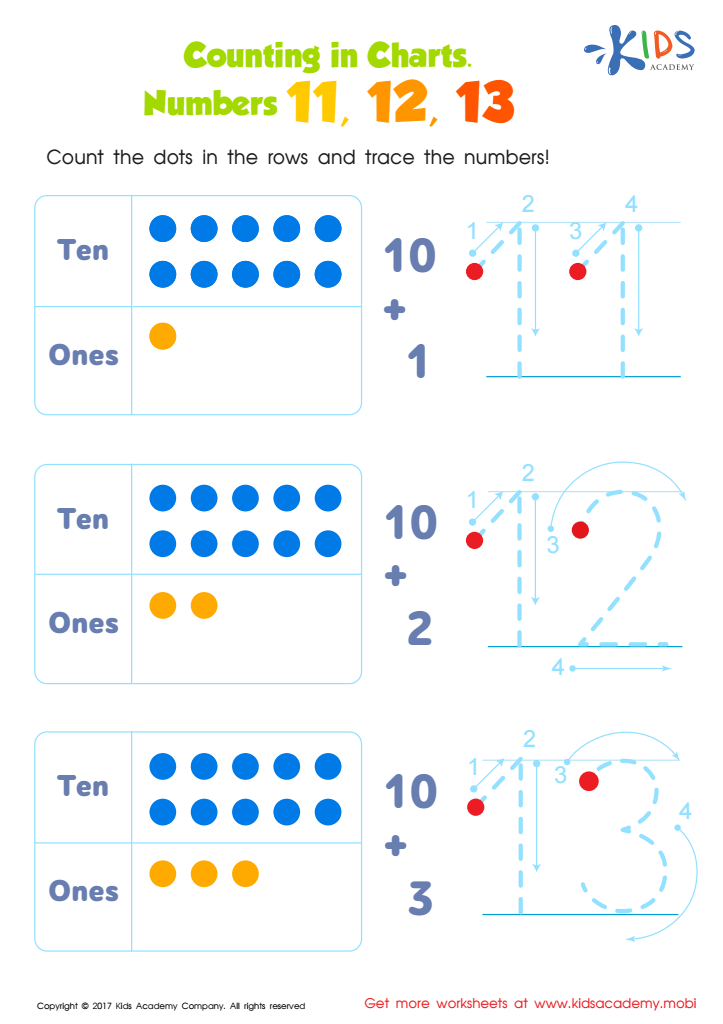

Number Tracing Worksheet For Kindergarten


Frog Countdown Worksheet

Eight Geese Worksheet


Pirate Ship Connect Dots Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet

Underwater Adventure Worksheet

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are fundamental for children aged 3-4 because they form the basis for many essential tasks and future learning experiences. These skills, which involve the small muscles in the hands and fingers, are critical for handling objects, buttoning clothes, cutting with scissors, and eventually writing. During these formative years, strengthening fine motor skills can significantly impact a child's ability to participate independently in daily activities, thereby boosting their confidence and self-esteem.
Children who develop strong fine motor skills can draw, write numbers, and manipulate small objects with greater control and precision. This early proficiency is crucial for academic success since writing and drawing are foundational components of early education. Activities like playing with blocks, threading beads, and practicing numbers through playful counting games or finger painting support the development of these skills.
For parents and teachers, fostering fine motor skill development means providing a supportive and stimulating environment with a variety of age-appropriate materials and activities. Encouraging children to practice these skills not only promotes physical dexterity but also enhances cognitive development, as hand-eye coordination and motor planning are closely linked with cognitive functions like problem-solving and concentration. Thus, caring about and nurturing fine motor skills in early childhood sets the groundwork for a child's comprehensive growth and academic future.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students