Fine Motor Skills Numbers Worksheets for Ages 3-5 - Page 2
70 filtered results
-
From - To
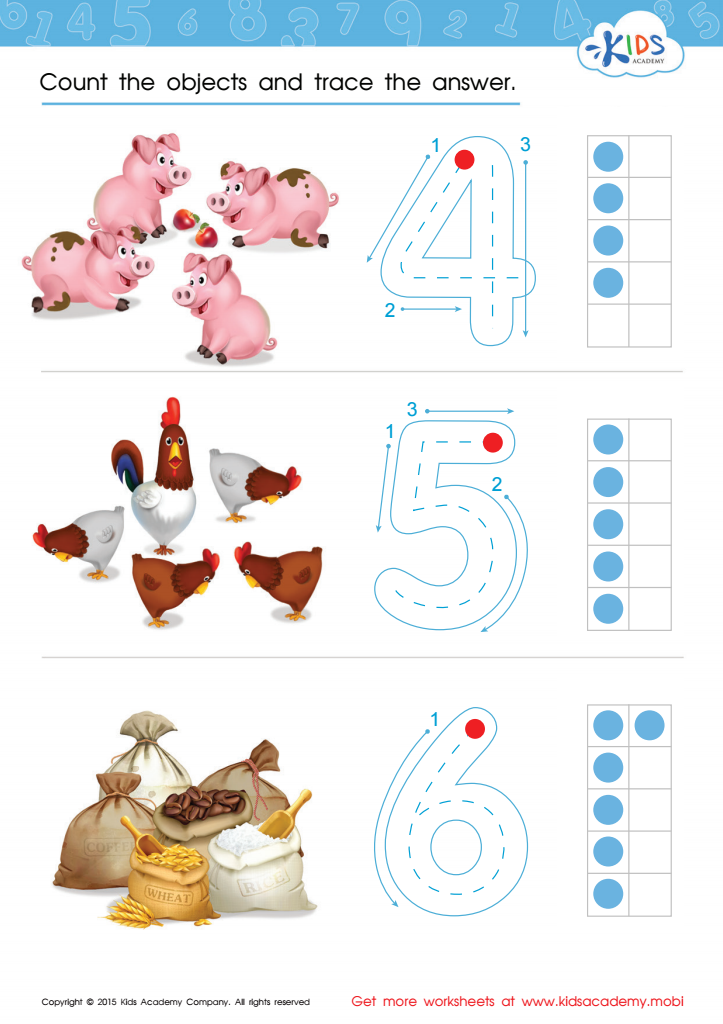

Count and Trace 4 – 6 Worksheet


Number 2 Printable


Count the Stegosaurus's Spikes Worksheet
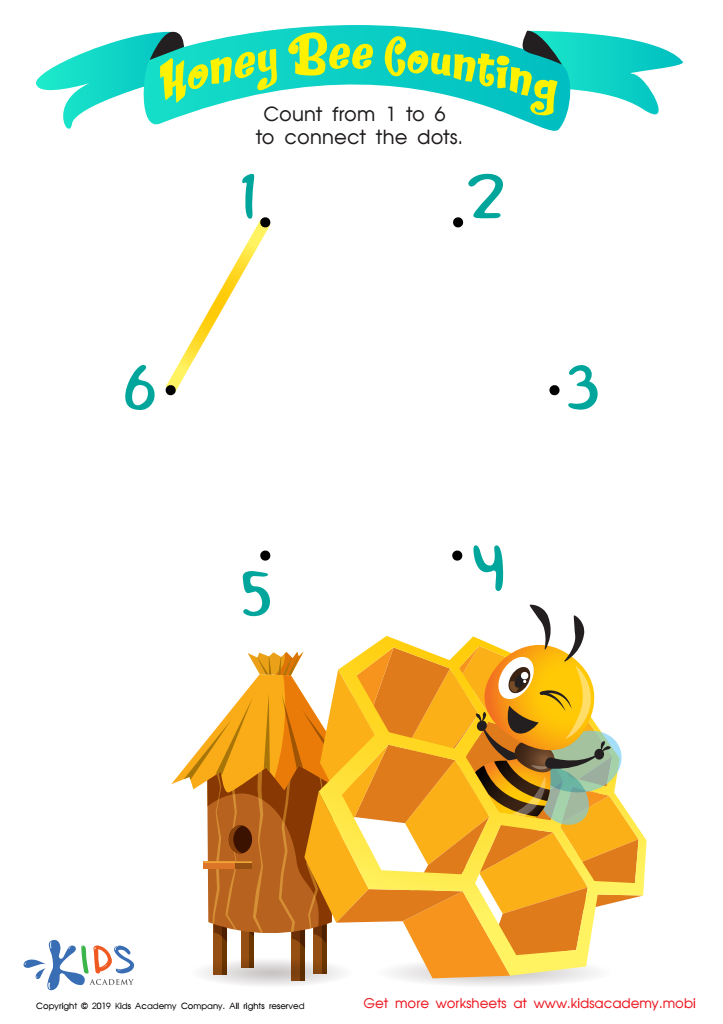


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Chicken & Egg Dot–to–dot Worksheet


Number 9 Printable


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Number 7 Worksheet


Count and Trace 1 – 3 Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Mary's Bag Worksheet


Counting Butterflies Worksheet


Counting Busy Bees Worksheet
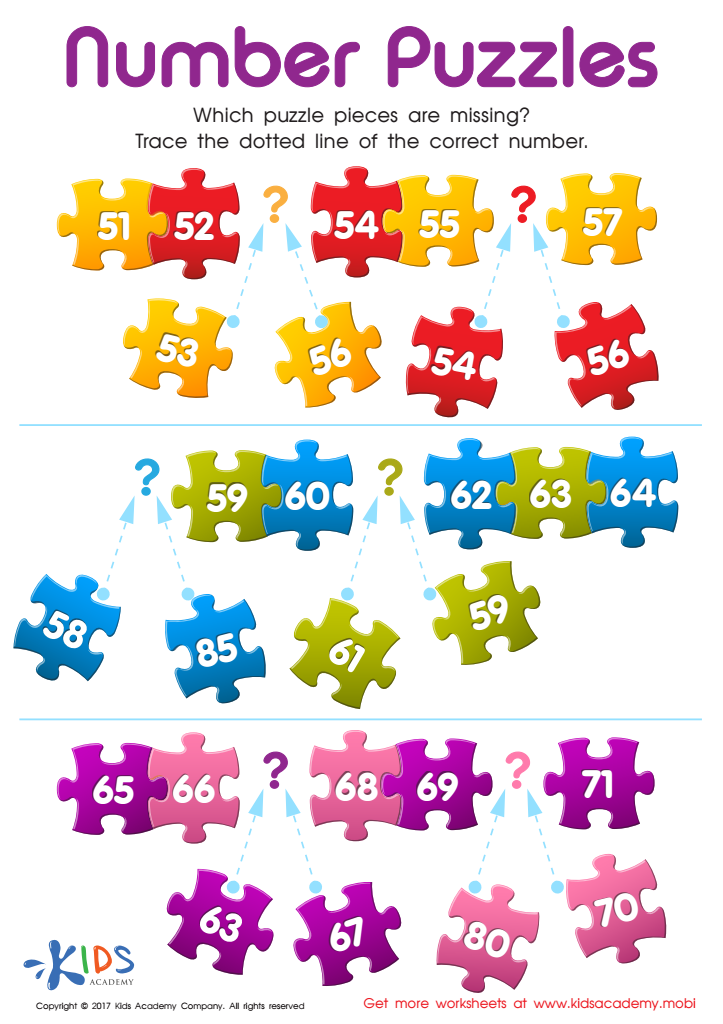

Number Puzzles Worksheet
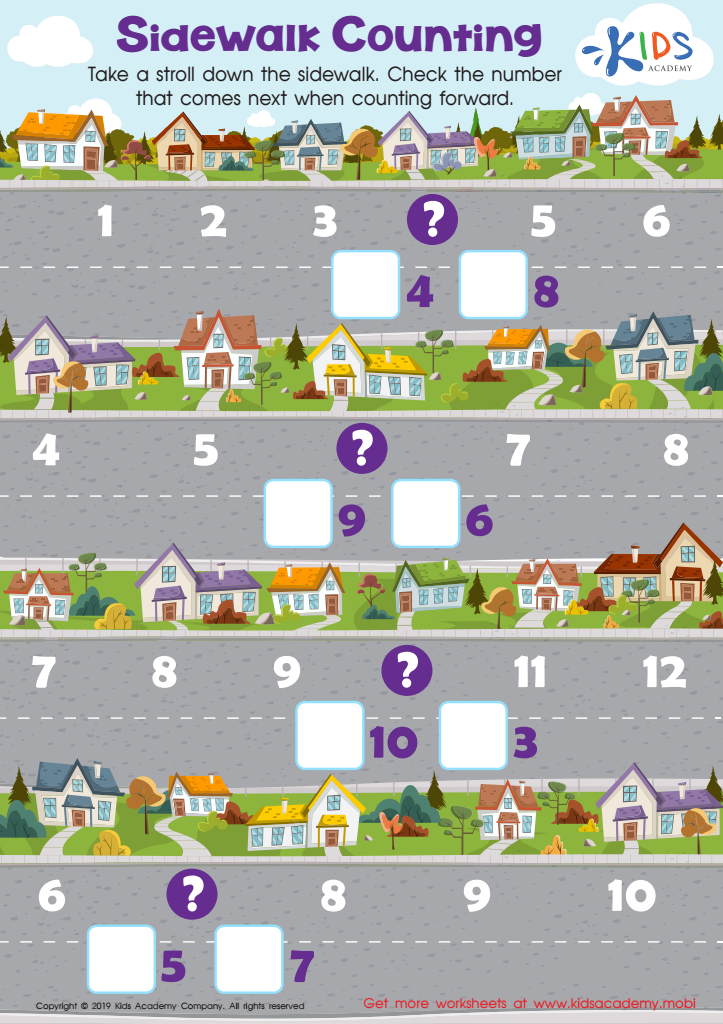

Sidewalk Counting Worksheet
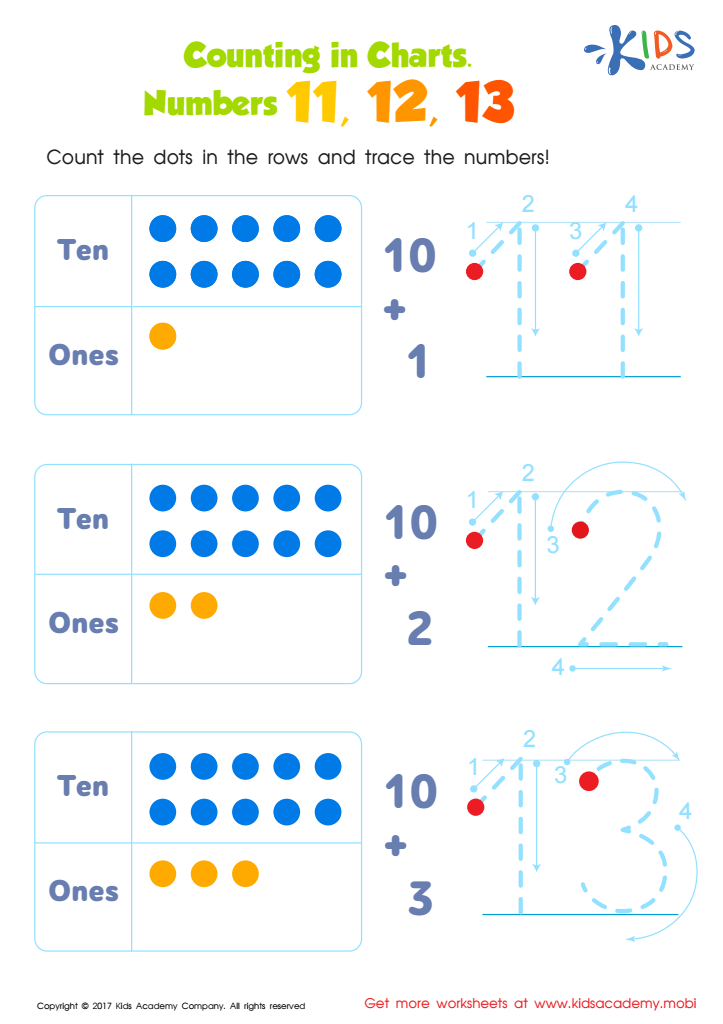

Number Tracing Worksheet For Kindergarten


Frog Countdown Worksheet

Eight Geese Worksheet


Pirate Ship Connect Dots Worksheet


Number 8 Printable


Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 1 Worksheet


Let's Pick Fruit Worksheet

Underwater Adventure Worksheet

Numbers 1, 2 and 3: Assessment 2 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are crucial developmental abilities that involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, essential for tasks such as writing, buttoning shirts, and using utensils. For children aged 3-5, fine motor skills numbers serve as foundational elements that parents and teachers should prioritize. During these early years, children are at a critical stage of developing control and dexterity.
Improving fine motor skills aids in numerous educational and everyday activities. When children practice activities like tracing numbers, coloring within the lines, or using scissors, they enhance their hand-eye coordination and precision. Such tasks also lay the groundwork for later academic skills including writing, drawing, and computer use, which are integral in today's technology-driven world.
Moreover, fostering fine motor skills can boost a child’s confidence and independence. Completing tasks like buttoning clothes or brushing teeth successfully allows children to feel capable and self-sufficient, which further encourages their willingness to learn new tasks.
Lastly, early fine motor practice supports cognitive development. Activities that require careful manipulation and coordination can enhance focus, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills, establishing essential pre-academic readiness. Therefore, prioritizing fine motor skills for children aged 3-5 prepares them for future academic and personal success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students




%20(1).jpg)











