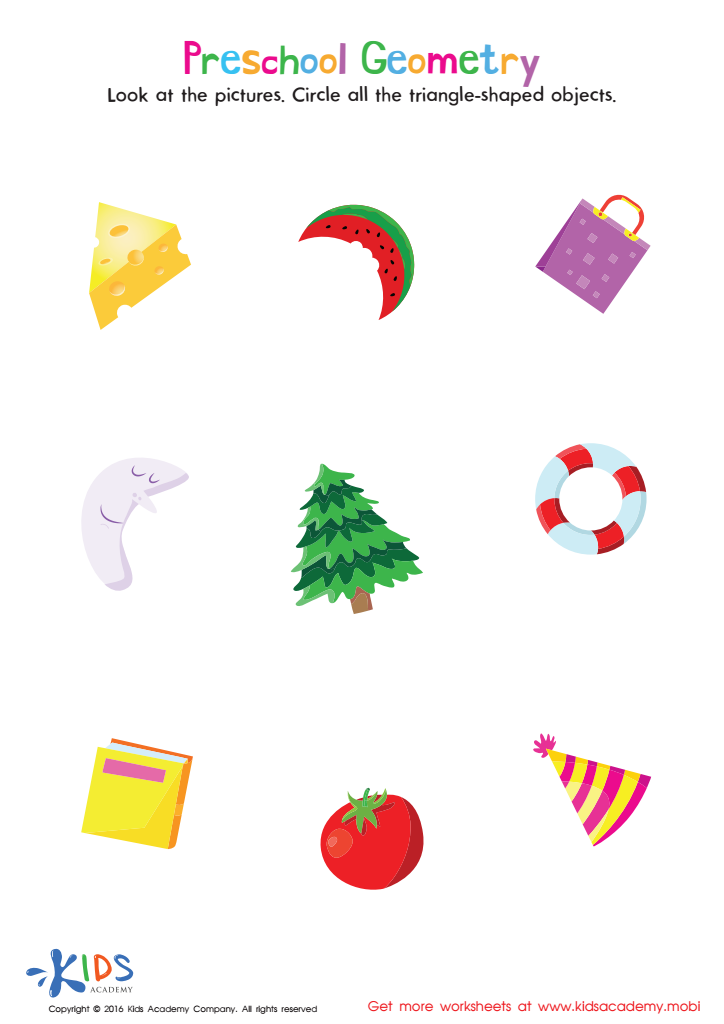
Shape Recognition Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-8 - Page 2
71 filtered results
-
From - To

Practicing to Draw Circles And Squares Printable


Woodpecker and Triangles Worksheet

Comparing Squares Rectangles Worksheet

Cutting Rectangles with Alien Worksheet

Odd Shape Out Worksheet for Grade 1


Shape Connections Worksheet

2D and 3D Shapes Worksheet

What's the Missing Side Worksheet


Cinderella Geometry Maze Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet

Shape Quest Worksheet

How Many Triangles Worksheet


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet

Shapes Maze Geometry Worksheet

Let's Learn to Draw Hearts And Stars Printable

Recognizing Shape Sides Worksheet

2D vs 3D Shapes Worksheet

Trace and Draw More Shapes Worksheet

Missing Shapes: Trains Worksheet
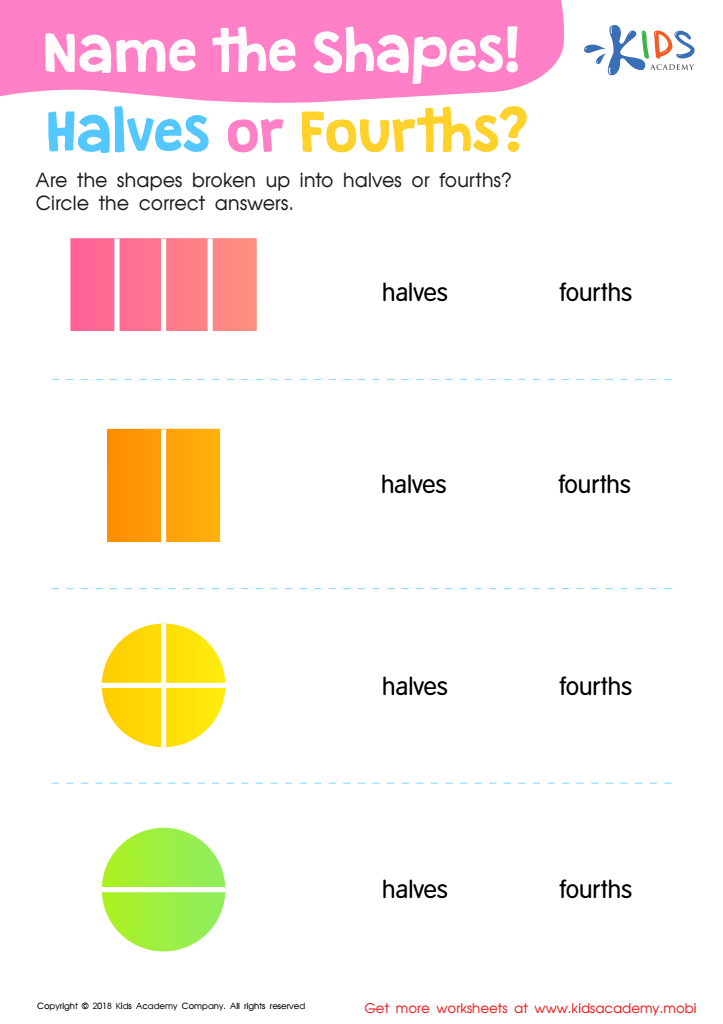

Name the Shapes Halves or Fourths? Worksheet
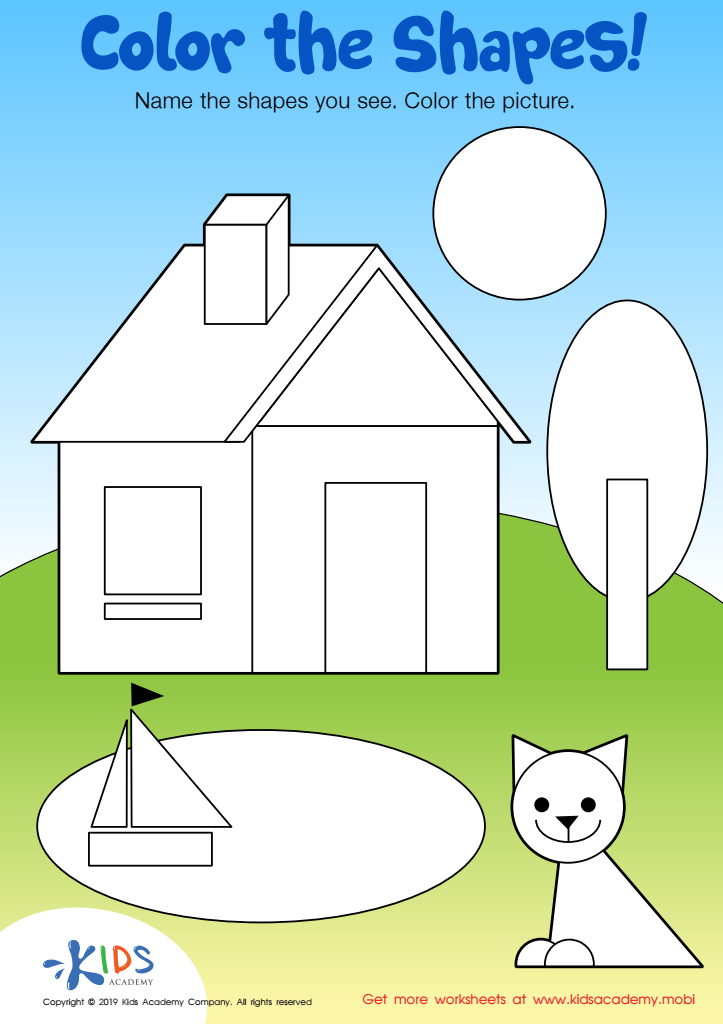

Color the Shapes Worksheet
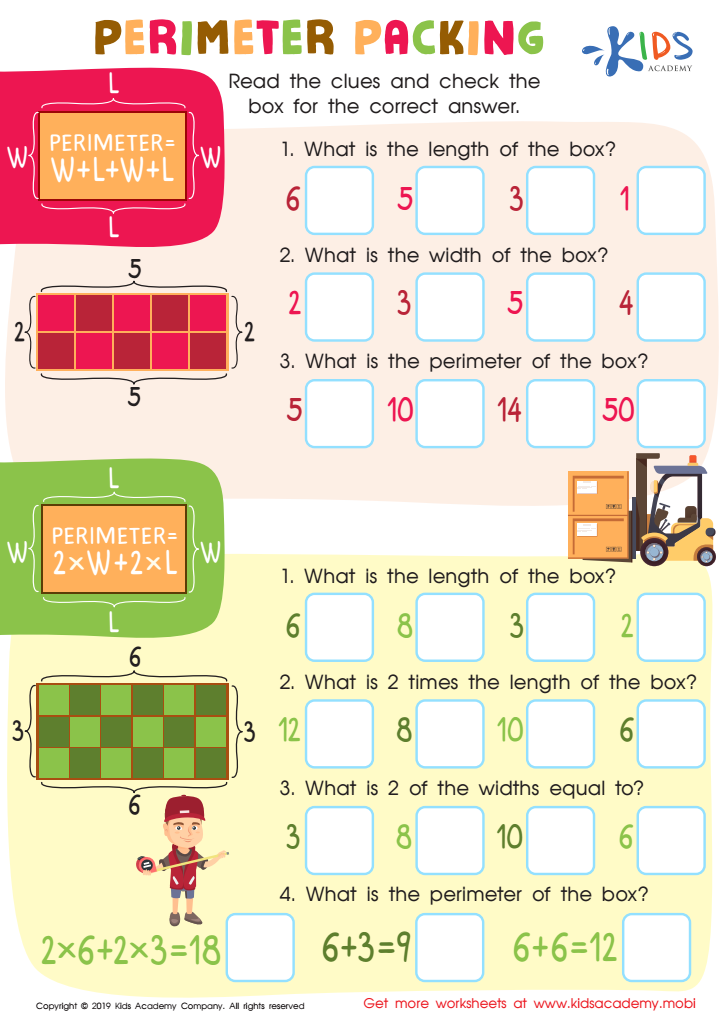

Perimeter Parking Worksheet
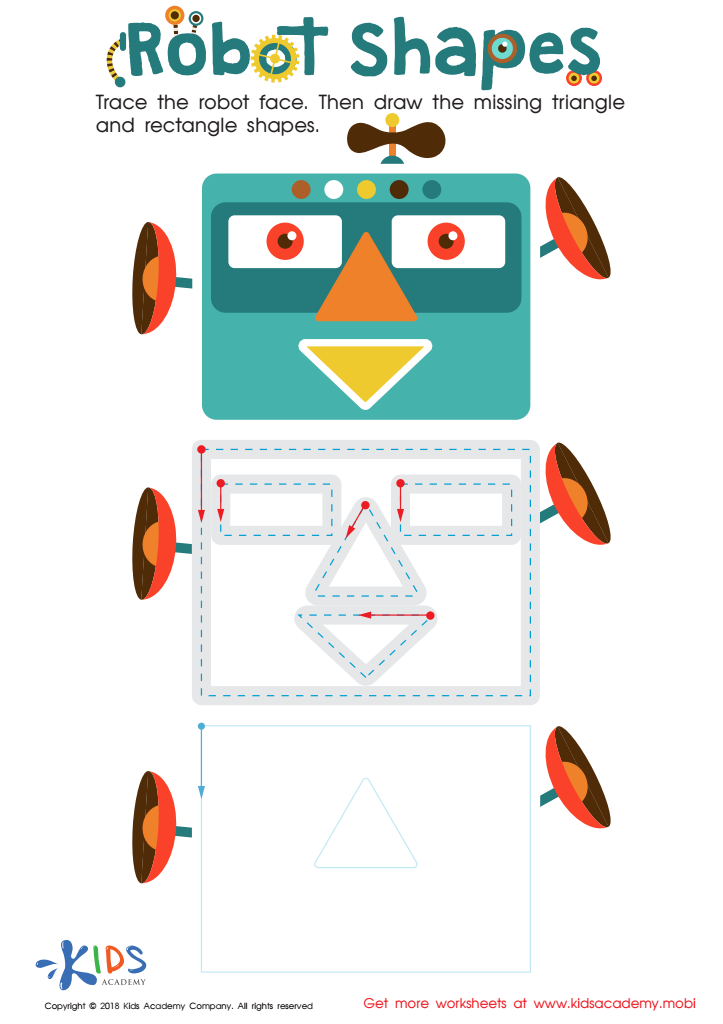

Robot Shapes Worksheet
Shape recognition is a fundamental aspect of early childhood education, particularly for children aged 3-8. During these formative years, engaging with geometry fosters critical thinking and cognitive development. By recognizing different shapes, children begin to understand spatial relationships and develop analytical skills, acting as a foundation for more complex mathematical reasoning later on.
Furthermore, shape recognition aids in fine motor skills as children manipulate objects to learn about shapes. Activities such as drawing, cutting, and constructing with shapes promote hand-eye coordination and dexterity. This tactile experience reinforces concept understanding through play, which is essential for young learners.
Parents and teachers should care about shape recognition because it also enhances language development. As children describe shapes—size, color, and attributes—they expand their vocabulary and communication skills.
Moreover, learning about shapes encourages problem-solving skills. Children will learn to classify and group objects, an ability that transcends mathematics into everyday life scenarios. In a rapidly advancing world, equipping children with strong foundational skills positions them for future academic success and lifelong learning. Therefore, prioritizing shape recognition contributes to holistic development in early childhood education, making it a vital component of learning during these critical years.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students