Hand-eye Coordination Math Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
66 filtered results
-
From - To


Estimating Length: Magician's Maze Worksheet
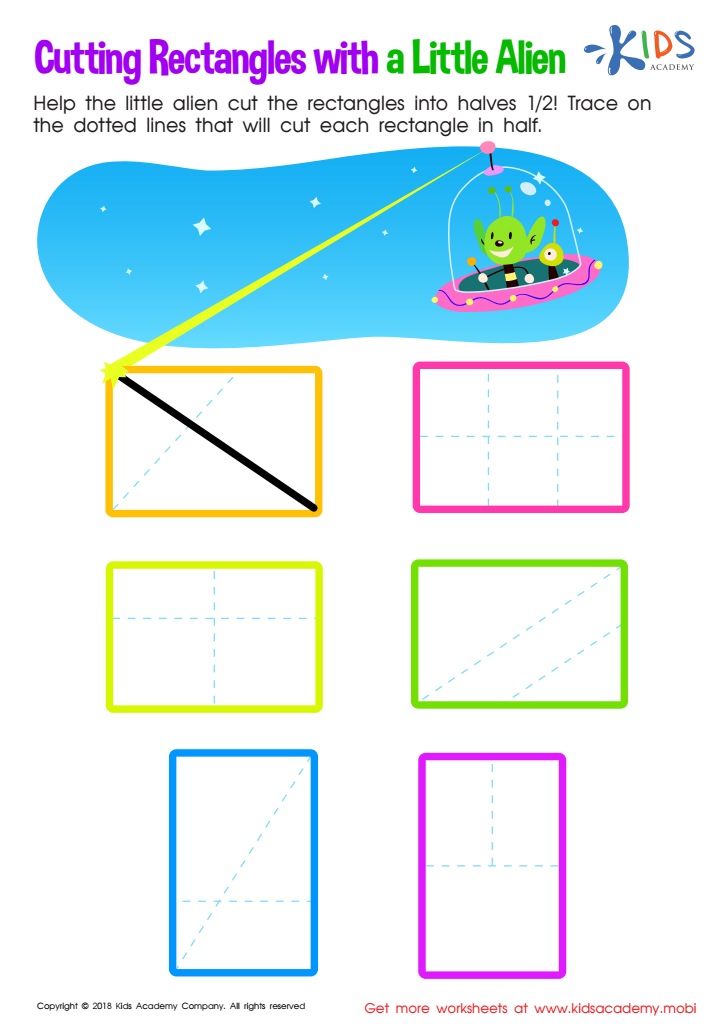

Cutting Rectangles with Alien Worksheet
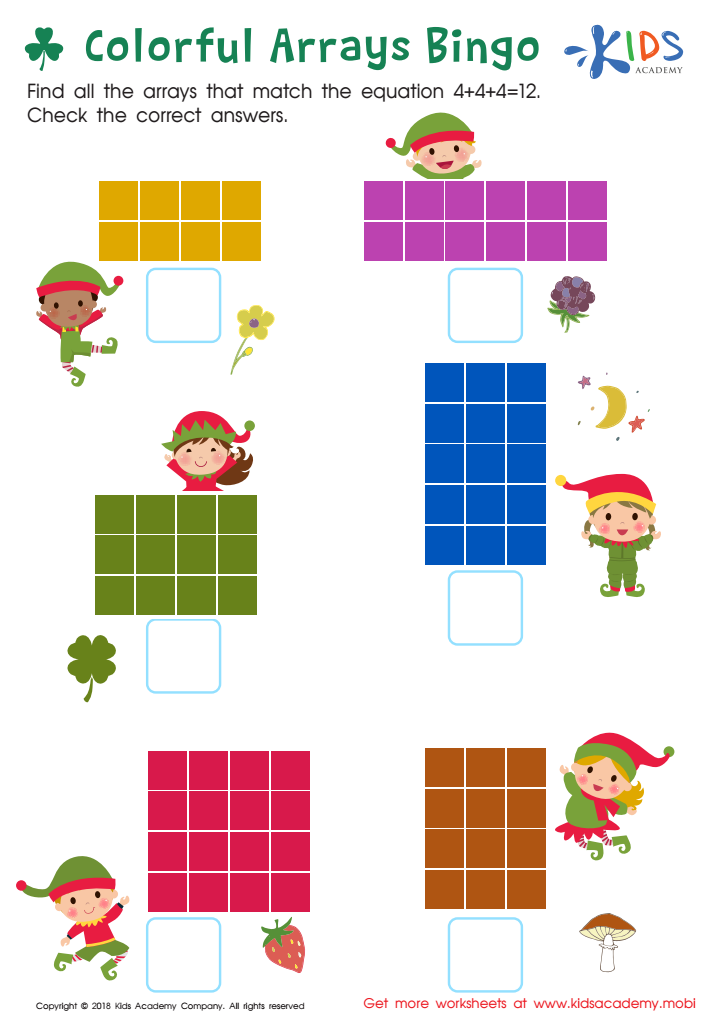

Colorful Arrays Bingo Worksheet
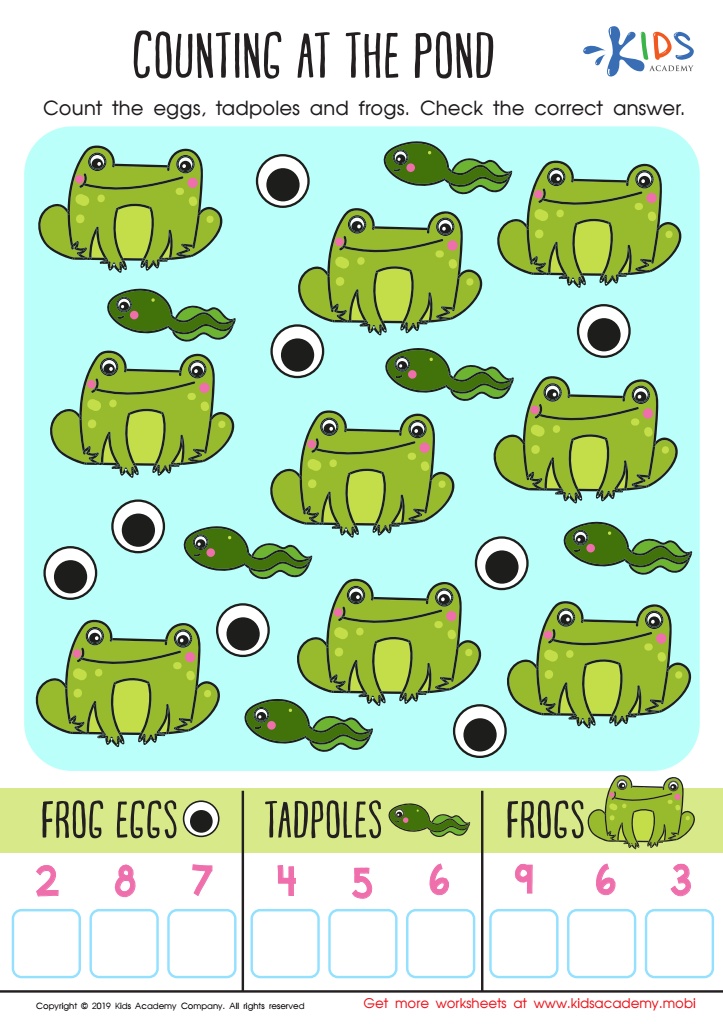

Counting at the Pond Worksheet
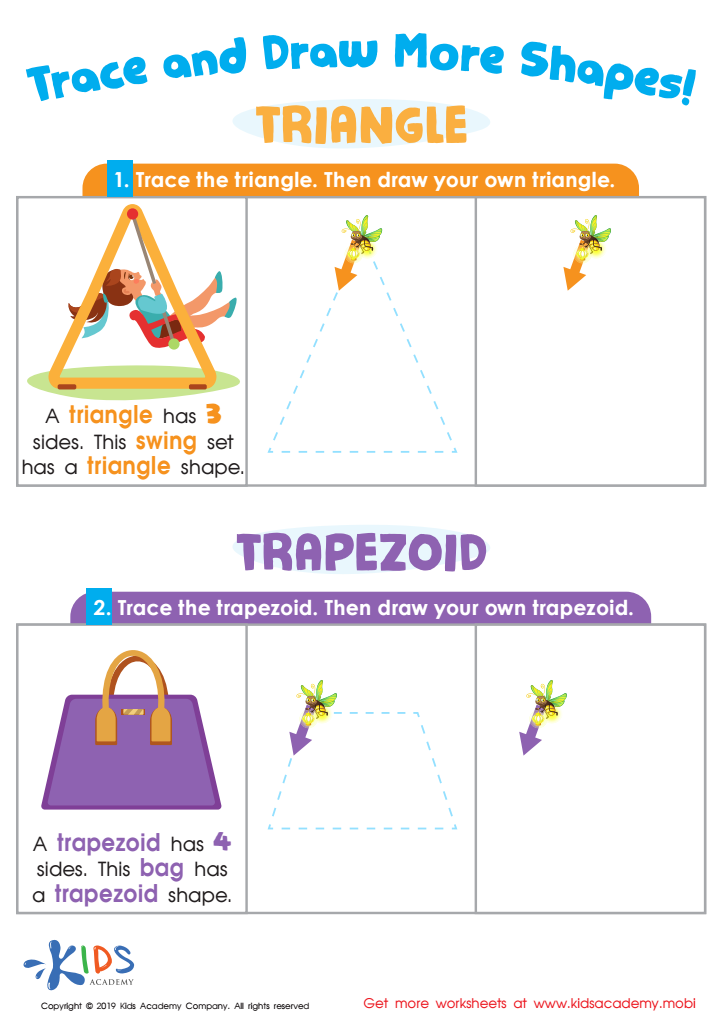

Trace and Draw More Shapes Worksheet


Ordering 11–20: Chicken & Egg Dot–to–dot Worksheet

Countdown from 5 Worksheet


Number 7 Worksheet


Dot to Dot Worksheet for 3rd Grade


Cursive Numbers: 1 Worksheet

Adding up With Water Worksheet


Practice Writing Number 5 Worksheet

Matching 3-2 Worksheet


Write 0 Worksheet

Sidewalk Counting Worksheet


Ten Pins is a Strike Worksheet
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial developmental skill, especially for children between the ages of 4 and 9, impacting not only physical abilities but also academic success, particularly in math. Engaging children in activities that combine math with hand-eye coordination lays a foundation for cognitive and motor development, fostering essential skills for later academic challenges.
First, hand-eye coordination activities facilitate neural connections that enhance problem-solving and critical thinking skills. For example, using building blocks to understand geometric shapes or counting objects while sorting them can lead to better spatial awareness—a fundamental aspect of math learning.
Furthermore, these activities help in developing fine motor skills, which are necessary for tasks such as writing numbers accurately and aligning them correctly in columns for calculations. Enhanced hand-eye coordination can translate to improved focus and patience, encouraging a child's ability to follow through on complex mathematical problems.
Lastly, incorporating physical movement with math problems makes learning more engaging and enjoyable. This multisensory approach ensures that children stay interested and reduce the frustration that can often accompany early math learning.
Therefore, parents and teachers should emphasize hand-eye coordination math activities to support overall cognitive development, smoother academic progress, and a more positive attitude towards math.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students