Fine Motor Skills Normal Math Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
43 filtered results
-
From - To


Learn Number 8 Easily Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Mary's Bag Worksheet


Three–Dimensional Shapes: Cylinder Worksheet


Counting Busy Bees Worksheet

Robot Shapes Worksheet
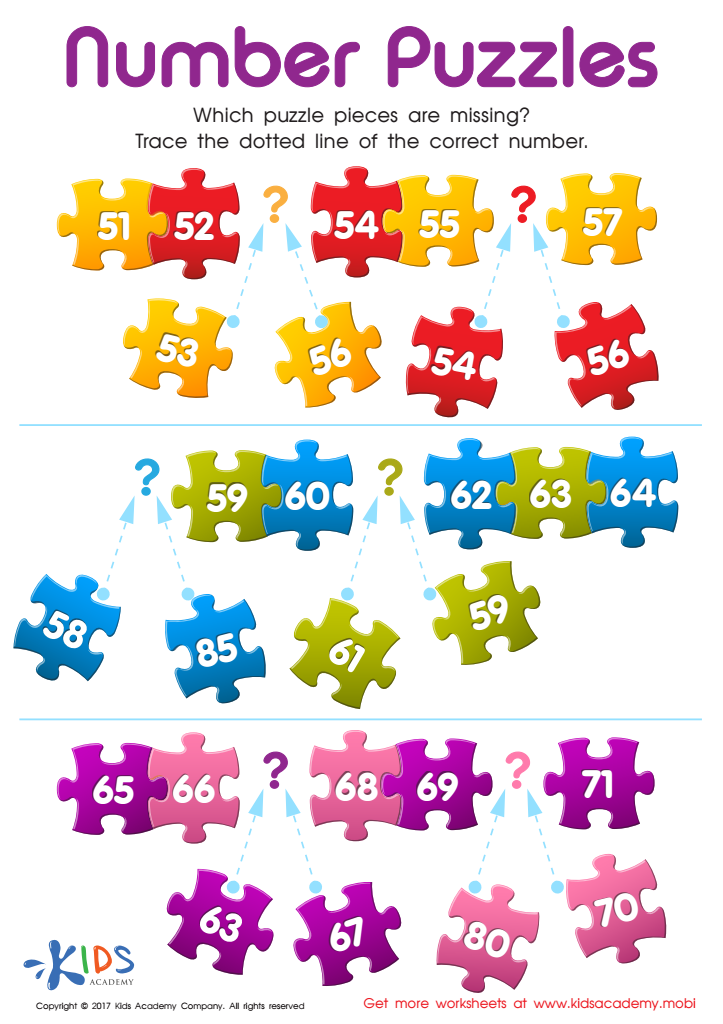

Number Puzzles Worksheet
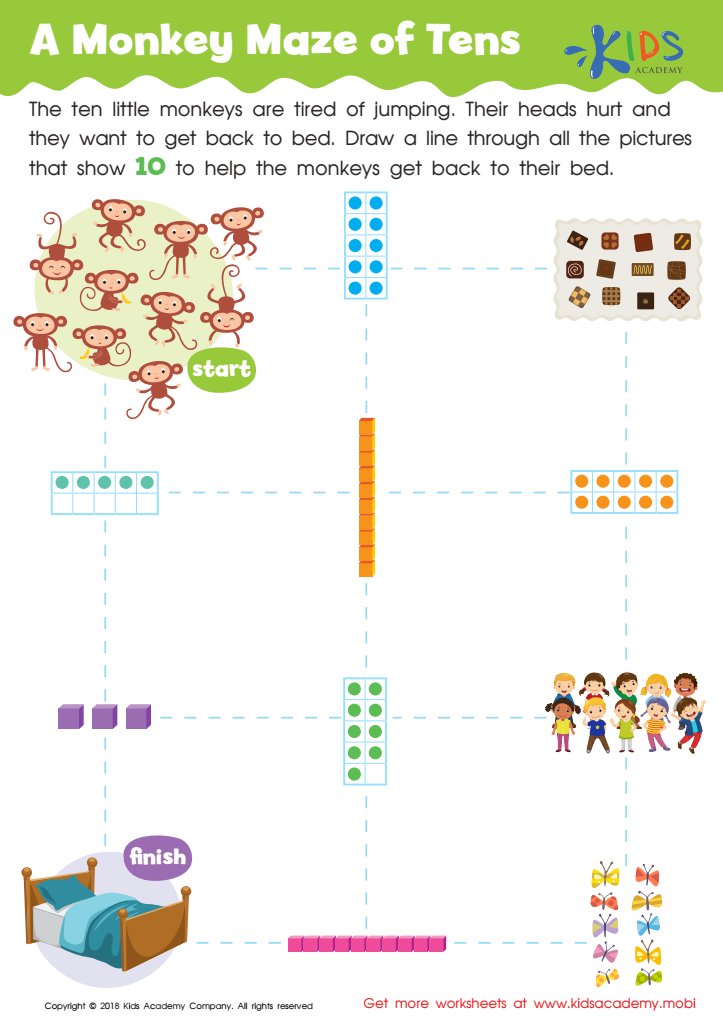

A Monkey Maze of Tens Worksheet


Shapes and Colors Worksheet


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet


Frog Countdown Worksheet


Reading Liquid Measurement Worksheet
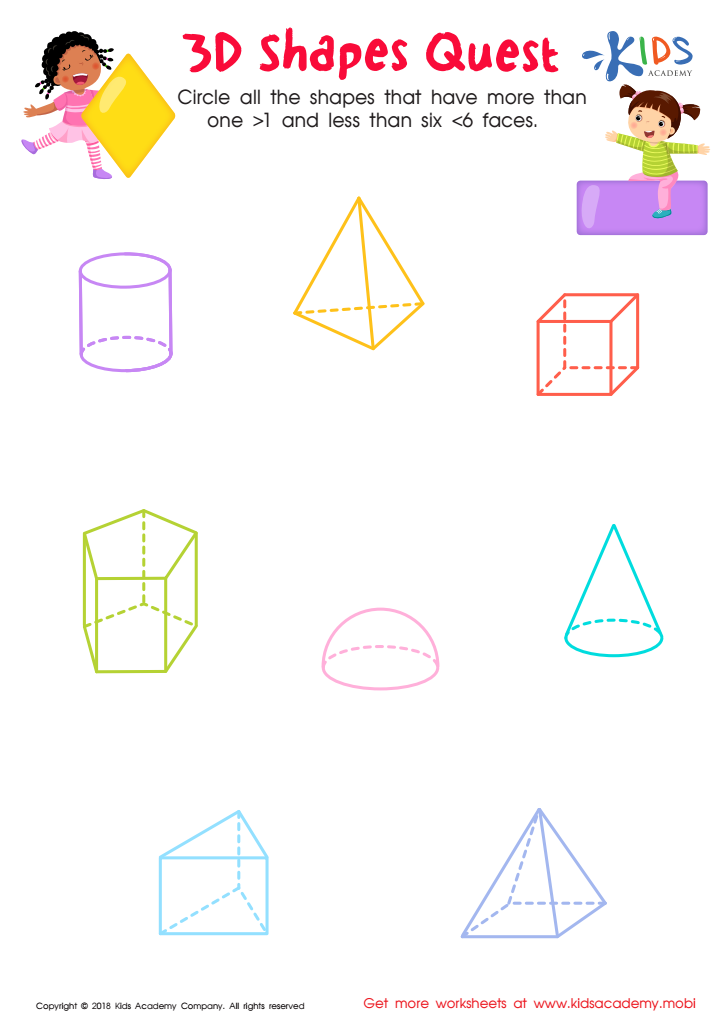

3D Shapes Quest Worksheet


Help the Bee Find 16 Flowers Worksheet


Addition Robot Sorter Worksheet


Bubble Matching Fun Worksheet


Learn to Write the Number 2 Worksheet
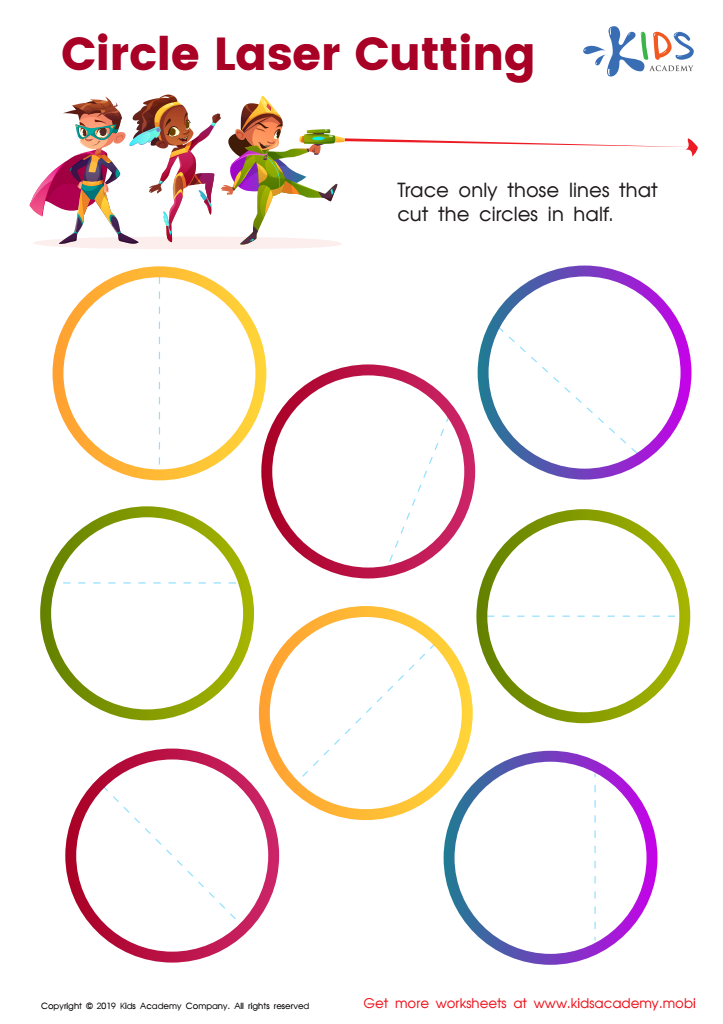

Circle Laser Cutting Worksheet


Octopus 8’s Worksheet


Ben Franklin’s Inventions – Count to 120 Worksheet
Fine motor skills are essential for young children between the ages of 4-9 because they form the foundation for many critical academic and daily activities. Developing strong fine motor skills aids in a child’s ability to perform tasks such as writing, drawing, buttoning clothes, and cutting with scissors. For educators and parents, supporting the development of these skills is crucial because these activities contribute both to academic success and overall independence.
Fine motor skills are closely linked to cognitive development, particularly in mathematical abilities. Handling tools like pencils, rulers, and manipulatives in math activities depends on refined movements. Skills such as counting small objects, aligning numbers, and drawing geometric shapes require precise muscle control. For instance, sorting beads helps in understanding patterns, which is a fundamental math skill.
Children struggling with fine motor tasks may also face higher emotional distress, impacting their social relationships and eagerness to engage in learning environments. Notably, early mastery of fine motor skills can lead to improved self-esteem as children become more competent and confident in their abilities.
Therefore, the development of fine motor skills isn't just about physical capability; it involves cognitive and emotional growth, preparing children for a lifetime of learning and daily functioning. By paying close attention to fine motor development, teachers and parents lay the groundwork for children's holistic success.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students