Normal 2D Shapes Worksheets for Ages 3-6 - Page 2
32 filtered results
-
From - To

Recognizing Shape Sides Worksheet


Trace And Draw a Circle And a Square Worksheet


Cinderella Geometry Maze Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet
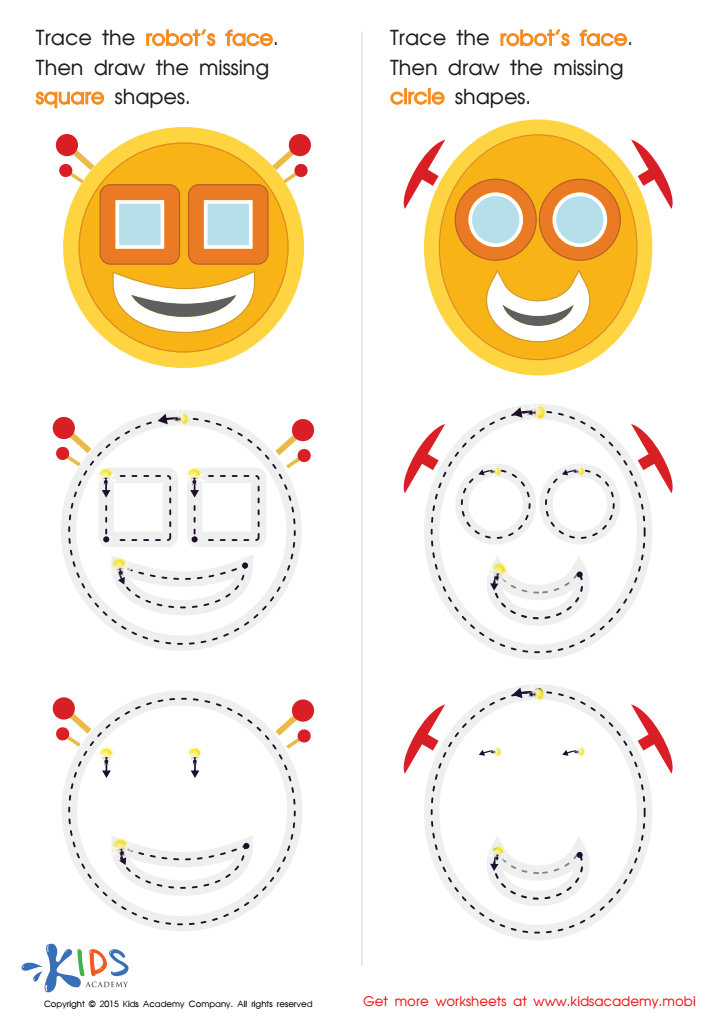

Practicing to Draw Circles And Squares Printable


Easy Drawing of Ovals And Rectangles Worksheet


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet
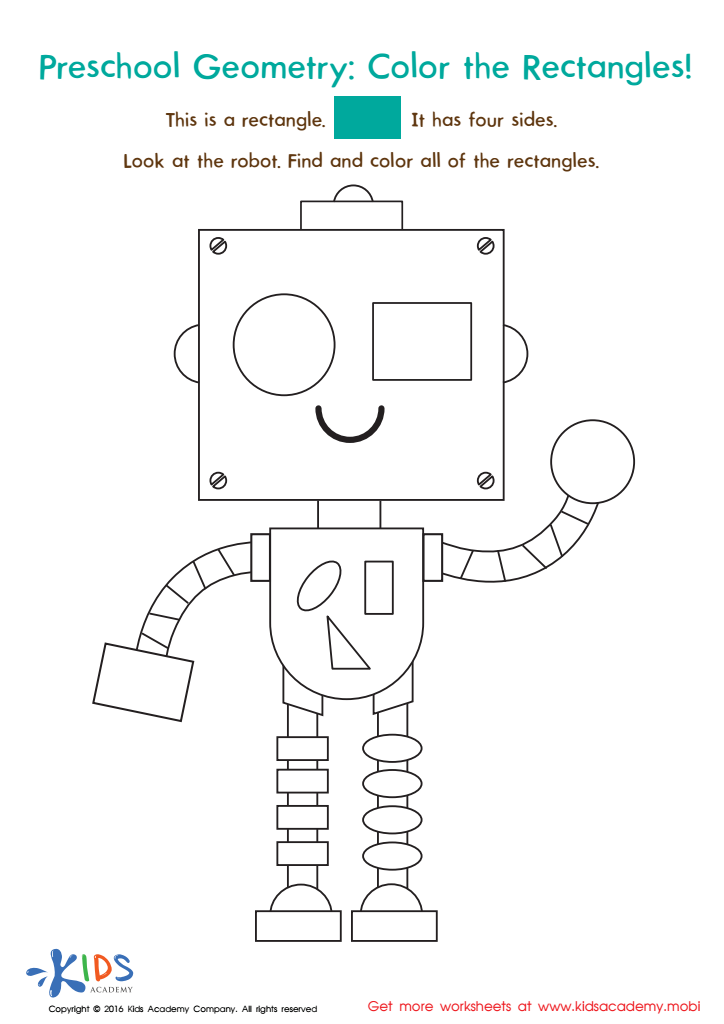

Geometry Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about introducing normal 2D shapes to children aged 3-6 because early shape recognition is foundational to developing essential math and cognitive skills. When children learn to identify and describe basic shapes like circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles, they are engaging in early geometric thinking, which is crucial for understanding more complex mathematical concepts later in life.
Familiarity with shapes enhances spatial awareness, helping children grasp concepts such as size, position, and orientation. This spatial reasoning is not only vital for math and science but also aids in everyday tasks like navigating spaces and understanding maps.
Moreover, learning about shapes improves language skills. When children describe shapes, their attributes, and where they see them, they expand their vocabulary and communication abilities. Shapes are ubiquitous in the environment; recognizing and naming them adds to a child’s observational skills.
Teachers and parents play a pivotal role in presenting these shapes in engaging, playful ways, such as through games, drawing, and hands-on activities. This stimulation helps foster a positive attitude toward mathematics and learning in general, establishing a strong foundation for future academic success. Thus, caring about shapes trains young minds to think critically, creatively, and logically.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students