Chess Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 4
86 filtered results
-
From - To
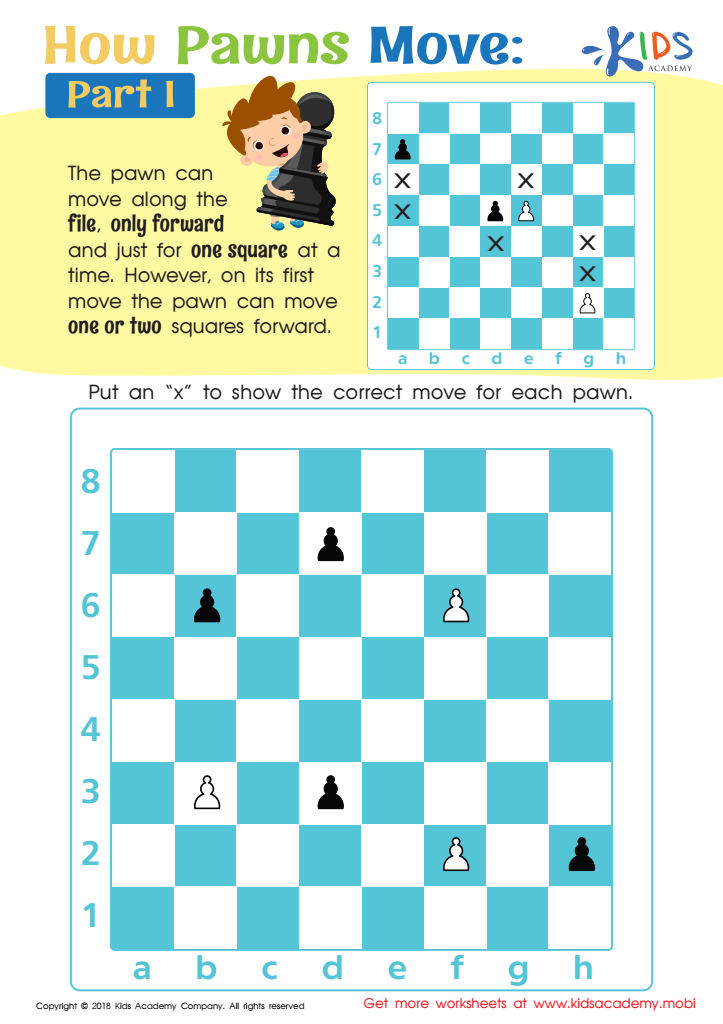

How Pawns Move: Part I Worksheet
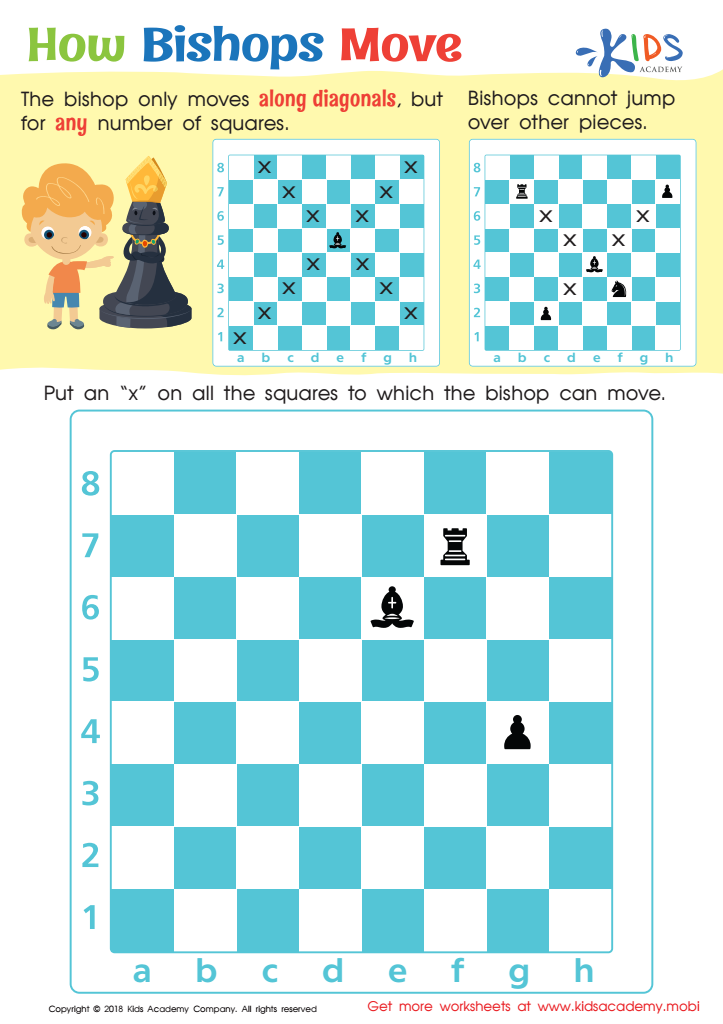

How Bishops Move Worksheet
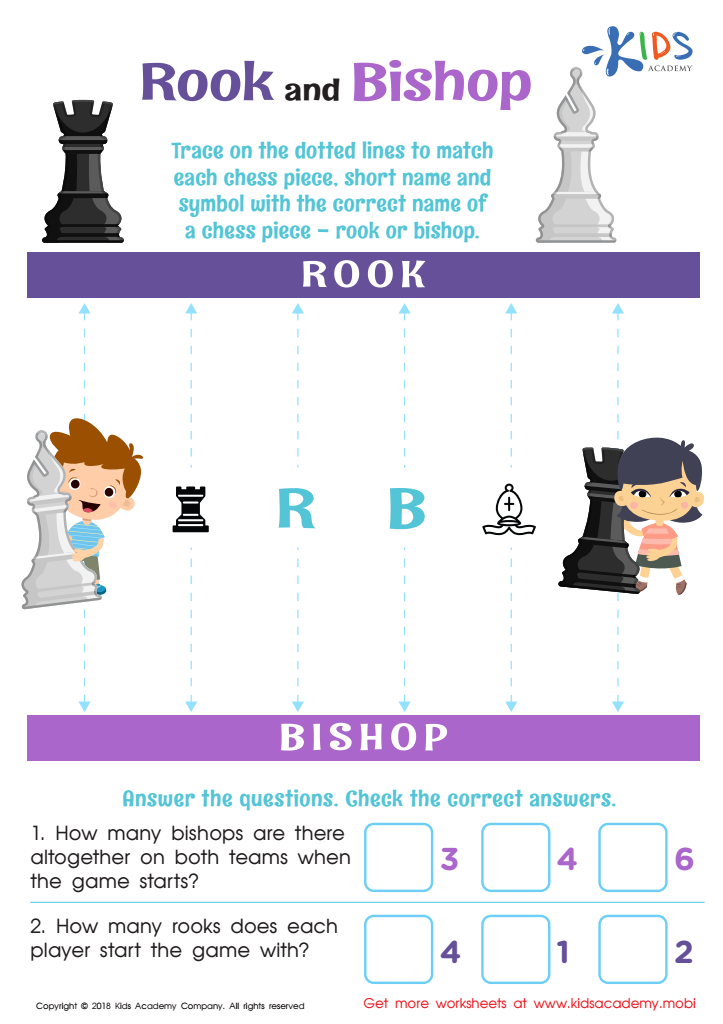

Rook and Bishop Worksheet
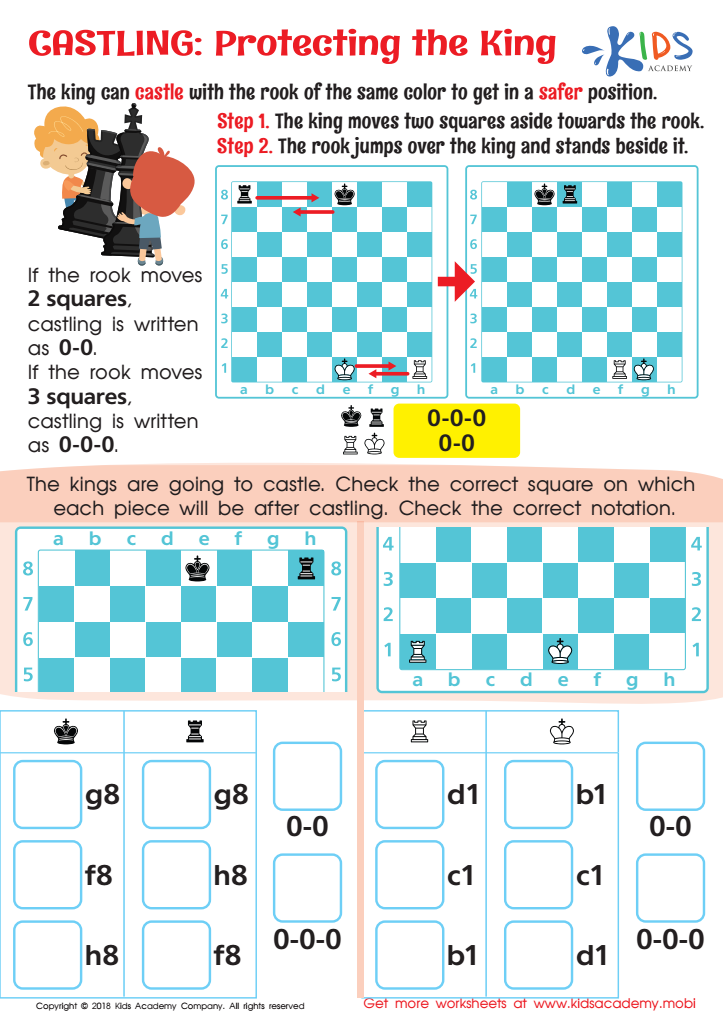

Castling: Protecting the King Worksheet
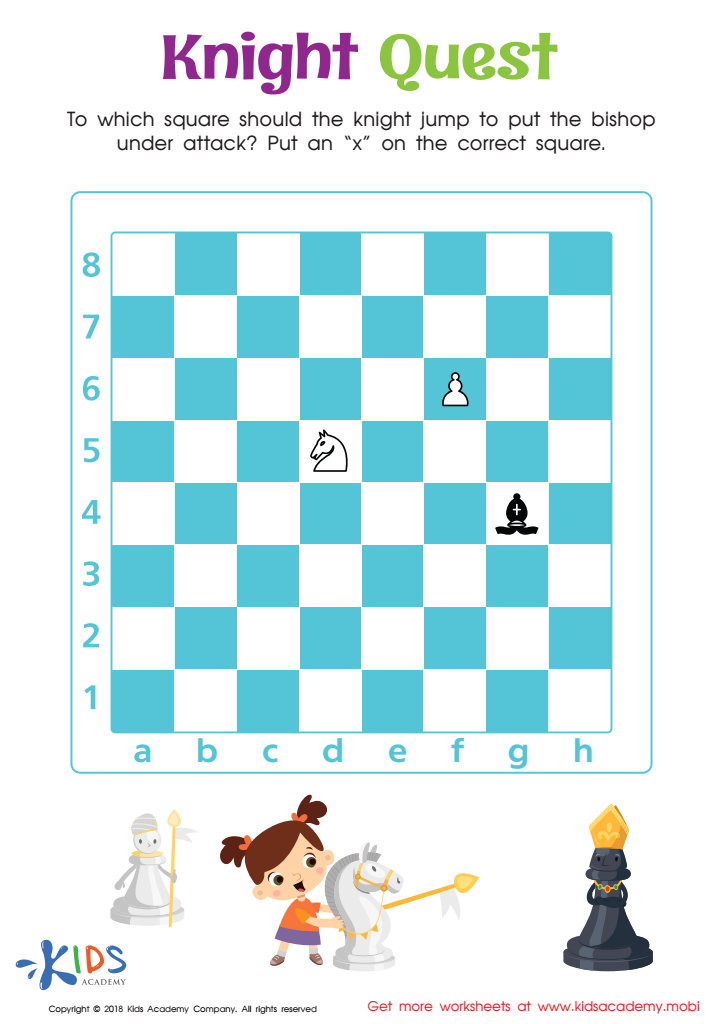

Knight Quest Worksheet
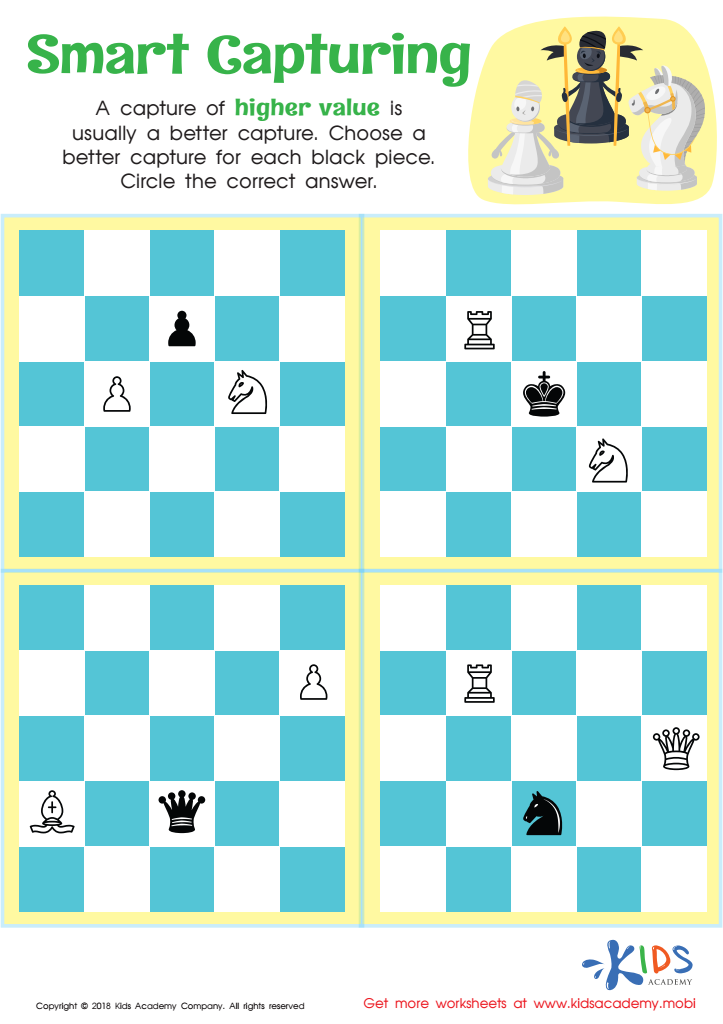

Smart Capturing Worksheet
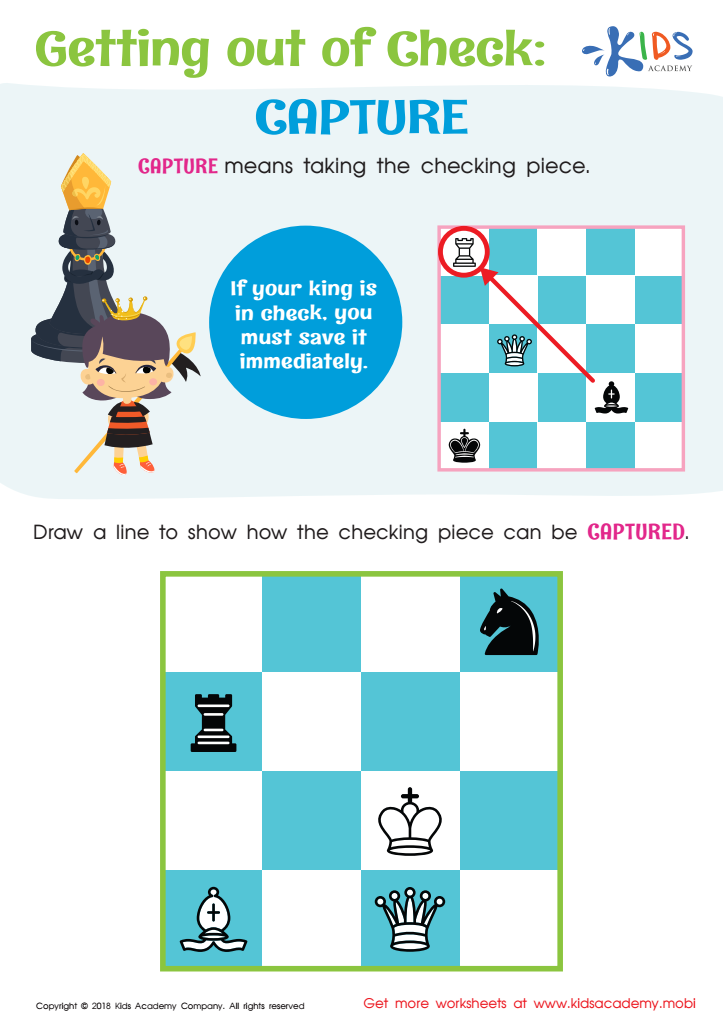

Getting out of Check: Capture
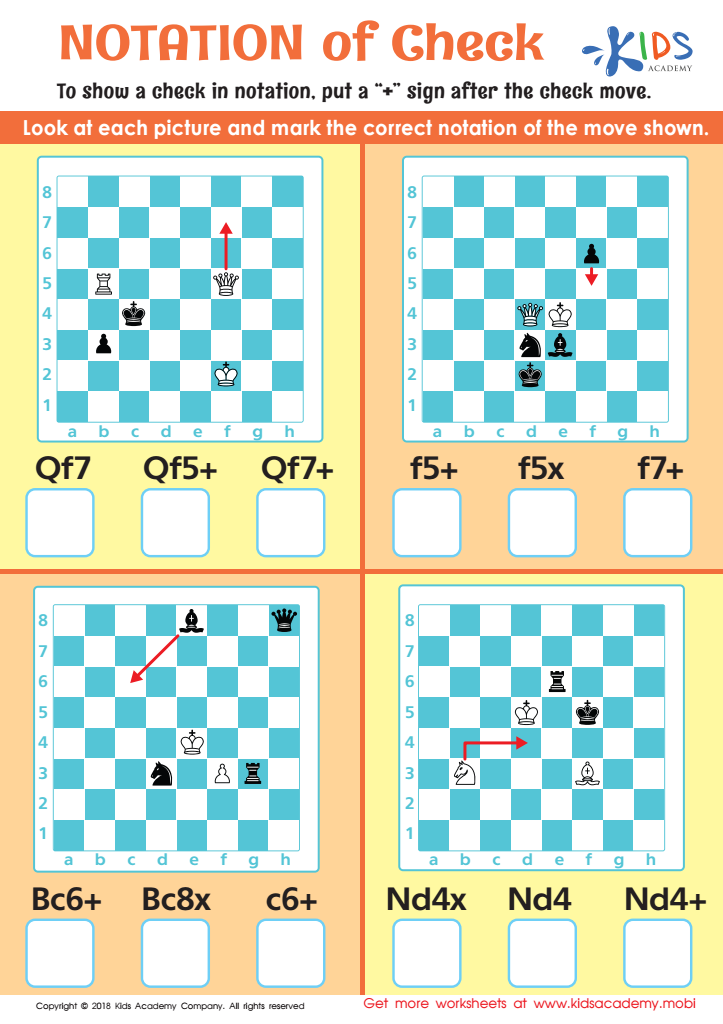

Notation of Check Worksheet
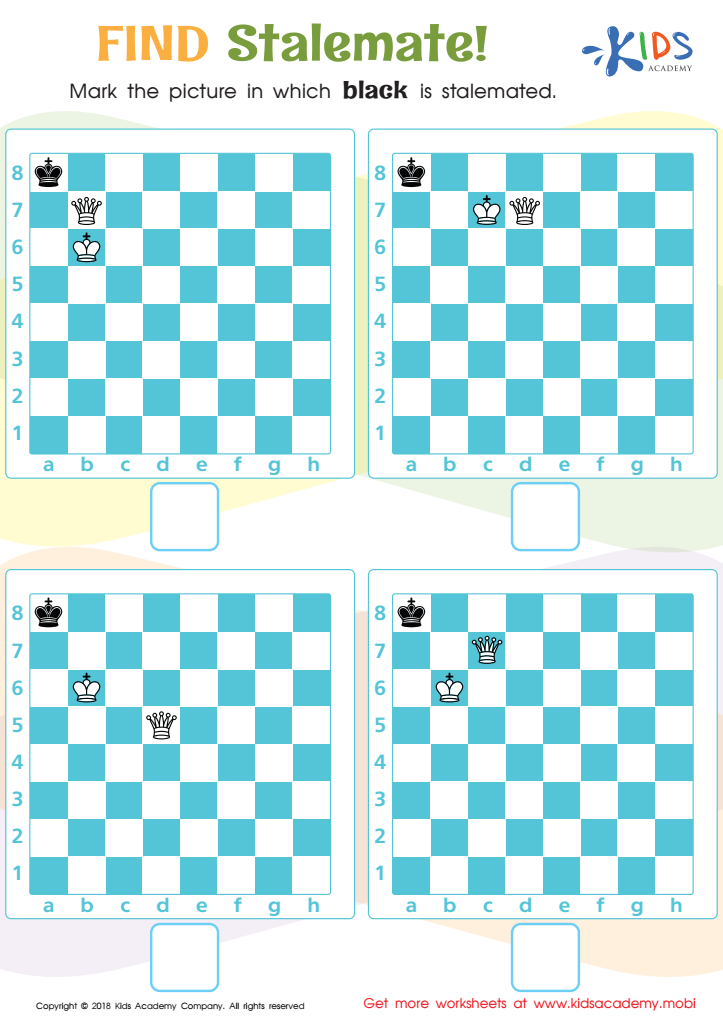

Find Stalemate! Worksheet
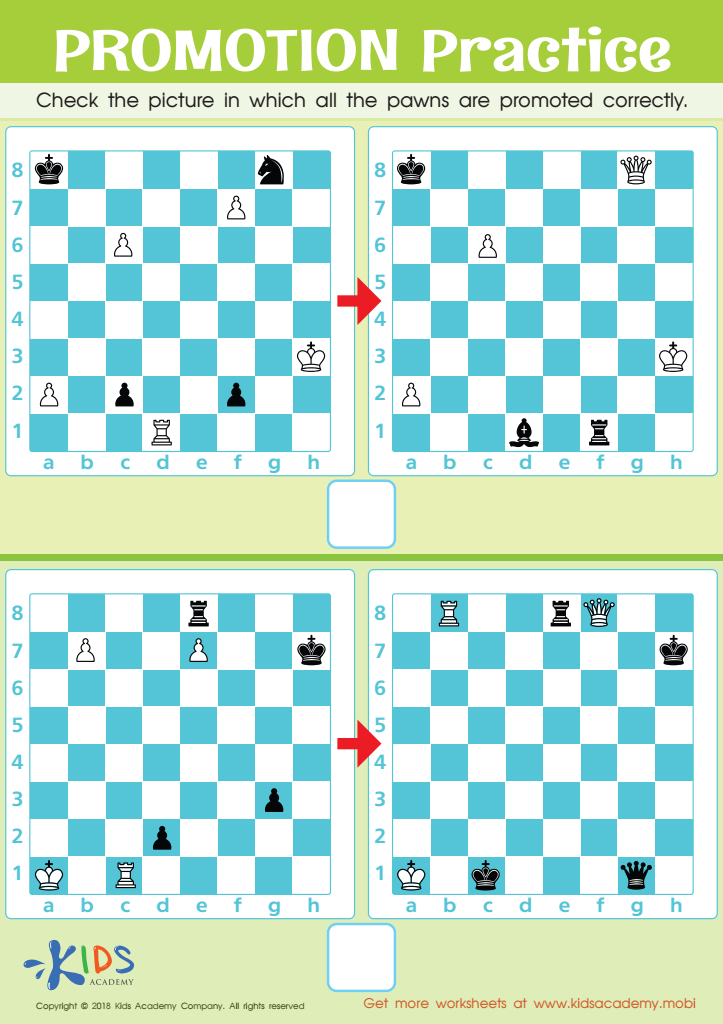

Promotion Practice Worksheet
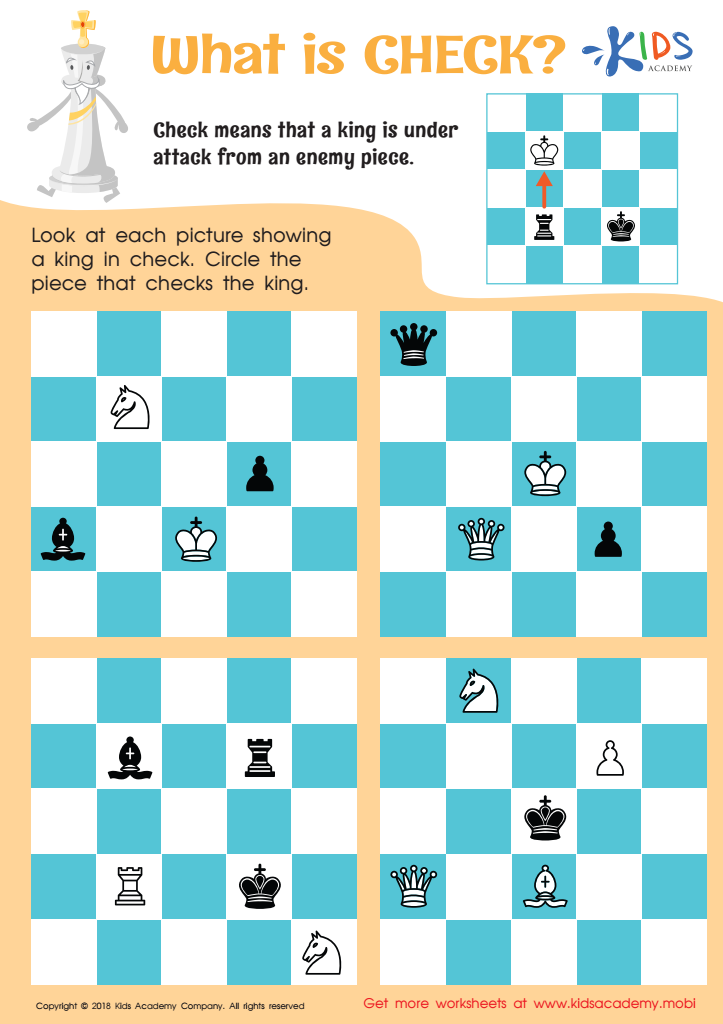

What is Check? Worksheet
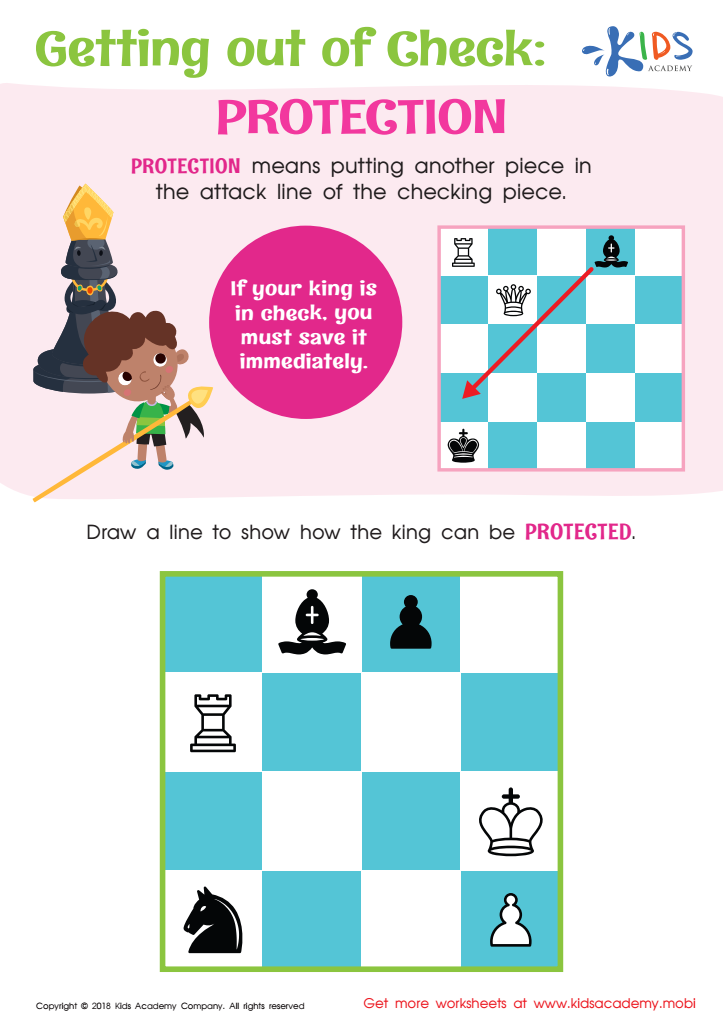

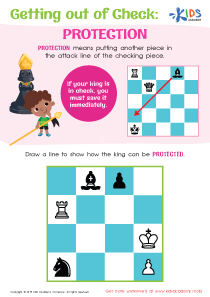
Getting out of Check: Protection
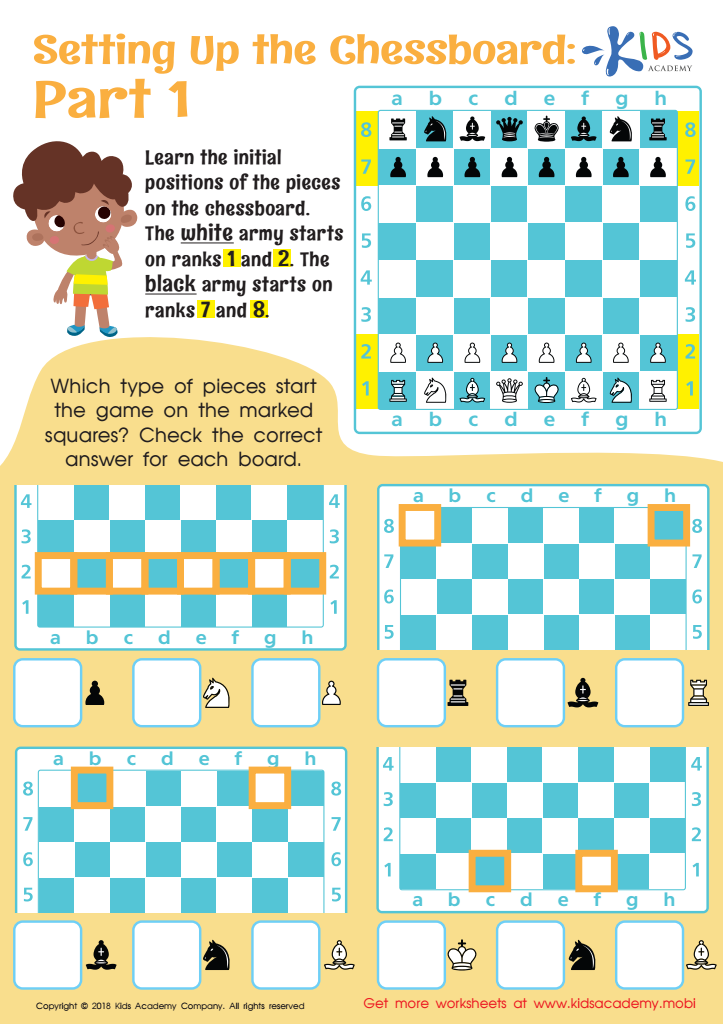

Setting up the Chessboard: Part 1 Worksheet
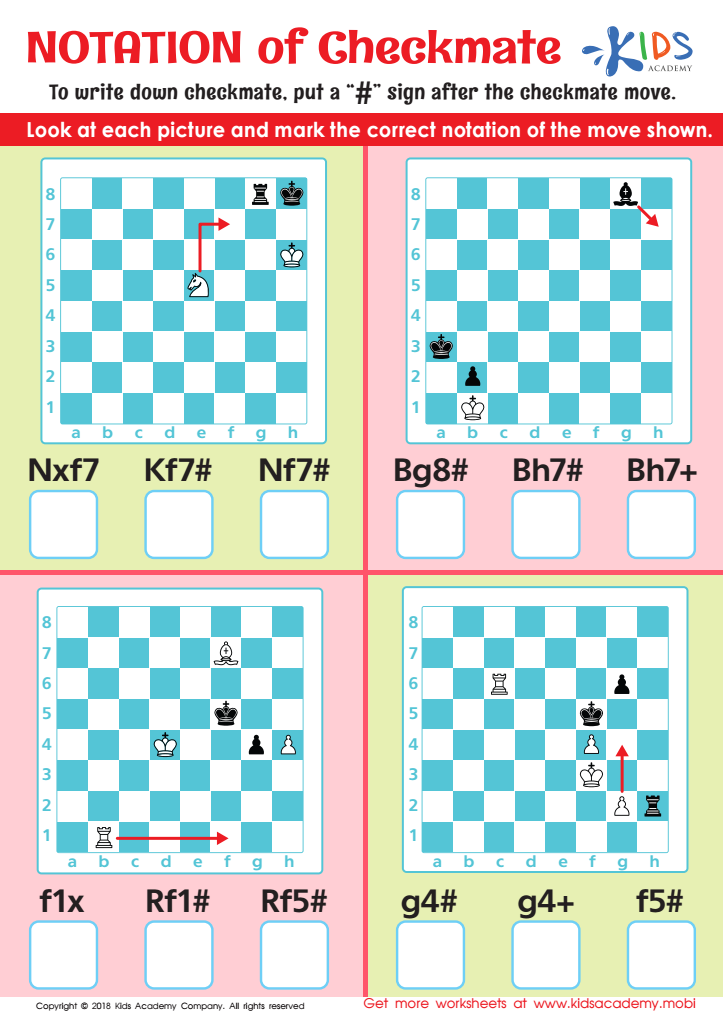

Notation of Checkmate Worksheet
Introducing chess to children between the ages of 3 and 7 can provide numerous educational and developmental benefits that should attract the attention of both parents and teachers. Firstly, chess promotes crucial cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and strategic planning. The game encourages children to think several steps ahead and visualize potential outcomes, which can enhance their logical reasoning abilities.
Secondly, chess can improve concentration and patience. Young children often have short attention spans, but engaging in a game that requires focused thought can help extend their ability to concentrate and persist through challenges.
Moreover, chess also teaches important social and emotional skills such as sportsmanship and coping with both winning and losing gracefully. These lessons foster resilience and adaptability, essential qualities for overall emotional development.
Chess can even support academic learning. There is evidence to suggest that chess may enhance mathematical skills since the game involves patterns, sequences, and problem-solving methodologies similar to those used in math and geometry.
Lastly, chess is an inclusive activity that crosses cultural and language barriers, making it an excellent tool for promoting inclusivity and interaction among diverse groups of children. Given these multifaceted benefits, integrating chess into activities for children ages 3-7 is a worthwhile investment in their educational and social development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students