Writing Worksheets for Ages 3-7 - Page 3
234 filtered results
-
From - To

Adverbs That Tell Where Worksheet


Words with Un– Worksheet

Adjective Maze Worksheet


Words with Multiple Meanings Worksheet


A Pup, a Cap and a Pea Spelling Worksheet

Plurals: "–es" or "–es"? Worksheet


Italian Word Tracing: Ciao Worksheet


Guess the Meaning Worksheet


Yellow Tracing Color Words Worksheet


Capitalization. Punctuation. Spelling: Assessment 1 Worksheet


A Pen, a Hen and a Fox Spelling Worksheet


French Word Tracing: Bonjour Worksheet


Identify Individual Words Worksheet

Words Families "ig" and "ick" Spelling Worksheet


Snowman Tracing Winter Words Worksheet


Dog Worksheet Sight Words Worksheet


Reading: How Many Syllables Worksheet
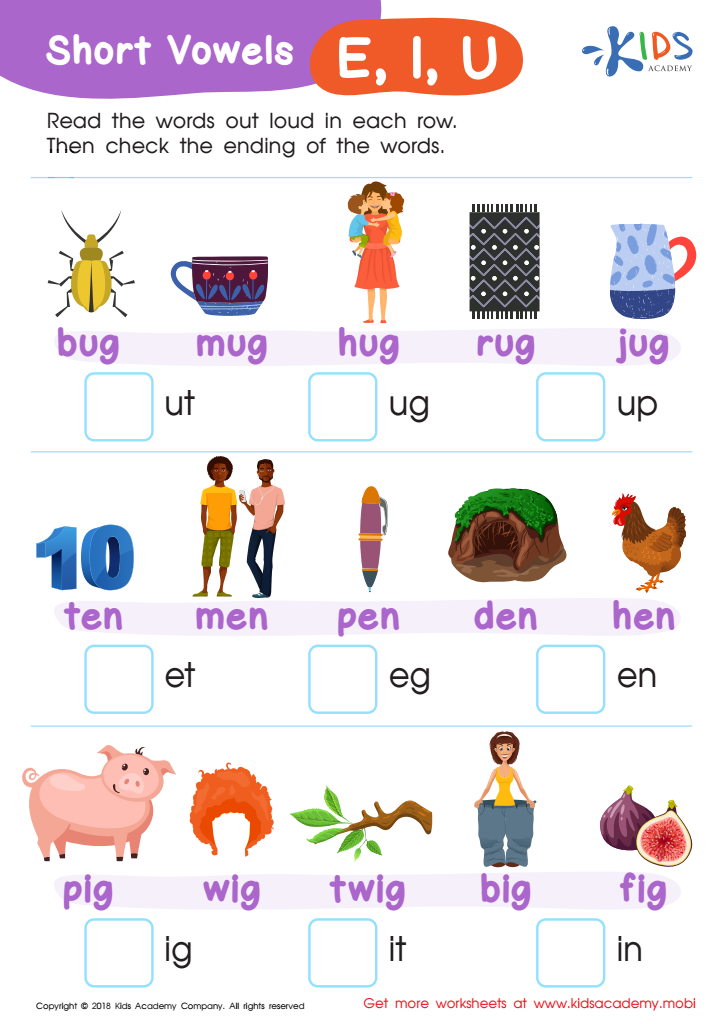

Short Vowels /e/, /i/, and /u/ Worksheet


Sentences That End in an Question Mark Worksheet
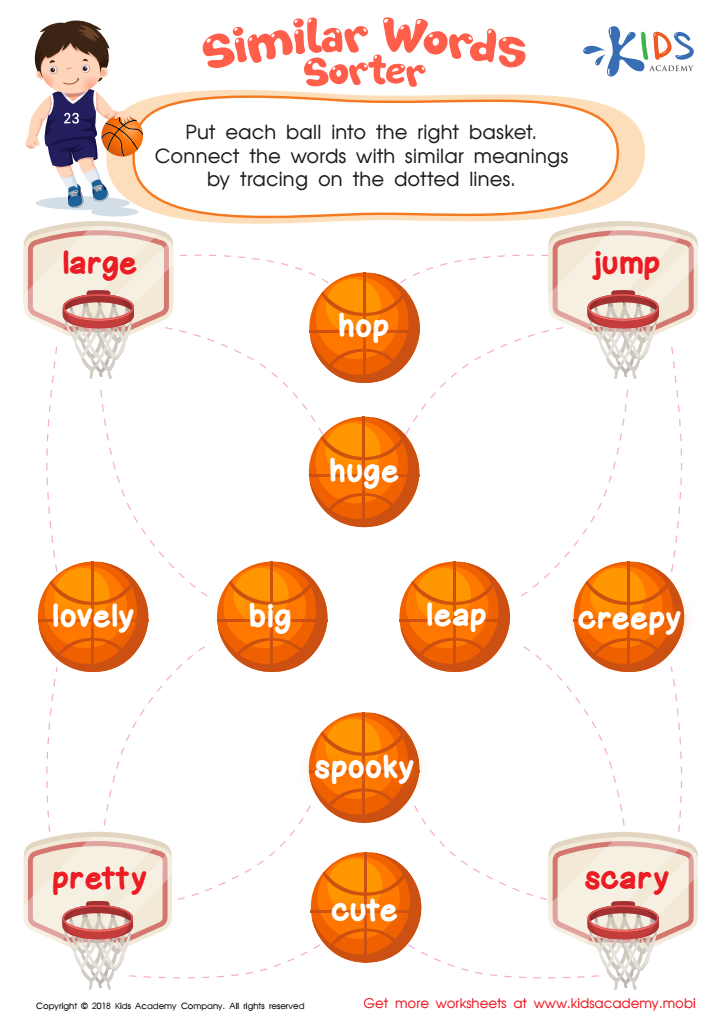

Similar Words Worksheet


Which Punctuation Mark Worksheet


End Punctuation: At the Zoo Worksheet
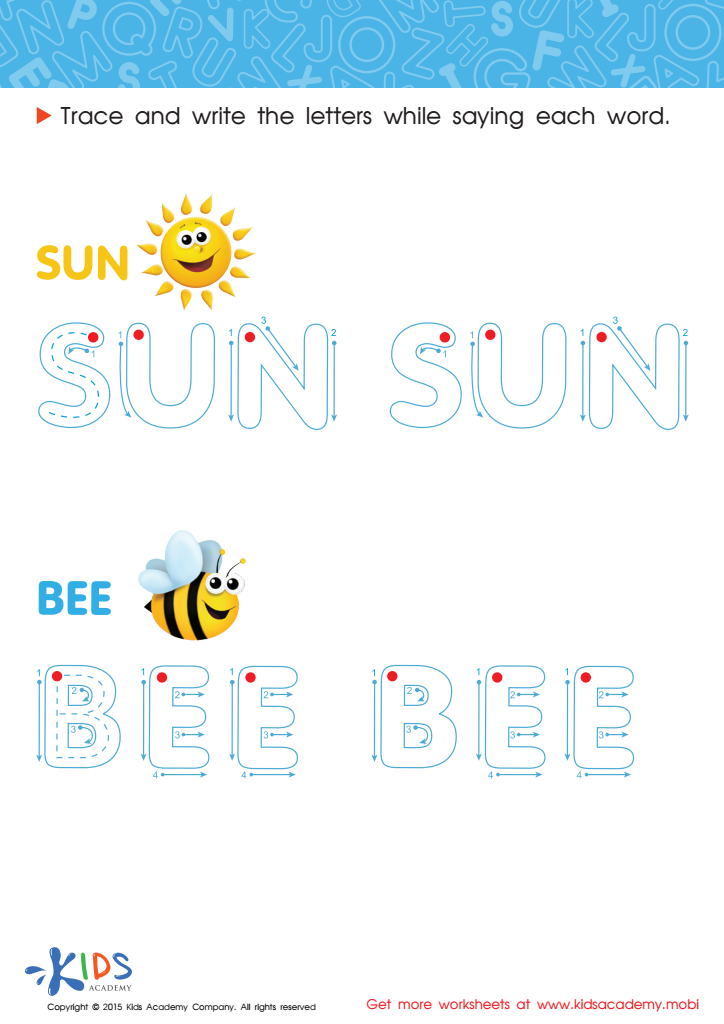

The Sun and a Bee Spelling Worksheet


Let's Practice Compound Words Word Structure Worksheet
Encouraging writing in children aged 3-7 is crucial for multiple developmental reasons. At this early stage, children are in rapid cognitive and motor-skill development—fundamental components in learning to write. Writing activities engage fine motor skills, such as finger strength and dexterity, which are necessary for tasks like buttoning clothes and using utensils. Understanding writing also fuels language development by expanding vocabulary, enhancing sentence structure, and fostering storytelling abilities.
Additionally, writing helps young children express themselves and comprehend their thoughts and feelings. This practice builds self-esteem and communication skills, vital for social interactions and emotional intelligence. Early writing activities can range from drawing shapes and lines to forming simple letters and words, making learning enjoyable and effectively strengthening their writing foundation.
From an educational standpoint, early exposure to writing prepares children for more sophisticated literacy skills in school. It aids in recognizing patterns, symbols, and sequencing, all foundational for reading proficiency. When parents and teachers invest time in nurturing writing skills, they contribute significantly to a child's overall academic success and lifelong learning abilities. Thus, fostering writing in early childhood not only supports immediate educational outcomes but also ensures a robust start for future academic and personal endeavors.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students



.jpg)












