Geometry Worksheets for Ages 3-9 - Page 5
201 filtered results
-
From - To


Find the Last! Worksheet
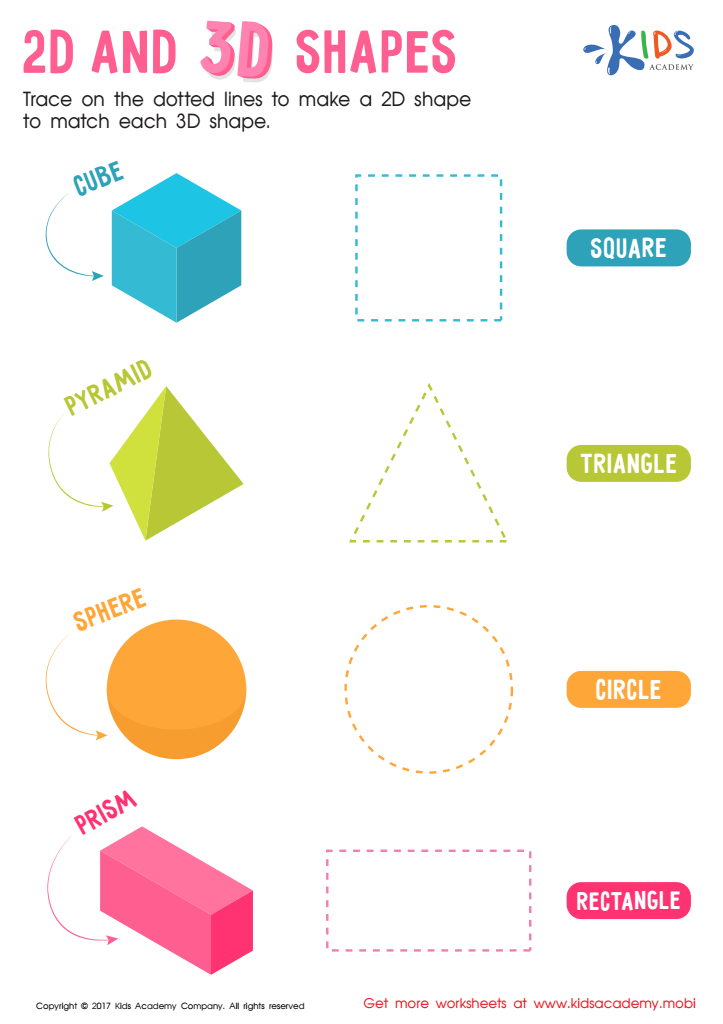

2D and 3D Shapes Worksheet
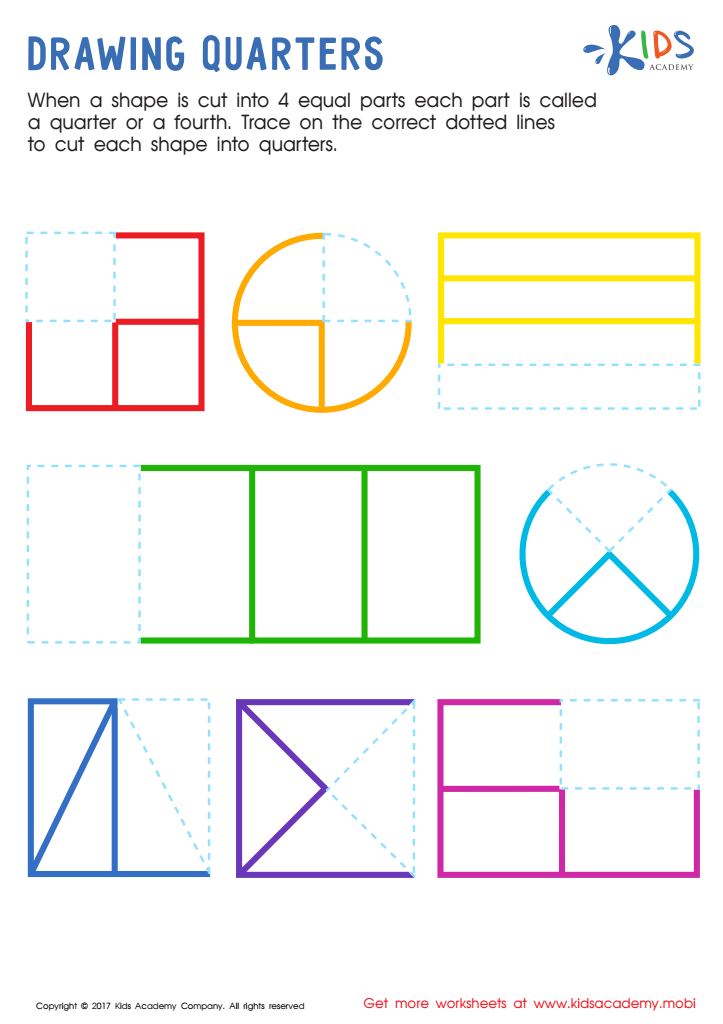

Drawing Quarters Worksheet
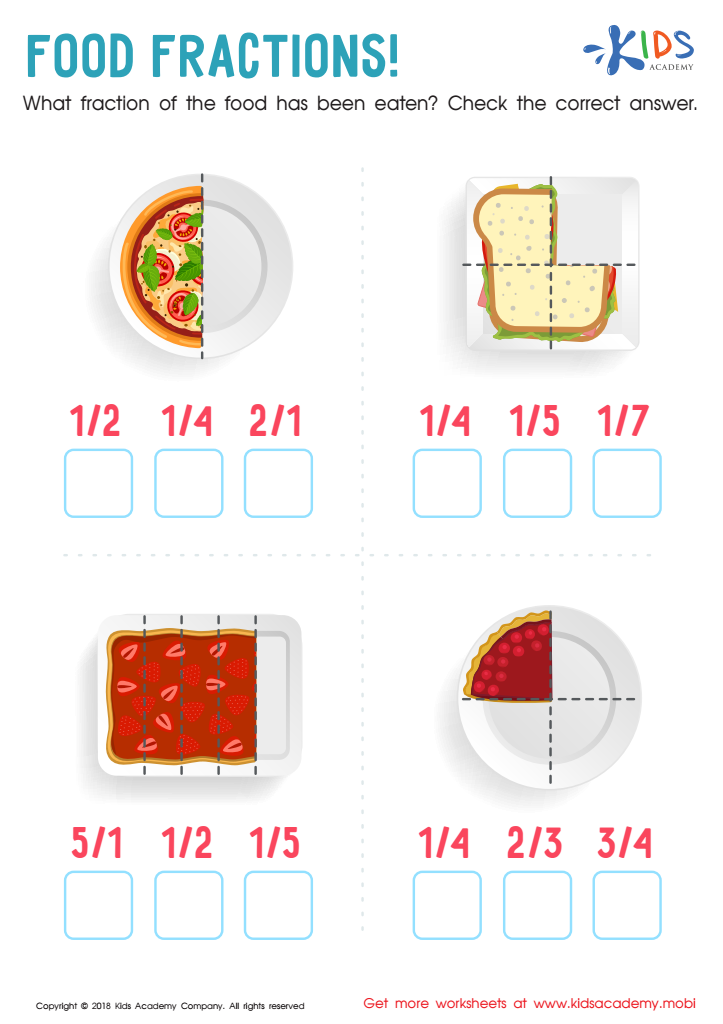

Food Fractions Worksheet
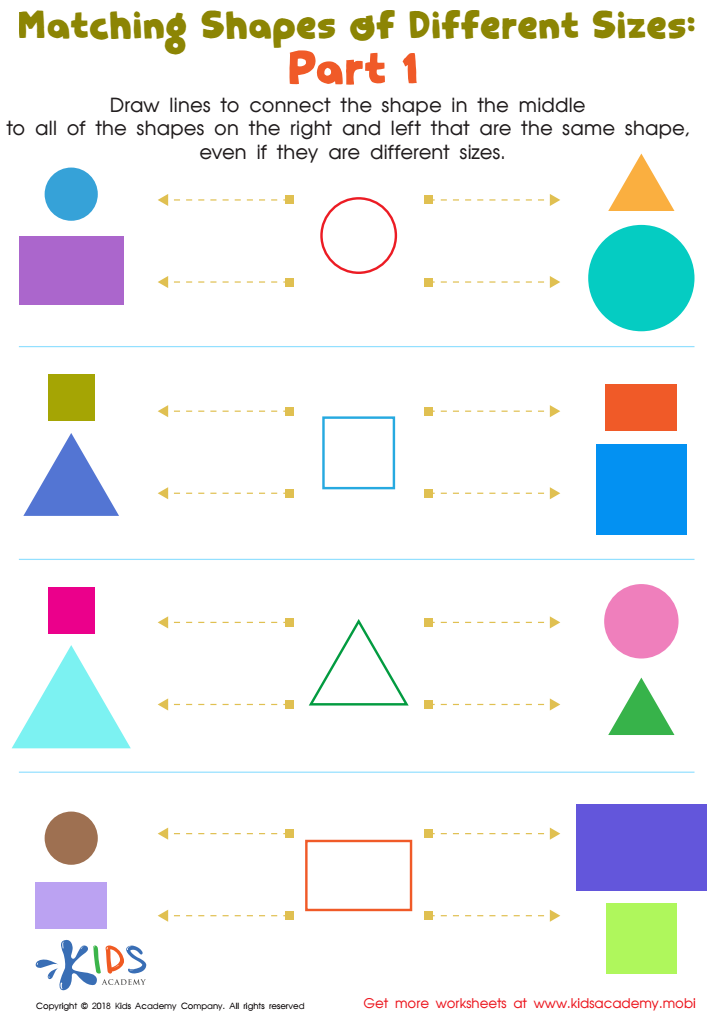

Geometry: part 1 Worksheet
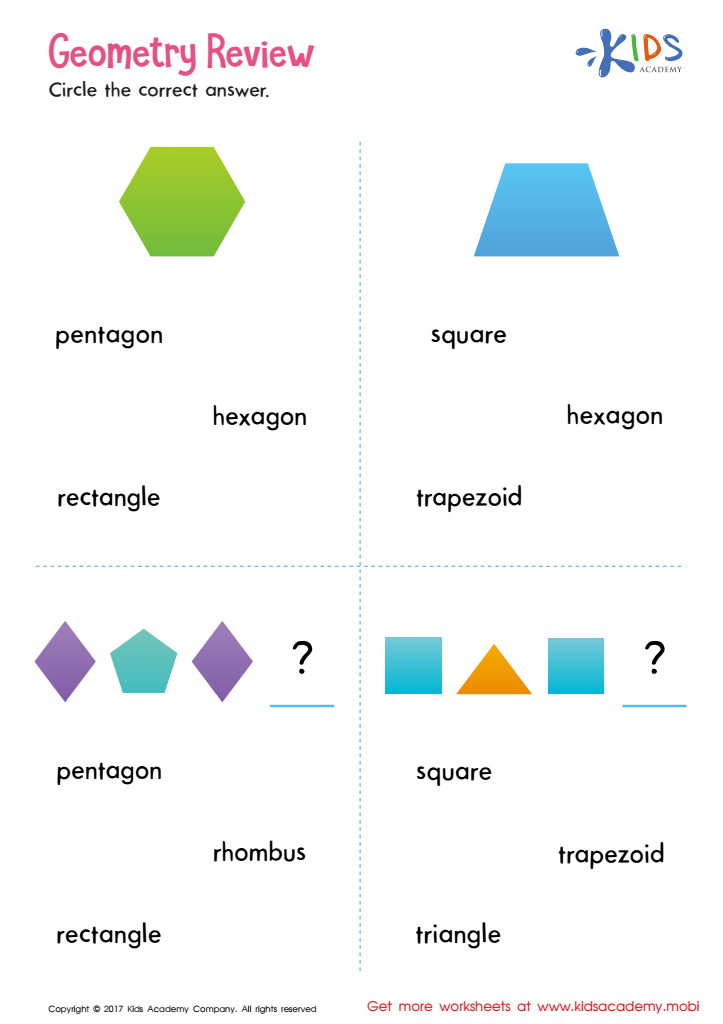

Geometry Review Printable
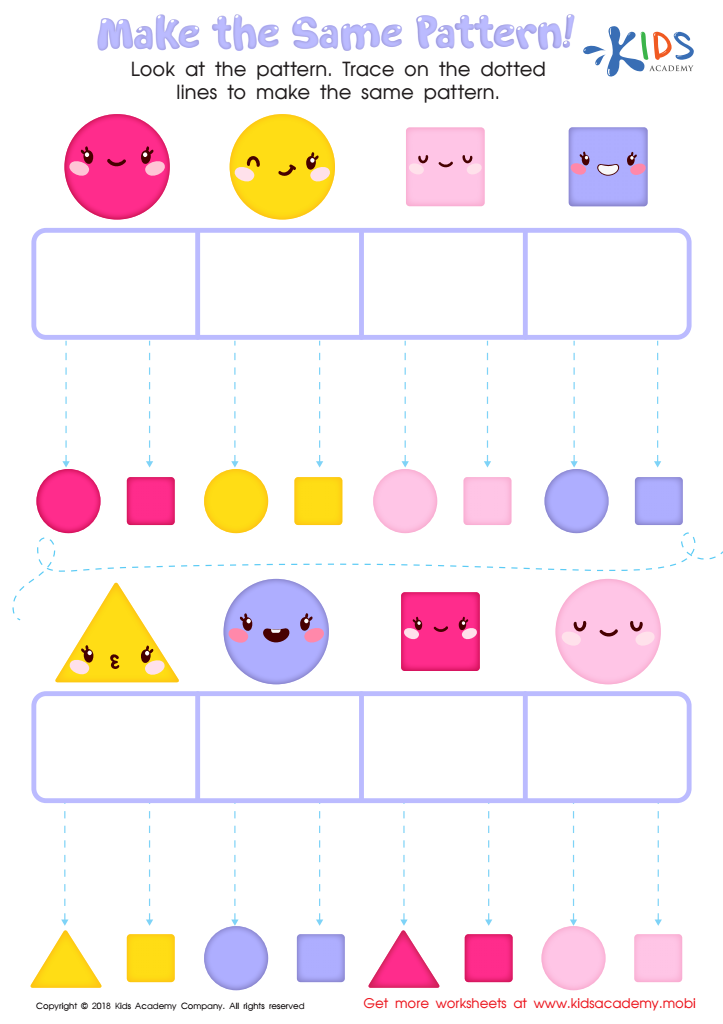

Make the Same Pattern Worksheet
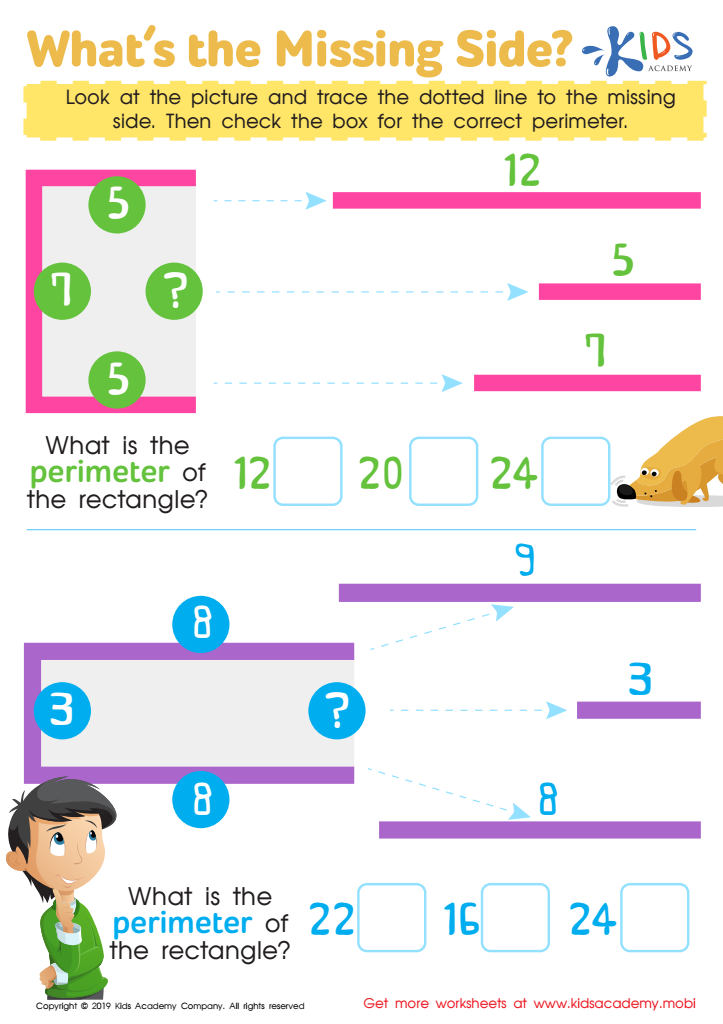

What's the Missing Side Worksheet


Is It a Triangle? Worksheet


Drawing with a Little Monster Worksheet


Cinderella Geometry Maze Worksheet
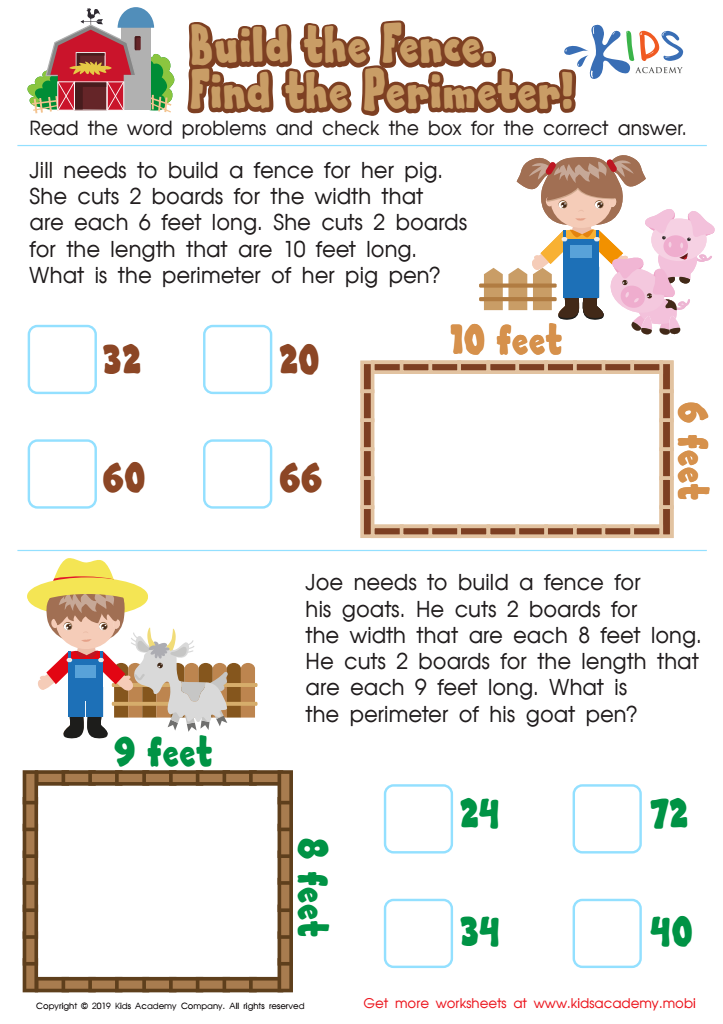

Build the Fence, Find the Perimeter Worksheet


Draw a Rhombus And a Hexahedron Printable
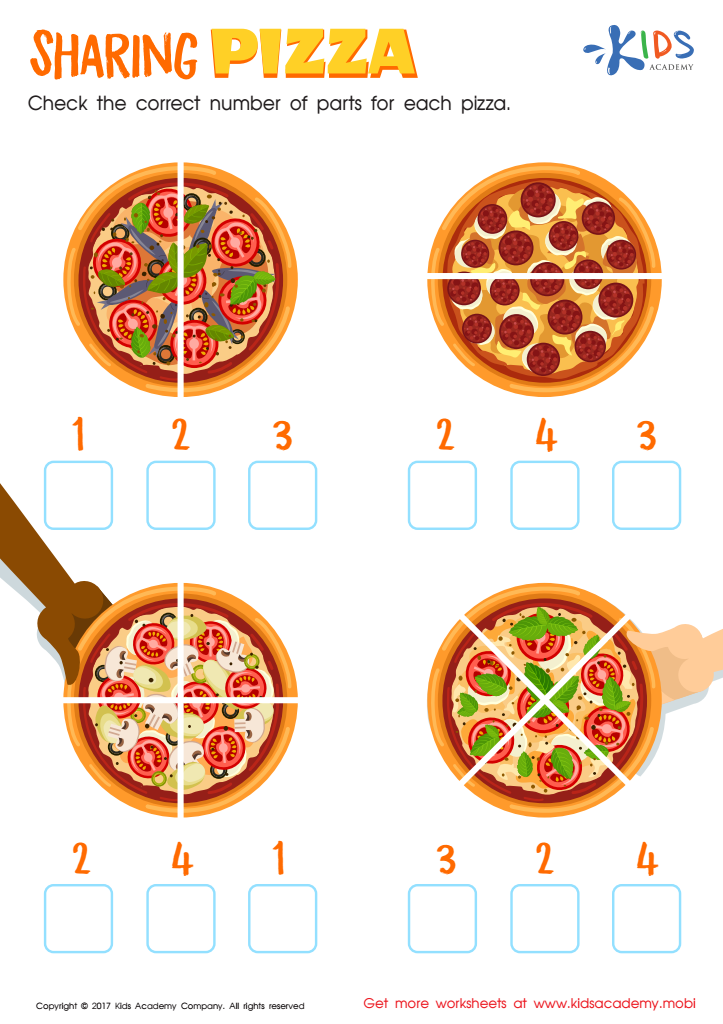

Sharing Pizza Worksheet


Preschool Geometry Match Up Worksheet
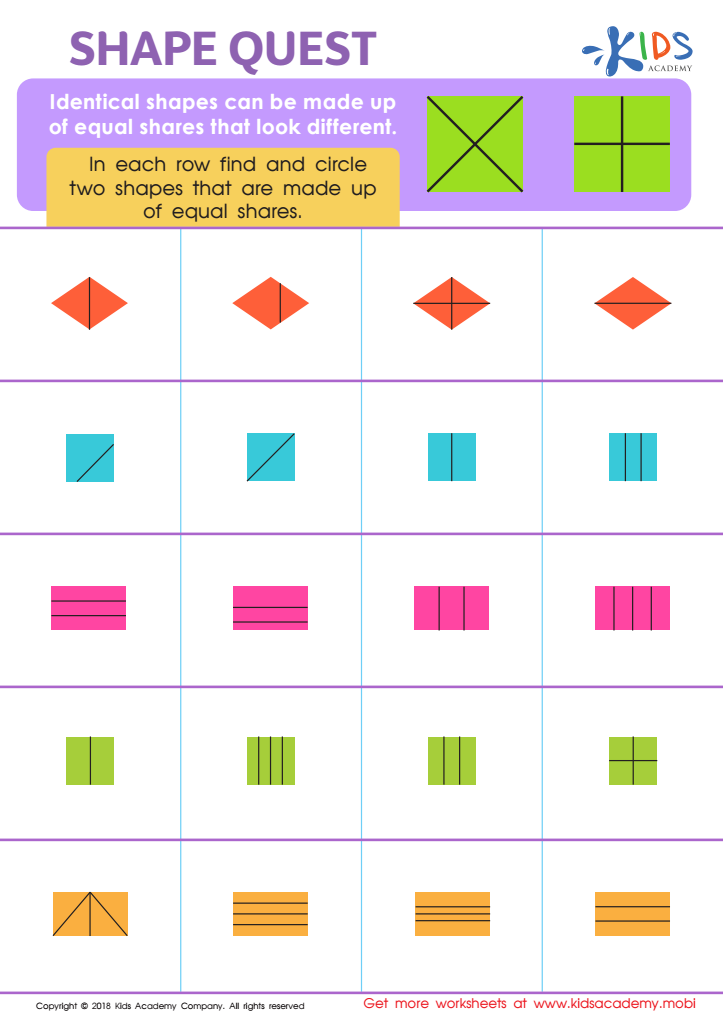

Shape Quest Worksheet
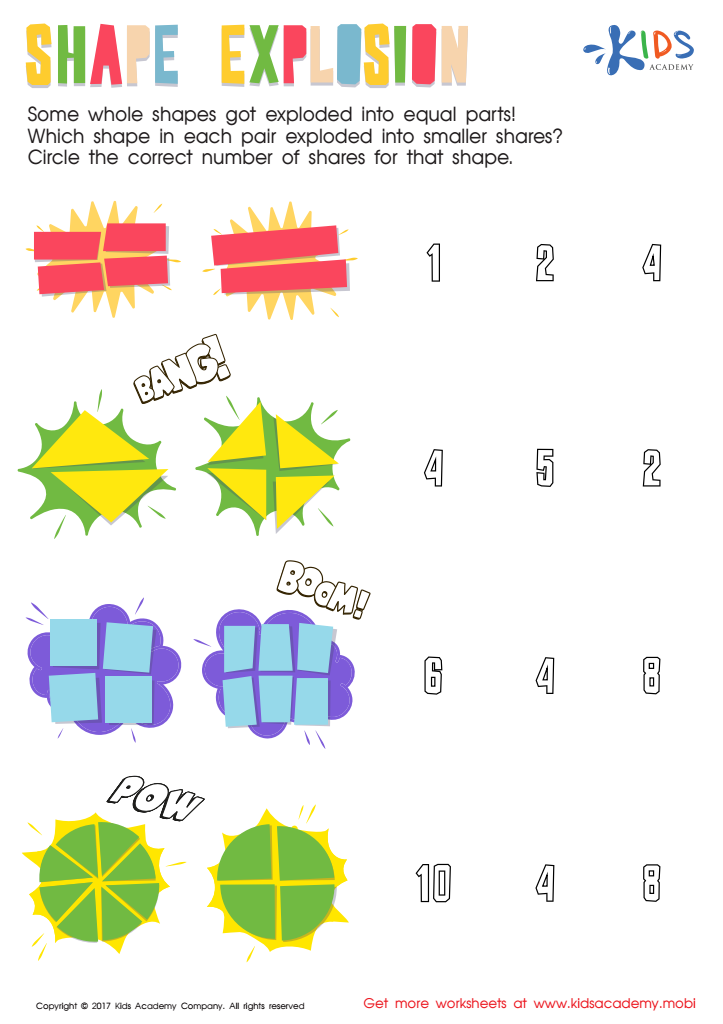

Shape Explosion Worksheet
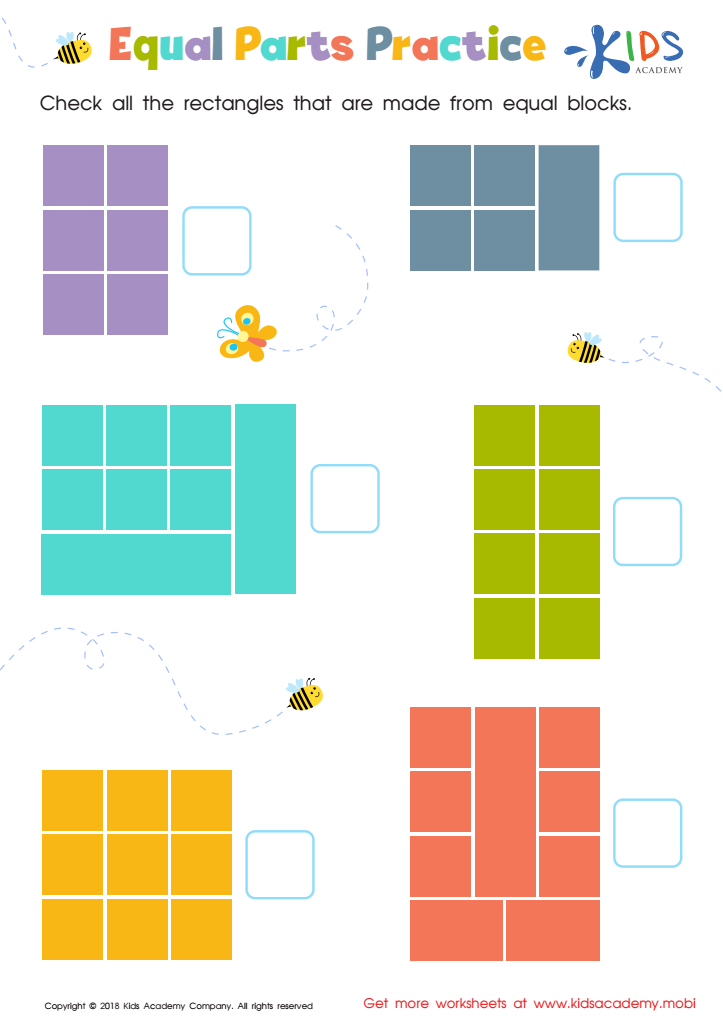

Equal Parts Practice Worksheet


Learning to Draw Crescents And Triangles Worksheet
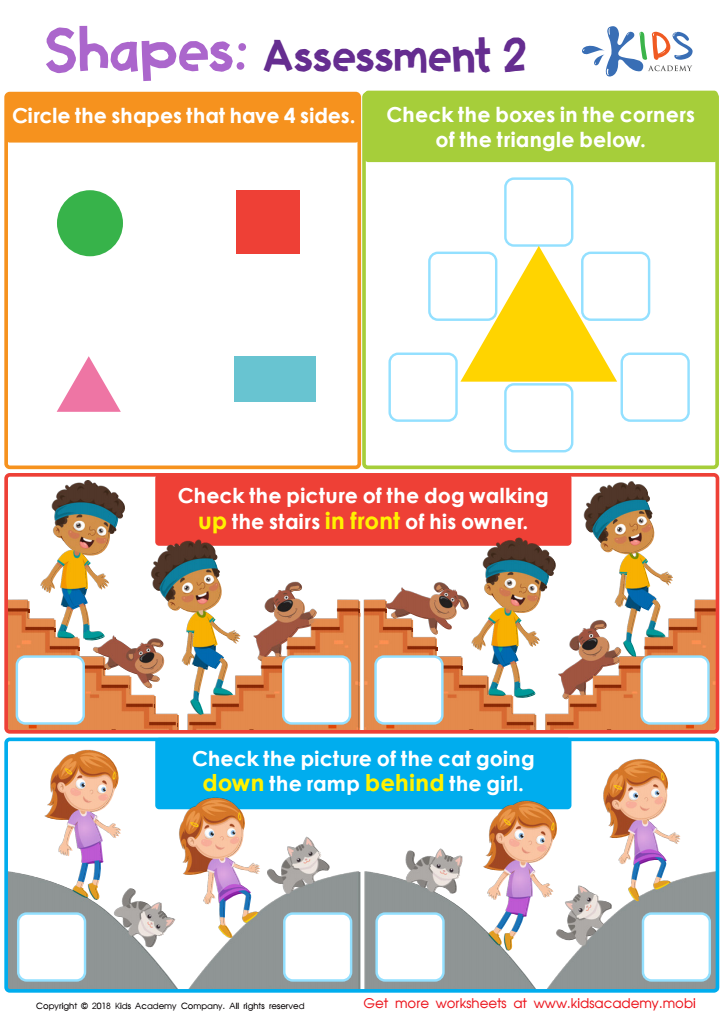

Shapes: Assessment 2 Worksheet
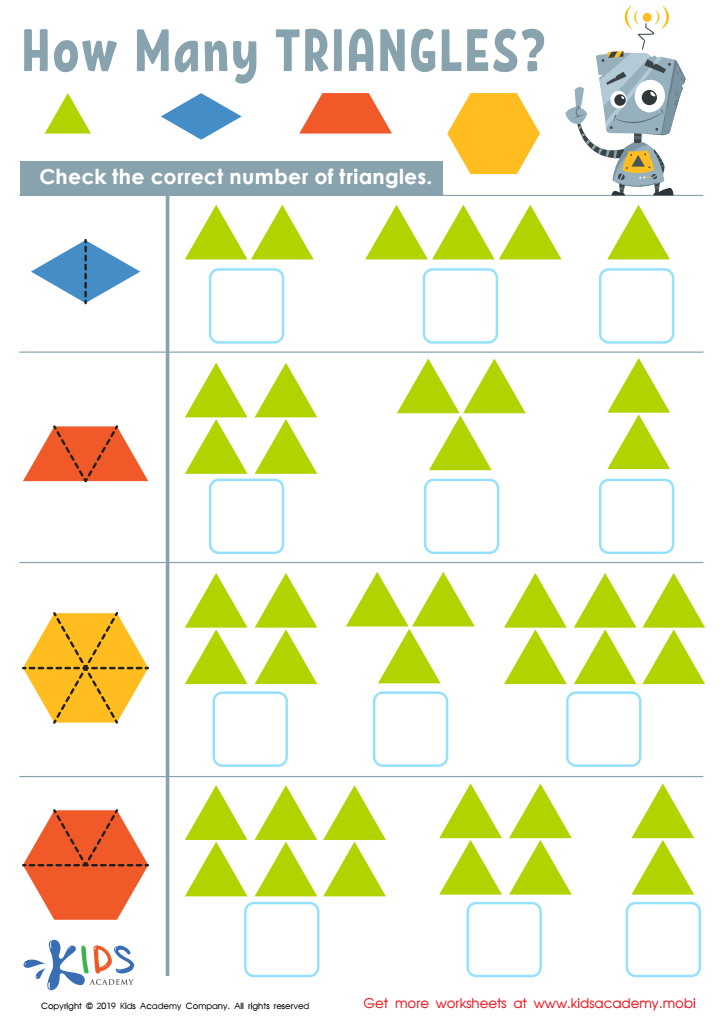

How Many Triangles Worksheet

Quadrilateral Maze Worksheet

Cutting Circles Worksheet
Geometry plays a crucial role in the cognitive development of children aged 3 to 9, and both parents and teachers should prioritize its teaching for several reasons. First, geometric concepts enhance spatial reasoning, which is essential for critical thinking and problem-solving. Children begin to understand shapes, sizes, and spatial relationships during these formative years, which lays the groundwork for future math skills.
Moreover, geometry supports language development. Describing shapes and exploring their properties encourages children to use and expand their vocabulary, fostering communication skills. Engaging in geometric play also aids fine motor development, as children manipulate objects, draw shapes, and solve puzzles.
Additionally, geometry is woven into everyday life. Understanding basic shapes and their characteristics helps children navigate their environment, enhancing their ability to observe and make sense of the world around them. This foundational knowledge is not just academic; it paves the way for competencies in science, engineering, technology, and art.
Lastly, introducing geometric concepts early can ignite a lifelong passion for learning. Engaging activities, such as shape sorting games or building with blocks, make geometry fun while ensuring children appreciate the beauty of mathematics and its applications. Therefore, a strong emphasis on geometric learning fosters well-rounded, capable learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students