Fine Motor Skills Kindergarten Letter I Worksheets
3 filtered results
Difficulty Level
Grade
Age
-
From - To
Subject
Activity
Standards
Favorites
With answer key
Interactive
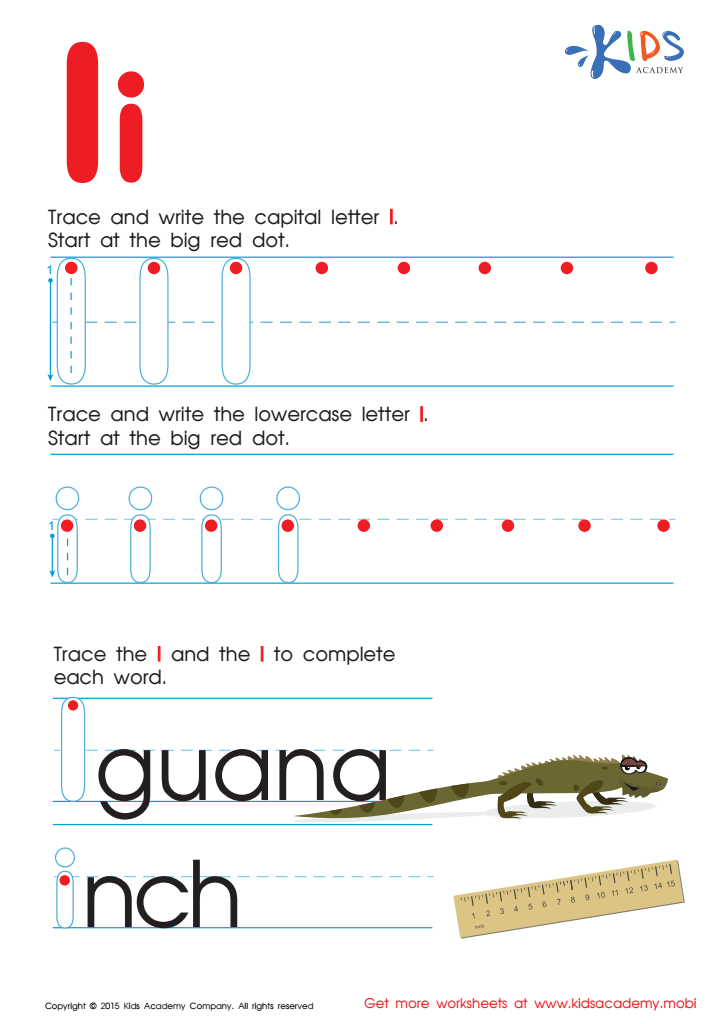

Letter I Tracing Page
Trace and write "I" uppercase and lowercase. An iguana's tail looks like the uppercase "I" and the lowercase "i" is as small as an inch. Make learning fun with Kids Academy worksheets.
Letter I Tracing Page
Worksheet


Letter I Tracing Worksheet
Kids can hone tracing, writing and identifying skills for the letter 'I' with this worksheet. Whether visual or reading/writing learners, every child can benefit from the tasks - tracing, writing and circling objects beginning with 'I'. This free sheet will soon get preschoolers confident with the 'I' letter!
Letter I Tracing Worksheet
Worksheet


Letter I Coloring Sheet
This coloring page helps your child recognize the letter "I" and the positional word "in". It also introduces them to sight words, enhancing language skills. It's great for teaching parts of speech and boosting your little learner's confidence!
Letter I Coloring Sheet
Worksheet
 Assign to the classroom
Assign to the classroom